2009 Lecture 4
Week 3 Development
Introduction
This lecture will continue from the second week into the third week and discuss early placentation and gastrulation. Note that we will be covering only the early events of placentation and a later lecture will cover this topic in more detail.
- Lectopia Lecture Audio
- 2010 Lecture - Week 3 | Science 2010
Lecture Overview
- Understand broadly the events of week 2-3 of human development
- Understand the process early placentation, villi formation
- Understand the process of gastrulation
- Understand the process of axis formation
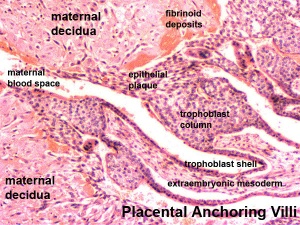
Early Placentation
The trophoblast layer has now differentiated into two morphologically distinct cellular layers.
- Syncitiotrophoblasts - form a multinucleated cytoplasmic mass by cytotrophoblast cell fusion and both invade the decidua and secrete hCG
- Cytotrophoblasts - form a cellular layer around the blastocyst, proliferates and extends behind syncitiotrophoblasts
Early Utero-Placental exchange - transfer of nutrition from maternal lacunae filled with secretions from uterine glands and maternal blood from blood vessels. The development of trophoblast villi extending into the uterine decidua.
There are three stages of villi development:
- Primary Villi - cytotrophoblast
- Secondary Villi - cytotrophoblast + extraembryonic mesoderm
- Tertiary Villi - cytotrophoblast + extraembryonic mesoderm+ blood vessels
There are two main types of early villi:
- Anchoring villi - attached to decidua
- Floating villi - not attached to decidua, floating in maternal lacunae.
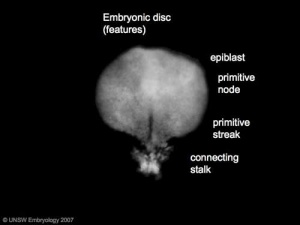
Gastrulation
Gastrulation, (Greek = belly) means the formation of gut, but has been used in a more looser sense to to describe the formation of the trilaminar embryo. The epiblast layer, consisting of totipotential cells, derives all 3 embryo layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. The primitive streak is the visible feature which represents the site of cell migration to form the additional layers.
Historically, gastrulation was one of the earliest observable morphological event occurring in the frog embryo. Currently, the molecular and physical mechanisms that regulate patterning and migration during this key event are being investigated in several different animal models. In humans, it is proposed that similar mechanisms regulate gastrulation to those found in other vertebrates.
- primitive node - region in the middle of the early embryonic disc epiblast from which the primitive streak extends caudally (tail)
- nodal cilia establish the embryo left/right axis
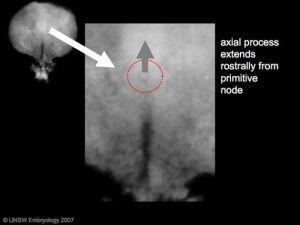
- axial process extends from the nodal epiblast
- primitive streak - region of cell migration from the epiblast layer forming sequentially the two germ cell layers (endoderm and mesoderm)
Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition
Epithelial cells (organised cellular layer) which loose their organisation and migrate/proliferate as a mesenchymal cells (disorganised cellular layers) are said to have undergone an Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT). Mesenchymal cells have an embryonic connective tissue-like cellular arrangement, that have undergone this process may at a later time and under specific signaling conditions undergo the opposite process, mesenchyme to epithelia. In development, this process can be repeated several times during tissue differentiation.
This process occurs at the primitive streak where epiblast cells undergo an epithelial to mesenchymal transition in order to delaminate and migrate.
MH - there are a number of common cellular changes that occur during embryonic development at different times and in different tissues, which we can classify into "developmental mechanisms". Mechanisms
Notochord
Movie - notochord 1 | - notochord 2
The notochord is a structure which has an early mechanical role in embryonic disc folding and a major signaling role in patterning surrounding embryonic tissue development. This signaling role patterns many different tissues (neural plate, neural tube, somites, endodermal organs). It has its own sequence of development from a primitive axial process and is a developmental feature not present in the adult anatomy.
- axial process an initial epiblast hollow epithelial tube which extends in the midline from the primitive pit, cranially in the embryonic disc (toward the oral membrane).
- neuroenteric canal is a transient communication between the amnionic cavity and the yolk sac cavity formed by the axial process.
- notochordal plate forms from the axial process merging with the endoderm layer.
- notochord forms from the notochordal plate which then separates back into the mesoderm layer as a solid column of cells lying in the midline of the embryonic disc and running rostro-caudally (head to tail).
- An alternate name for the notochord is "axial mesoderm".
MH - Much of our knowledge of this structure comes from the study of animal models of development.
UNSW Embryology Links
- Week 3 Slides Lecture 4 2008 | Lecture 4 2008 slides
- Week 3 Movies Movie - Implantation | Movie - Gastrulation | Chorionic cavity Movie - notochord 1 | - notochord 2 | Extracoelomic cavity | Nodal Cilia Movement
- Week 3 Notes Week 3 | Gastrulation | Trilaminar Embryo | Neural Tube Formation | Early Somite Formation | Developmental Mechanisms | Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition | Molecular Development | Abnormalities |
References
Textbooks
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Chapter 3
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 3
Online Textbooks
- Developmental Biology by Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000 Figure 11.22. The cleavage of a single mouse embryo in vitro | Figure 11.25. Mouse blastocyst hatching from the zona pellucida | Figure 11.20. Development of a human embryo from fertilization to implantation | Figure 11.24. Implantation of the mammalian blastocyst into the uterus
- Molecular Biology of the Cell 4th ed. Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter New York and London: Garland Science; c2002 - Fertilization | Figure 21-84. Scanning electron micrographs of the early mouse embryo | Figure 21-69. The blastula
- Molecular Cell Biology by Lodish, Harvey; Berk, Arnold; Zipursky, S. Lawrence; Matsudaira, Paul; Baltimore, David; Darnell, James E. New York: W. H. Freeman & Co.; c1999 Chapter 13. Regulation of the Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
- The Cell - A Molecular Approach by Cooper, Geoffrey M. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000 Figure 14.37. Meiosis of vertebrate oocytes
- HSTAT - In Vitro Fertilization As A Medical Treatment For Male or Female Infertility
- Human Molecular Genetics 2 Strachan, Tom and Read, Andrew P. New York and London: Garland Science; c1999 Figure 8.19. Changes in DNA methylation during mammalian development
Search
- Bookshelf placentation | placenta | implantation | gastrulation | notochord
- Pubmed placentation | placenta | implantation | gastrulation | notochord
Movies
| Implantation | Mesoderm | Chorionic Cavity | Amniotic Cavity | Week 3 |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Course Content 2009
Embryology Introduction | Cell Division/Fertilization | Cell Division/Fertilization | Week 1&2 Development | Week 3 Development | Lab 2 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Lab 3 | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Lab 4 | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Lab 5 | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Lab 6 | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Lab 7 | Kidney | Genital | Lab 8 | Sensory - Ear | Integumentary | Lab 9 | Sensory - Eye | Endocrine | Lab 10 | Late Vascular Development | Fetal | Lab 11 | Birth, Postnatal | Revision | Lab 12 | Lecture Audio | Course Timetable
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 1) Embryology 2009 Lecture 4. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2009_Lecture_4
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G