2011 Lab 6 - Trilaminar Embryo
| 2011 Lab 6: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Week 3
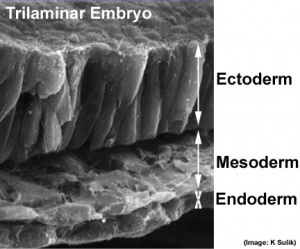
Gastrulation/Neuralation: In the third week, gastrulation establishes the 3 germ cell layers, endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. All 3 layers will later contribute specific components of the face and ear.
Also present from these early weeks is the buccopharyngeal membrane or oral membrane. The membrane forms in the midline towards the cranial end of of the trilaminar embryo. Initially as a small circular region during gastrulation where ectoderm and endoderm associate closely together, without mesoderm between the layers (like the cloacal membrane at the other end of the disc). Folding of the embryonic disc will change its relative position.
The primitive streak extends from the primitive node towards the connecting stalk end of the disc. The primitive node (Hensen's node) is also the beginning of an axial process that extends in the opposite direction within the mesoderm layer. The axial process can extend cranially only as far as the buccopharyngeal membrane an differentiates to form then notochord. The notochord regulates development, both differentiation and folding, in the surrounding tissues. The regulation is initially physical, as a dense column of cells (folding) and then by secretion of developmental factors (differentiation) that pattern the surrounding ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
Germ Layer Contributions
Now consider how each of the germ layers will eventually contribute specific components of the face and ear. The list below is a simple overview, by the end of todays pracrical you should be able to identify the germ layer embryonic origin of many different components.
Endoderm
- buccopharyngeal (oral) membrane
- pharynx
- tubotympanic recess
- endocrine
Mesoderm
- unsegmented paraxial mesoderm
- somites
Ectoderm
- neural tube - central nervous system, posterior pituitary
- neural crest - (ectomesenchyme) connective tissues of head
- sensory placodes
- epithelium
Embryonic Folding
As we discussed in gastrointestinal tract development, initial folding of the embryonic disc occurs ventrally around the notochord, which forms a rod-like region running rostro-caudally in the midline.
Folding in relation to the notochord:
- Laterally (either side of the notochord) lies mesoderm.
- Rostrally (above the notochord end) lies the buccopharyngeal membrane, above this again is the mesoderm region forming the heart.
- Caudally (below the notochord end) lies the primitive streak (where gastrulation occurred), below this again is the cloacal membrane.
- Dorsally (above the notochord) lies the neural tube then ectoderm.
- Ventrally (beneath the notochord) lies the mesoderm then endoderm.
Week 4
| 2011 Lab 6: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, February 27) Embryology 2011 Lab 6 - Trilaminar Embryo. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2011_Lab_6_-_Trilaminar_Embryo
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G