Y
| Embryology - 27 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Y
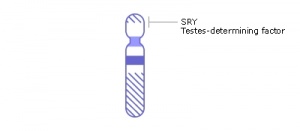
Y chromosome
- The male sex chromosome which contains the sry gene producing Testis-Determining Factor required for male phenotype and can only be inherited from father. In humans the chromosome contains 200+ genes and consists of 50 million base pairs. Testis-Determining Factor (TDF; Testis-Determining Factor on Y, TDY ) is a protein transcription factor and a member of the high mobility group (HMG)-box family of DNA binding proteins. See also the transcription factor SRY-related protein, SOX9 (SRY-related high-mobility group (HMG) box 9).
- (More? Y Chromosome | Genital - Male Development | Sex Determination | Molecular Development | Week 1 | OMIM)
Y ligament
- (iliofemoral ligament) A ligament that extends from the anterior inferior iliac spine to the intertrochanteric line of the femur.
Yamanaka factors
- Molecular development term for the three transcription factors Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4 and the proto-oncogene product c-Myc used to generate inducible pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from differentiated cells. Named after the author of papers on the generation or iPSCs PMID20660764.
- (More? Stem Cells | PMID 20660764)
yolk
- The name given to the fluid contents of the yolk sac in reptiles and birds, it has the function of providing nutrition for embryonic growth.
- (More? Week 2)
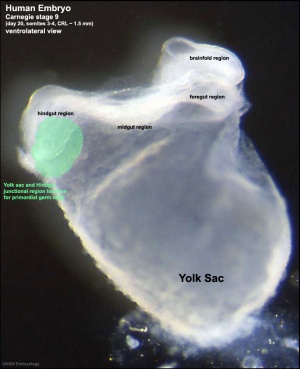
yolk sac
- An extraembryonic membrane which is endoderm origin and covered with extraembryonic mesoderm. Yolk sac lies outside the embryo connected initially by a yolk stalk to the midgut with which it is continuous with. The endodermal lining is continuous with the endoderm of the gastrointestinal tract. The extra-embryonic mesoderm differentiates to form both blood and blood vessels of the vitelline system. In reptiles and birds, the yolk sac has a function associated with nutrition. In mammals the yolk sac acts as a source of primordial germ cells and blood cells. Note that in early development (week 2) a structure called the "primitive yolk sac" forms from hypoblast, this is an entirely different structure.
- (More? Gastrointestinal Tract Development | Embryonic folding animation | Week 2 | Cardiovascular System - Blood)
yolk stalk
- (vitelline duct, omphalomesenteric duct, Latin, vitellus = yolk of an egg) The endodermal connection between the midgut and the yolk sac. See vitelline duct.
Yucheng
- Name of a city in Taiwan where children during 1978-1979 were prenatally exposed persistent organic pollutants in the form of rice oil contaminated with polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and their heat-degradation products, mainly polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs). Children of the exposed women were born with retarded growth, with dysmorphic physical findings, and, during development, with delayed cognitive development, increased otitis media, and more behavioral problems than unexposed children.
Glossary Comments
Use this page to access brief definitions of specific embryology terms. Additional information can be accessed from links listed at the end of each definition. Glossary from the UNSW Embryology program compiled and written by Dr Mark Hill. Reference material used in preparing this glossary list includes: texts listed on page 1 "Reading" of each notes section, Department of Anatomy Publications, WWW resources from NCBI, NIH, OMIM, NHMRC (Australia), AMA (USA), Office of Rare Diseases (USA), PubMed Medline Dictionaries, MSDS, Merck Manual home edn. and WHO ART terminology (2009).
These notes are for Educational Purposes Only Please email Dr Mark Hill if you wish to make a comment about this current project.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Y. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Y
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G