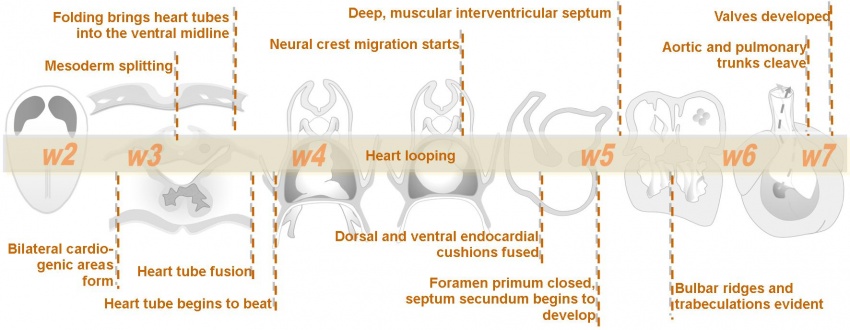
Intermediate - Outflow Tract
| Begin Intermediate: | Primordial Heart Tube | Heart Tube Looping | Atrial Ventricular Septation | Outflow Tract | Heart Valves | Cardiac Abnormalities | Vascular Overview |
| Cardiac Embryology | Begin Basic | Begin Intermediate | Begin Advanced |
Active proliferation of neural crest mesenchymal cells in the bulbus cordis during the fifth week creates bulbar ridges which are continuous in the truncus arteriosus. The neural crest cells migrate through the primordial pharynx and over the aortic arch arteries to reach the outflow tract (pictured below). The bulbar ridges undergo a 180° spiral to create the helical aorticopulmonary septum. As the ridges grow and develop myocardium they fuse in a distal-to-proximal direction. Fusion occurs during the sixth week, allowing for cleavage of the aorta and pulmonary trunk. The spiralling nature of the ridges causes the pulmonary trunk to twist around the aorta. Note that the bulbus cordis accounts for the smooth conus arteriosus (or infundibulum) in the right ventricle and the aortic vestibule in the left ventricle.
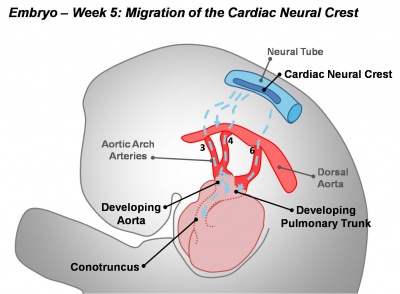
Migration of the cardiac neural crest |
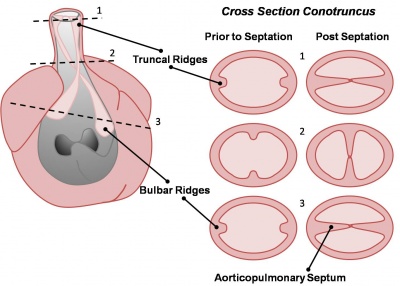
Cross-sections of the outflow tract illustrating the truncal and bulbar ridges |
The following animation shows the process occuring in a right oblique view of the heart with the anterolateral wall of the right ventricle having been removed.
<html5media>File:Heart outflow tract 002.mp4</html5media>
| Back to Septation | Next: Development of Heart Valves | |
| Go to this section in the basic level | Go to this section in the advanced level |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Aorta: The largest artery in the human body originating in the left ventricle. The aorta ascends, arches over the heart and then descends through the abdomen.
Aortic arch arteries: (Or pharyngeal arch arteries.) Each early developing pharyngeal arch contains a lateral pair of arteries arising from the aortic sac, above the heart, and running into the dorsal aorta. Later in development these arch arteries are extensively remodelled to form specific components of the vascular system.
Aortic vestibule: Smooth-walled portion of the left ventricle directly below the aortic valve.
Aorticopulmonary septum: Division between the aorta and the pulmonary trunk formed from the bulbar ridges.
Bulbus cordis: A region of the early developing heart tube forming the common outflow tract, will differentiate to form three regions of the heart.
Conus arteriosus: An embryological heart outflow structure, that forms in early cardiac development and will later divides into the pulmonary artery and aorta. Term is also used clinically to describe the malformation of the cardiac outflow pattern, where only one artery arises from the heart and forms the aorta and pulmonary artery.
Infundibulum: Smooth-walled portion of the right ventricle directly below the pulmonary valve.
Neural crest mesenchyme: Connective tissue arising from critical cells in the cranial region of the embryo. These paired dorsal lateral streaks of cells migrate throughout the embryo and can differentiate into many different cell types (= pluripotential). Those that remain on the dorsal neural tube form the sensory spinal ganglia (DRG), those that migrate ventrally form the sympatheitic ganglia. Neural crest cells also migrate into the somites and regions throught the entire embryo.
Outflow tract: Exit of blood from the heart tube formed by the truncus arteriosus.
Pharynx: (Or throat) Forms the initial segment of the upper respiratory tract divided anatomically into three regions: nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). Anatomically extends from the base of the skull to the level of the sixth cervical vertebra.
Pulmonary trunk: A vessel that arises from the right ventricle of the heart, extends upward, and divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries that transport deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Truncus arteriosus: An embryological heart outflow structure, that forms in early cardiac development and will later divides into the pulmonary artery and aorta. Term is also used clinically to describe the malformation of the cardiac outflow pattern, where only one artery arises from the heart and forms the aorta and pulmonary artery.