User:Z3332178
Lab 4 Online Assessment
- The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
- Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching. (Add to project page and your individual assessment page)
Lab attendance
--z3332178 12:55, 28 July 2011 (EST)
--z3332178 13:04, 4 August 2011 (EST)
--z3332178 11:07, 11 August 2011 (EST)
--z3332178 11:09, 18 August 2011 (EST)
--z3332178 11:06, 25 August 2011 (EST)
--z3332178 11:15, 1 September 2011 (EST)
--z3332178 11:53, 15 September 2011 (EST)
Online Assessments
Lab 1 Assessment
1. Identify the origin of In Vitro Fertilization and the 2010 nobel prize winner associated with this technique.
Robert Edwards first started research in human IVF after the successful attempts of fertilisation outside the womb in other animals by various scientists. After contacting Patrick Steptoe, a gynaecologist ,Edwards was able to begin practicing IVF on humans. Together they studied the hormone levels of female patients and worked out the optimal time for fertilisation to occur to increase the success rate of implantation. Edwards later implanted the first successful “test tube baby”, Louise Brown born on the 25th of July, 1978. In 2010, Robert Edwards was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the development of in vitro fertilisation.
2. Identify a recent paper on fertilisation and describe its key findings.
The article “Zona pellucida-based contraceptive vaccines for human and animal utility” addresses the potential use of the glycoproteins found in the zona pellucida as a vaccine to prevent pregnancies. The contraceptive vaccine would aim to prevent gamete production, fertilisation and therefore a successful pregnancy. The testing was performed mainly on wildlife animals and was found to be successful. However, before using it for the human population more research needs to be done to increase the success rate and variations of the antibodies amongst species and therefore the duration of the vaccines productivity has to be reassessed. There is also the issue of possible oophoritis that may develop in women using this method of contraception. Despite the limitations of the contraceptive vaccine for human use, it is still profitable for wildlife context.
Gupta SK. Gupta N. Suman P. Choudhury S. Prakash K. Gupta T. Sriraman R. Nagendrakumar SB. Srinivasan VA. Zona pellucida-based contraceptive vaccines for human and animal utility. [Review] Journal of Reproductive Immunology. 88(2):240-6, 2011 Mar.[1]
3. Identify 2 congenital anomalies.
Spina bifida
Bladder exstrophy
--Mark Hill 10:10, 3 August 2011 (EST) These answers are fine for the assessment.
Lab 2 Assessment
1. Identify the ZP protein that spermatozoa binds and how is this changed (altered) after fertilisation.
When the spermatozoa reaches the zona pellucida, ZP protein 3 binds with the spermatozoa. This reaction causes the release of degradative enzymes from the acrosome, thus allowing the sperm to enter the zona pellucida.
2. Identify a review and a research article related to your group topic.
Review Article
“The behavioral phenotype of Williams syndrome: A recognizable pattern of neurodevelopment” by Colleen A. Morris
The review article concludes that people with Williams syndrome share distinct cognitive and behavioural features. The phenotype of a typical patient will be due to the deleted genes of chromosome 7 q11.23.[2]
Research Article
“Impaired geometric reorientation caused by genetic defect” by Laura Lakusta, Banchiamlack Dessalegn, and Barbara Landau
By testing participants in a plain or single blue walled chamber, the study was able to show that Williams syndrome patients show a failure to reconstruct and use geometric representations of the chamber to find hidden objects.[3]
Lab 3 Assessment
1. What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development?
There are many nutritional requirements to promote greater success in late neural development. Iodine plays a role in the formation of the cerebellum and the thyroid, foliate in the closing of the neural tube and Omega 3 plays a special role in the development of the brain stem as well as other neural structures.
2. Upload a picture relating to you group project.
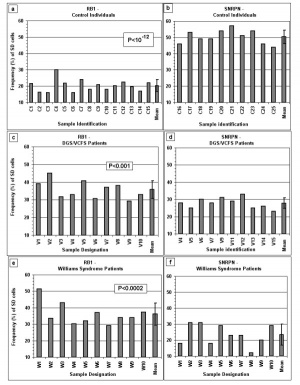
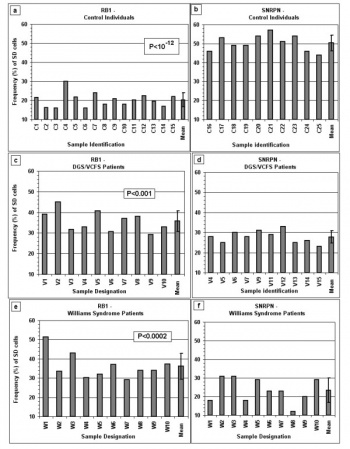
The frequency of SD cells for RB1 and SNRPN in WS and control individuals.
Lab 4 Assessment
1. The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
Initially formed by an invagination in the hindgut, and extends from the hindgut into the umbilical cord to the placenta.
2. Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Ductus Arteriosus – A shunt allowing blood flow to bypass the pulmonary artery straight into the aortic arch
- Ductus Venosus – Allowing blood flow from the umbilical vein into the inferior vena cava
- Foramen Ovale – Between right and left atrium allowing the flow of blood to bypass the right ventricle.
3. Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching.
1 Introduction
2 History of the disease
3 Etiology
4 Genetic Factors
5 *Physical Characteristics*
6 Associated medical conditions
7 *Cognitive, Behavioural and Neurological Problems*
8 Epidemiology
9 Management/treatment
10 Specialized Facilities/ supportive associations
11 Current research and developments
Lab 5 Assessment
1. Which side (L/R) is most common for diaphragmatic hernia and why?
The right side of the diaphragm is the first to close and therefore the left side is more susceptible to hernias.
Lab 6 Online Assessment
1. What week of development do the palatal shelves fuse?
9th week
2. What early animal model helped elucidate the neural crest origin and migration of neural crest cells?
Chicken model
3. What abnormality results from neural crest not migrating into the cardiac outflow tract?
The heart defect Tetralogy of Fallot
Lab 7 Online Assessment 1. Are satellite cells (a) necessary for muscle hypertrophy and (b) generally involved in hypertrophy?
(a) No, not for hypertrophy, but are essential for the formation of new muscle fibers.
(b) Yes, they can play a role in muscle regeneration however, it is not essetial.
2. Why does chronic low frequency stimulation cause a fast to slow fibre type shift?
The CLFS causes the muscle to continuously exhibit a slow muscle fiber type. Yhe strain induced on the fast muscle fibers causes the gradual shift of the fast to slow muscle fiber type.