Stem Cells: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
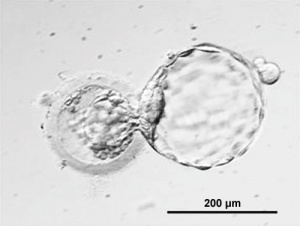
[[Image:CSt3.jpg|thumb|Human Blastocyst (Carnegie Stage 3) | [[Image:CSt3.jpg|thumb|Human Blastocyst (Carnegie Stage 3)]] | ||
The term "stem cell" is used so freely these days in many different forums that it is difficult sometimes understand without context what scientists, politicians, ethicists and commentators are discussing. In terms of human development, the embryonic stem cell with totipotential occurs at the blastocyst stage, mainly in the first and second week of development. After this period the inner cell mass, which forms the entire embryo, will differentiate into embryonic germ layers with restricted differentiation potential. | The term "stem cell" is used so freely these days in many different forums that it is difficult sometimes understand without context what scientists, politicians, ethicists and commentators are discussing. In terms of human development, the embryonic stem cell with totipotential occurs at the blastocyst stage, mainly in the first and second week of development. After this period the inner cell mass, which forms the entire embryo, will differentiate into embryonic germ layers with restricted differentiation potential. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 6: | ||
''In vitro'' fertilization and growth of the blastocyst, allows isolation of these cells and their subsequent use in stem cell research. It is the collection, production and possible therapeutic applications of these stem cells which has recently attracted worldwide attention. | ''In vitro'' fertilization and growth of the blastocyst, allows isolation of these cells and their subsequent use in stem cell research. It is the collection, production and possible therapeutic applications of these stem cells which has recently attracted worldwide attention. | ||
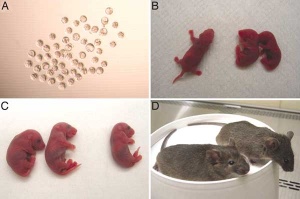
[[Image:Mice cloned from adult keratinocytes.jpg|thumb|Mice cloned from adult keratinocytes]] | |||
A key step in the development of stem cell research has been the identification of cell surface markers (proteins) which identify these cells and their state of undifferentiation. | A key step in the development of stem cell research has been the identification of cell surface markers (proteins) which identify these cells and their state of undifferentiation. | ||
Revision as of 14:27, 24 February 2010
Introduction
The term "stem cell" is used so freely these days in many different forums that it is difficult sometimes understand without context what scientists, politicians, ethicists and commentators are discussing. In terms of human development, the embryonic stem cell with totipotential occurs at the blastocyst stage, mainly in the first and second week of development. After this period the inner cell mass, which forms the entire embryo, will differentiate into embryonic germ layers with restricted differentiation potential.
Stem cells as well as having the capacity to differentiate into any (totipotential) or multiple (pluripotential) cell types, have the unique capacity of self-renewal.
In vitro fertilization and growth of the blastocyst, allows isolation of these cells and their subsequent use in stem cell research. It is the collection, production and possible therapeutic applications of these stem cells which has recently attracted worldwide attention.
A key step in the development of stem cell research has been the identification of cell surface markers (proteins) which identify these cells and their state of undifferentiation.
A useful guide (online PDF document) to stem cells was produced in a report by the National Institute of Health (NIH, USA, May 2000) Stem Cells: A Primer (note large size - 4.84 Mb) and more recently NIH has established a Stem Cell information page.
Other UNSW Embryology Pages: Stem Cell Ethics | Cord Blood | Adult Stem Cells | Neural Stem Cells | Week 2 Stem Cells | Cloning
Some Recent Findings
- Pluripotent stem cell-derived gametes: truth and (potential) consequences. Mathews DJ, Donovan PJ, Harris J, Lovell-Badge R, Savulescu J, Faden R. Cell Stem Cell. 2009 Jul 2;5(1):11-4. PMID: 19570509
- "An emerging body of data suggests that pluripotent stem cells may be able to differentiate to form eggs and sperm. We discuss the state of the science and the potential social implications and offer recommendations for addressing some of the ethical and policy issues that would be raised by the availability of stem cell-derived gametes. ...PSC-derived gamete research represents the convergence of several areas of ethical and policy debate and inquiry—stem cell research, human genetic research, reproductive technologies, and human enhancement—bringing many of today's most contentious ethical issues into the same conversation."
