User:Z3290270: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
--[[User:Z3290270|Maeda Sadeghpour]] 00:48, 1 September 2011 (EST) | --[[User:Z3290270|Maeda Sadeghpour]] 00:48, 1 September 2011 (EST) | ||
== '''Lab 6 Assignment: ''' == | |||
'''1. What week of development do the palatal shelves fuse?''' | |||
The palatal shelveds fuse in week 9 of development. The fusion takes place between both secondary and primary palate which is shapes at approximately week 6. | |||
'''2. What animal model helped elucidate the neural crest origin and migration of cells?''' | |||
The quail-chick chimeras. | |||
'''3. What abnormality results from neural crest not migrating into the cardiac outflow tract?''' | |||
Tetralogy of fallot which results in failure of the pulmonary trunk and aorta to divide functionally. | |||
--[[User:Z3290270|Maeda Sadeghpour]] 01:20, 15 September 2011 (EST) | |||
Revision as of 01:20, 15 September 2011
Lab attendence:
--Z3290270 12:56, 28 July 2011 (EST)
--Maeda Sadeghpour 11:48, 4 August 2011 (EST)
--z3290270 11:47, 11 August 2011 (EST)
--Maeda Sadeghpour 11:09, 18 August 2011 (EST)
--Maeda Sadeghpour 11:06, 25 August 2011 (EST)
--Maeda Sadeghpour 12:03, 1 September 2011 (EST)
Lab 1 Assignment:
1. Identify the origin of In Vitro Fertilization and the 2010 nobel prize winner associated with this technique. The history of IVF dates back to early as 1890s with physicians conducting experiemnts on animal embryo transplantation. With increased research into egg maturation cycle and optimal conditions of fertilization in the womb, the first IVF animal was born in 1959. Robert Edwards was awarded The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2010 for the "for the development of in vitro fertilization".
2. Identify a recent paper on fertilisation and describe its key findings.
Carson C, Kelly Y, Kurinczuk J, Sacker A, Redshaw M, Quigley M. (2011). Effect of pregnancy planning and fertility treatment on cognitive outcomes in children at ages 3 and 5: longitudinal cohort study. BMJ, 343(d4473). The UK based cohort study recorded cognitive outcomes in children born after planned and unplanned pregnancy. The study found that there is no evidence that pregnancy planning, subfertility, or assisted fertility had a direct affect on the subject’s cognitive development at age 3 or 5. Children conceived through unplanned pregnancies score poorly in comparison to those born as a result of planned pregnancy but this was linked to socioeconomic factors and inequalities.
3. Identify 2 congenital anomalies.
Hirschsprung’s disease, Spina bifida
--Mark Hill 09:49, 3 August 2011 (EST) These answers are fine, you seem to be able to work online for this course. I will also be showing you how the reference can be linked to the internet database.
Lab 2 Assignment:
1. Identify the ZP protein that spermatozoa binds and how is this changed (altered) after fertilisation.
ZP3 – Zona pellucida glycoprotein 3, which acts as a receptor for spermatozoa. ZP3 stimulates the acrosome reaction, allowing enzymes to be released from the acrosome of the sperm which subsequently digest a path through the zona pellucida. This causes intracellular calcium levels in the oocyte to increase, causing the activation of cortical granules. An enzyme of the cortical granules clips the terminal sugar residues of ZP3 carbohydrate chains which makes the egg impenetrable by another sperm.
2. Identify a review and a research article related to your group topic. (Paste on both group discussion page with signature and on your own page)
Review: Padmanabhan, R. (2006). Etiology, pathogenesis and prevention of neural tube defects. Congenital Anomalies, 46(2), 55-67.
Research: Joó, J. G., Beke, A., Papp, C., Tóth-Pál, E., Csaba, A., Szigeti, Z., Papp, Z. (2007). Neural tube defects in the sample of genetic counselling. Prenatal Diagnosis, 27(10), 912-21.
Lab 3 Assignment:
What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development?
Iodine, 250μg/day. Iodine is critical in the synthesis of thyroid hormones which have a significant role in fetal development.
Shah, D., & Sachdev, H. P. (2004). Maternal micronutrients and fetal outcome. Indian J Pediatr, 71(11), 985-90.
Establishment of HD hybrid cell line
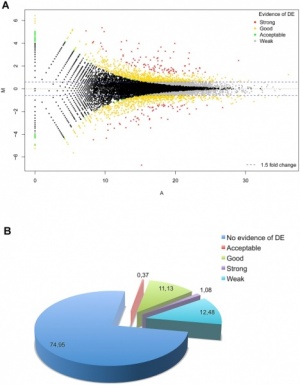
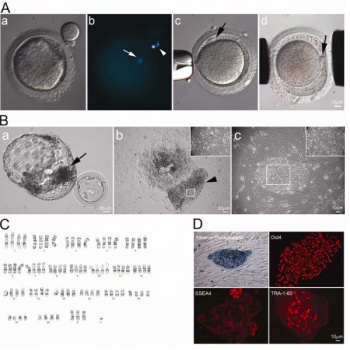
(A) First polar body of mature rhesus macaque oocyte was removed by gentle squeezing through a slit of zona pellucida (A-a). Staining of 1st polar body DNA (arrowhead) and oocyte DNA (arrow) (A-b). HD monkey skin cell was placed under the zona pellucida (black arrow) (A-c). Reconstructed oocyte with HD monkey skin cell (A-d; yellow arrow) was placed between two electrodes for electrofusion (A-d). (B) Day 12 hatching blastocyst derived from HD monkey hybrid embryo (B-a; arrow indicated ICM). HD monkey hybrid blastocyst outgrowth at six days after attached onto feeder cells (B-b). High magnification of selected region (inset) of the ICM outgrowth (arrowhead). HD monkey hybrid cell line (TrES1) at passage 10 (B-c). (C) G-banding analysis of TrES1. Cytogenetic analysis of TrES1 demonstrated tetraploid chromosome (84; XXXY). (D) Expression of ES-cell specific markers: Alkaline phosphatase, Oct4, SSEA4 and TRA-1-60.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2833146/?tool=pmcentrez
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. --Maeda Sadeghpour 21:21, 17 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 4 Assignment:
1. The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
Ventral outgrowth of the hindgut in developing embryo, expanding from the caudal wall of the yolk sac.
2. Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
1. Ductus Venosus - connecting portal and umbilical veins to the inferior vena cava.
2. Ductus Arteriosus - connects pulmonary trunk to aorta.
3. Foramen Ovale - connects right and left atrium.
3. Identify the group project sub-section that you will be researching.
- Pathogenesis
- Genetics --z3290270 23:31, 24 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 5 Assignment:
Which side (L/R) is most common for diaphragmatic hernia and why?
Diaphragmatic hernias are more common on the left side. It is most likely due to the earlier closure of the right pleuroperitoneal opening. This could be life threatening due to compression of the lungs and other organs.
--Maeda Sadeghpour 00:48, 1 September 2011 (EST)
Lab 6 Assignment:
1. What week of development do the palatal shelves fuse?
The palatal shelveds fuse in week 9 of development. The fusion takes place between both secondary and primary palate which is shapes at approximately week 6.
2. What animal model helped elucidate the neural crest origin and migration of cells?
The quail-chick chimeras.
3. What abnormality results from neural crest not migrating into the cardiac outflow tract?
Tetralogy of fallot which results in failure of the pulmonary trunk and aorta to divide functionally.
--Maeda Sadeghpour 01:20, 15 September 2011 (EST)