Template:Main Page News: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|-bgcolor="CEDFF2" | |-bgcolor="CEDFF2" | ||
| colspan=2|<span style="font-size:150%">''' | | colspan=2|<span style="font-size:150%">'''Embryo Epigenetics'''</span> | ||
|-bgcolor="F5FAFF" | |-bgcolor="F5FAFF" | ||
| | | | ||
[[File: | [[File:Epigenetics_cartoon.jpg|250px|left]] | ||
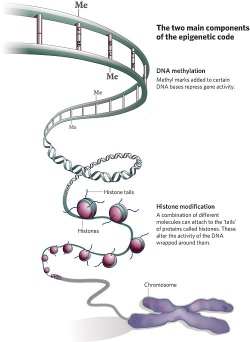
| ''' | | '''Embryos Reprogram their Epigenetics''' | ||
Two recent studies show that after fertilisation human embryos loose DNA methylation from most of the genome. This implies that there is an early "reprogramming" or "resetting" of the embryo's epigenetic status. | |||
:(More? [[ | :(More? [[Molecular Development - Epigenetics|Epigenetics]] | Nature. 2014 Jul PMID 25079558 PMID 25079557) | ||
[[Template_talk:Main_Page_News|Older News Articles]] | [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News|Older News Articles]] | ||
* WHO - Trends in Maternal Mortality 1990 to 2013. [[Statistics - Maternal Mortality]] | [http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/monitoring/maternal-mortality-2013/en WHO Report Page] | |||
* The World Health Organization says polio has re-emerged as a public health emergency. [[Abnormal Development - Polio Virus|Polio Virus]] | * The World Health Organization says polio has re-emerged as a public health emergency. [[Abnormal Development - Polio Virus|Polio Virus]] | ||
* Trisomy 21 [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News#March|Genome-wide Effects]] | * Trisomy 21 [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News#March|Genome-wide Effects]] | ||
* RIKEN Panel Finds Misconduct in Reprogrammed Stem Cell Papers [http://www.riken.jp/en/pr/press/2014/20140401_2/RIKEN press release April 1, 2014] | [http://news.sciencemag.org/asiapacific/2014/04/riken-panel-finds-misconduct-reprogrammed-stem-cell-papers Science April 2014] | * RIKEN Panel Finds Misconduct in Reprogrammed Stem Cell Papers [http://www.riken.jp/en/pr/press/2014/20140401_2/RIKEN press release April 1, 2014] | [http://news.sciencemag.org/asiapacific/2014/04/riken-panel-finds-misconduct-reprogrammed-stem-cell-papers Science April 2014] | ||
|}<noinclude>[[Category:Template]][[Category:2014]]</noinclude> | |}<noinclude>[[Category:Template]][[Category:2014]]</noinclude> | ||
Revision as of 17:16, 4 August 2014
| Embryo Epigenetics | |
| Embryos Reprogram their Epigenetics
Two recent studies show that after fertilisation human embryos loose DNA methylation from most of the genome. This implies that there is an early "reprogramming" or "resetting" of the embryo's epigenetic status.
| |