- Conrad S, Renninger M, Hennenlotter J, Wiesner T, Just L, Bonin M, Aicher W, Bühring HJ, Mattheus U, Mack A, Wagner HJ, Minger S, Matzkies M, Reppel M, Hescheler J, Sievert KD, Stenzl A, Skutella T. Generation of pluripotent stem cells from adult human testis. Nature. 2008 Oct 8. PMID: 18849962
- "Human primordial germ cells and mouse neonatal and adult germline stem cells are pluripotent and show similar properties to embryonic stem cells. Here we report the successful establishment of human adult germline stem cells derived from spermatogonial cells of adult human testis."
- Kondo T, Sheets PL, Zopf DA, Aloor HL, Cummins TR, Chan RJ, Hashino E. Tlx3 exerts context-dependent transcriptional regulation and promotes neuronal differentiation from embryonic stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 7
- "The T cell leukemia 3 (Tlx3) gene has been implicated in specification of glutamatergic sensory neurons in the spinal cord. ...The sequential and coordinated expression of the proneural and neuronal subtype-specific genes identifies Tlx3 as a selector gene in ES cells undergoing neural differentiation."
- USA Food and Drug Administration (FDA) first public hearing on the safety of therapies that use human embryonic stem cells. "Cellular Therapies Derived from Human Embryonic Stem Cells –Considerations for Pre-Clinical Safety Testing and Patient Monitoring, April 10, 2008" The biotech company Geron plans to trial a stem cell based therapy for patients with acute spinal-cord injury. (More?FDA Meeting Briefing Document PDF)
Australian Stem Cells
2006 A private members bill was introduced (19Oct06) and passed (7Nov06) in the Australian Senate amending an earlier act relating to stem cells research. Prohibition of Human Cloning for Reproduction and the Regulation of Human Embryo Research Amendment Act 2006 This will allow stem research using human embryos under strict controls and now requires passing through the House of Represenatives before the Amendment will become law. [../pdf/SenateStemCell06Bill19100603.pdf PDF - Amendment Bill 2006]
2005Lockhart Review "On 17 June 2005, the former Minister for Ageing, the Hon Julie Bishop MP, appointed a committee to conduct independent reviews of Australia's Prohibition of Human Cloning Act 2002 and the Research Involving Human Embryos Act 2002. The Committee was required to consult with the Australian, State and Territory governments and a broad range of people with expertise or experience in relevant disciplines. The Committee called for written submissions on the scope and operation of the two Acts." Lockhart Review | Lockhart Review - Media Release
See also [#NHMRC Australian NHMRC Information]
Stem Cell Use
Results from a recent Australian survey into couples' views on the use of supernumerary embryos ([#16716313 Hammarberg and Tinney, 2006]).
40% (123/311) returned completed questionnaires.
42% most common decision was donation to research (altruistic motives and desire not to waste embryos were determinants of embryo donation).
Determinants of disposal were not wanting a full sibling to existing children and opposition of embryo research.
45% found deciding distressing.
69% approved of embryo donation to stem-cell research.
Cord Blood Stem Cell
Placental cord blood is a rich souce of haematopoietic stem cells for transplantation. Cord blood can collected at birth, with no impact on the mother or neonate, and stured in cord blood banks for later use. (More? [stemcell4.htm Stem Cells - Cord Blood])
BBC (UK) A brief article on Cord Blood stem cells and their therapeutic potential.
Spermatogonial Stem Cell (SSC)
In the male testes are a population of spermatogonia cells that differentiate and meiotically divide to form spermatozoa cells (male germ cells).
