User:Z3389806: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
:: Chronic low frequency stimulation subjects the fast muscles to activity of low frequency and thereby, changing the pattern of motor activity imposed upon them. This alters the contractile characteristics of the fast muscles, making it to contract more slowly. This corresponds to the fast to slow fibre type shift.<ref><pubmed>4736724</pubmed></ref> | :: Chronic low frequency stimulation subjects the fast muscles to activity of low frequency and thereby, changing the pattern of motor activity imposed upon them. This alters the contractile characteristics of the fast muscles, making it to contract more slowly. This corresponds to the fast to slow fibre type shift.<ref><pubmed>4736724</pubmed></ref> | ||
3. '''Write a comment about the online page on Trisomy 21 based upon the group assessment criteria.''' | 3. '''Write a comment about the online page on [[Trisomy 21|Trisomy 21]] based upon the group assessment criteria.''' | ||
Revision as of 14:13, 18 September 2011
Lab 4 Online Assessment
- The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
- Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching. (Add to project page and your individual assessment page)
Lab Assessments
Lab 1 Assessment
1. Identify the origin of in vitro fertilisation and the 2010 Nobel Prize winner associated with this technique.
- In vitro fertilisation (IVF) technique was conceptualized by Sir Robert Geoffrey Edwards when he first managed to fertilise a human egg successfully in the laboratory in 1968. This led to the birth of the first baby conceived through IVF, Louise Brown, on 25th July 1978. Sir Robert Geoffrey Edwards is also the 2010 Nobel Prize winner associated with in vitro fertilisation.
2. Identify a recent paper on fertilisation and describe its key findings.
- A recent paper on fertilisation is titled “Women with high telomerase activity in luteinised granulosa cells have a higher pregnancy rate during in vitro fertilisation treatment”[1] by Hong Chen et al. It was reported in the paper that telomerase activity (TA) in the luteinized granulosa cells is positively correlated with clinical pregnancy rate. Clinical pregnancy rate increases with level of TA. This would mean that the success rate of the IVF treatment (resulting in pregnancy) can be predicted by measuring the levels of TA in the granulosa cells.
3. Identify 2 congenital anomalies.
- The two congenital anomalies are spina bifida, in which the embryonic neural tube is only partially closed, and hydrocephalus, in which there is an unusual accumulation of fluid in the brain.
--Mark Hill 00:44, 30 July 2011 (EST) Good wiki coding. Though I am not a fan of Wikipedia linking, should seek scientific references where possible, nobel prize link is better.
Lab 2 Assessment
1. Identify the ZP protein that spermatozoa binds and how is this changed (altered) after fertilisation.
2. Identify a review and a research article related to your group topic.
--Nur Sharalyn Abdullah 11:47, 9 August 2011 (EST)
--Nur Sharalyn Abdullah 14:20, 10 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 3 Assessment
1. What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development?
- The maternal dietary requirement for late neural development is iodine. Iodine is essential in the production of thyroid hormones which play a role in brain development.[5]
- Lack in iodine intake can result in cretinism. The recommended iodine intake during pregnancy is 200-250 micrograms per day.[6]
2. Upload a picture relating to your group project.
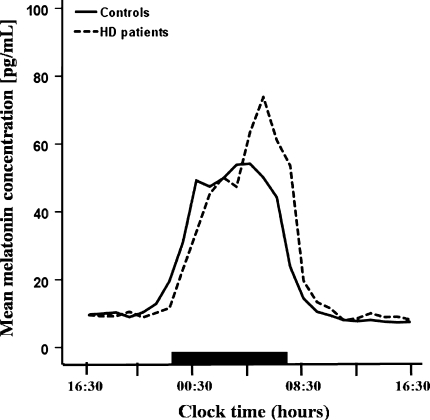
Melatonin levels in Huntington's disease patients and controls
The diurnal melatonin rise was significantly delayed in HD patients by about 01:30 h (p = 0.048). The black bar on the abscissa indicates the dark period (23:00–7:30 h).
--Nur Sharalyn Abdullah 12:47, 16 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 4 Assessment
1. The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
- The allantois, which originates from the hindgut, is continuous with the bladder.
2. Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Ductus arteriosus: located between pulmonary artery and aortic arch
- Ductus venosus: located between umbilical vein and inferior vena cava
- Foramen ovale: located between left atrium and right atrium
3. Identify the group project sub-section that you will be researching.
- History
- Treatment
- Epidemiology
--Nur Sharalyn Abdullah 21:47, 20 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 5 Assessment
1. Which side (L/R) is most common for diaphragmatic hernia and why?
- The left side is the most common for diaphragmatic hernia. It is thought that this is due to the earlier closure of the right pleuroperitoneal opening.[7]
--Z3389806 19:10, 31 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 6 Assessment
1. What week of development do the palatal shelves fuse?
- The fusion of palatal shelves fuse during week 9 of embryonic development.
2. What animal model helped elucidate the neural crest origin and migration of cells?
- The animal model which helped elucidate neural crest origin and migration of cells is the quail-chick chimeras.[8]
3. What abnormality results from neural crest not migrating into the cardiac outflow tract?
--Z3389806 22:52, 13 September 2011 (EST)
Lab 7 Assessment
1. Are satellite cells (a) necessary for muscle hypertrophy and (b) generally involved in hypertrophy?
- (a) No, satellite cells are not necessary for muscle hypertrophy.
- (b) Yes, satellite cells are generally involved in hypertrophy.
2. Why does chronic low frequency stimulation cause a fast to slow fibre type shift?
- Chronic low frequency stimulation subjects the fast muscles to activity of low frequency and thereby, changing the pattern of motor activity imposed upon them. This alters the contractile characteristics of the fast muscles, making it to contract more slowly. This corresponds to the fast to slow fibre type shift.[11]
3. Write a comment about the online page on Trisomy 21 based upon the group assessment criteria.
Attendance
--Z3389806 18:01, 29 July 2011 (EST)
--Z3389806 12:55, 4 August 2011 (EST)
--Z3389806 11:41, 11 August 2011 (EST)
--Z3389806 11:07, 18 August 2011 (EST)
--Z3389806 11:12, 25 August 2011 (EST)
--Z3389806 11:11, 1 September 2011 (EST)
--Z3389806 11:13, 15 September 2011 (EST)
References
- ↑ Chen H, Wang W, Mo Y, Ma Y, Ouyang N, Li R, Mai M, He Y, Bodombossou-Djobo MM, Yang D. Women with high telomerase activity in luteinised granulosa cells have a higher pregnancy rate during in vitro fertilisation treatment. J Assist Reprod Genet.: 2011 PMID:21717175 [1]
- ↑ <pubmed>9369183</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>19778707</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>21674647</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15107513</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>19088150</pubmed>
- ↑ Moore, K.L. & Persuad, T.V.N. (2008). The Developing Human: clinically oriented embryology (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders, p. 153
- ↑ <pubmed>3058162</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>3568286</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>3791607</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>4736724</pubmed>