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Ikawa M, Takehashi M, Ogonuki N, Miki H, Inoue K, Kazuki Y, Lee J, Toyokuni S, Oshimura M, Ogura A, Shinohara T. Production of knockout mice by random or targeted mutagenesis in spermatogonial stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 23;103(21):8018-23.
Ehmcke J, Wistuba J, Schlatt S. Spermatogonial stem cells: questions, models and perspectives. Hum Reprod Update. 2006 May-Jun;12(3):275-82.
Aponte PM, van Bragt MP, de Rooij DG, van Pelt AM. Spermatogonial stem cells: characteristics and experimental possibilities. APMIS. 2005 Nov-Dec;113(11-12):727-42.
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Ogonuki N, Iwano T, Lee J, Kazuki Y, Inoue K, Miki H, Takehashi M, Toyokuni S, Shinkai Y, Oshimura M, Ishino F, Ogura A, Shinohara T. Genetic and epigenetic properties of mouse male germline stem cells during long-term culture. Development. 2005 Sep;132(18):4155-63.
Ogawa T, Ohmura M, Yumura Y, Sawada H, Kubota Y. Expansion of murine spermatogonial stem cells through serial transplantation. Biol Reprod. 2003 Jan;68(1):316-22.
Adult Stem Cell
Adult stem cells, with pluropotentiality, are found in three main body systems: intestinal epithelium, epidermis, and bone marrow. (More? Adult Stem Cells)
Inducible Stem Cells
Stem Cell Markers
In order to carry out research on stem cells, it is important to be able to identify them. A number of different research groups in the late 90's generated several antibodies which specifically identified undifferentiated, differentiating or differentiated stem cells from a number of different sources and species. Note that the nomenclature in some cases is based upon the antibody used to identify the cell surface marker.
- Stage-Specific Embryonic Antigen-1 (SSEA-1) cell surface embryonic antigen which has a role in cell adhesion, migration and differentiation and is often differentially expressed during development. Can be identified by Davor Solter monoclonal antibody MC-480 (SSEA-1).
- Stage-Specific Embryonic Antigen-4 (SSEA-4) cell surface embryonic antigen of human teratocarcinoma stem cells (EC), human embryonic germ cells (EG) and human embryonic stem cells (ES) which is down-regulated following differentiation of human EC cells. Antigen not expressed on undifferentiated murine EC, ES and EG cells but upregulated on differentiation of murine EC and ES cells. Can be identified by Davor Solter monoclonal antibody MC-813-70 (SSEA-4)
- Tumor Rejection Antigen (TRA-1-60) Sialylated Keratan Sulfate Proteoglycan expressed on the surface of human teratocarcinoma stem cells (EC), human embryonic germ cells (EG) and human embryonic stem cells (ES).
- Tumor Rejection Antigen (TRA-1-81) antigen expressed on the surface of human teratocarcinoma stem cells (EC), human embryonic germ cells (EG) and human embryonic stem cells (ES). Both TRA antibodies identify a major polypeptide (Mr 240 kDa) and a minor polypeptide (Mr 415 kDa).
- Oct-4 (Pou5f1 – Mouse Genome Informatics) gene has an essential role in control of developmental pluripotency (Oct4 knockout embryo blastocysts die at the time of implantation). Oct4 also has a role in maintaining viability of mammalian germline.
- Stem Cell Antigen 1 (Sca-1) member of the Ly-6 family of GPI-linked surface proteins (Mr 18 kDa) and a major phenotypic marker for mouse hematopoietic progenitor/stem cell subset.
- CD133, AC133, prominin 5 transmembrane glycoprotein (865 aa) expressed on stem cells with hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic differentiation potential.
- Alpha 6 integrin
References
Shamblott M.J. et. al. (1998). PNAS 95: 13726-13731 ; Schuldiner M. et. al. (2000). PNAS 97: 11307 - 11312 ; Thomson J.A. et. al. (1998). Science 282: 1145-1147 ; Reubinoff B.E. et. al. (2000). Nature Biotechnology 18: 399-404 ; Henderson J.K. et. al. (2002). Stem Cells 20: 329-337; Pera M. et. al. (2000). J. Cell Science 113: 5-10.; The Human Embryonal Carcinoma Marker Antigen TRA-1-60 Is a Sialylated Keratan Sulfate Proteoglycan; [www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi%3Fcmd=Retrieve&%20db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=15486564 Oct4 is required for primordial germ cell survival.]; Sca-1 expression identifies stem cells in the proximal region of prostatic ducts with high capacity to reconstitute prostatic tissue;
Data based on information from Appendix E.II. NIH Report "Stem Cells: Scientific Progress and Future Research Directions", Chemicon International- Stem cell marker antibodies OMIM and other sources.
Stem Cell Fake Result
Hwang Woo-suk (Korean pioneer of stem cell research) Resigns A Seoul National University investigation of the original data in Science paper Jun (2005;308: 1777-83) "Eleven human embryonic stem cells (hESC) lines were established by nuclear transfer (SCNT; NT) of skin cells from patients with disease or injury into donated oocytes." announced 29 Dec 2005 that he had faked the results. The journal Science also announced it will retract the original paper (see links below). (BMJ 07 Jan) Stem Cells | Science News 06 Jan | Special Online Collection: Hwang et al. and Stem Cell Issues | Original Reference with link to Erratum (Science. 2005 Dec 16;310(5755):1769)
Cancer
There is a hypothesis that several cancers may arise from somatic stem or progenitor cells that exist in different tissues. These cancer stem cells are called "side population" (SP) cells and have been identified in: leukemia, breast cancer and several human cancer cell lines (central nervous system, gastrointestinal tumors, retinoblastoma). There is still a "chicken and egg" problem to be resolved, in that the cancer cells may have dedifferentiated to a stem cell-like population.
A recent paper has also identified SP cells in ovarian cancer which have properties similar to stem cells.
Reference: Szotek PP, Pieretti-Vanmarcke R, Masiakos PT, Dinulescu DM, Connolly D, Foster R, Dombkowski D, Preffer F, Maclaughlin DT, Donahoe PK. Ovarian cancer side population defines cells with stem cell-like characteristics and Mullerian Inhibiting Substance responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 18
References
Journals | Reviews | Articles | Online Textbooks | Search Textbooks | Search PubMed |
Journals
- Cell Stem Cell is the official affiliated journal of the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR).
- Stem Cells welcomes original articles and concise reviews describing basic laboratory investigations of stem cells and the translation of their clinical aspects of characterization and manipulation from the bench to patient care. The journal covers all aspects of stem cells: embryonic stem cells; tissue-specific stem cells; cancer stem cells; the stem cell niche; stem cell genomics and proteomics; and translational and clinical researc
Reviews
- Pluripotent stem cell-derived gametes: truth and (potential) consequences. Mathews DJ, Donovan PJ, Harris J, Lovell-Badge R, Savulescu J, Faden R. Cell Stem Cell. 2009 Jul 2;5(1):11-4. PMID: 19570509
- Moore KA, Lemischka IR. Stem cells and their niches. Science. 2006 Mar 31;311(5769):1880-5.
- Li L, Xie T. Stem cell niche: structure and function. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:605-31.
Articles
- Hiroyama T, Miharada K, Aoki N, Fujioka T, Sudo K, Danjo I, Nagasawa T, Nakamura Y. Long-lasting in vitro hematopoiesis derived from primate embryonic stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2006 Jun;34(6):760-9.
- Meshorer E, Misteli T. Chromatin in pluripotent embryonic stem cells and differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006
- Yamazoe H, Kobori M, Murakami Y, Yano K, Satoh M, Mizuseki K, Sasai Y, Iwata H. One-step induction of neurons from mouse embryonic stem cells in serum-free media containing vitamin B12 and heparin. Cell Transplant. 2006;15(2):135-45.
- Skottman H, Dilber MS, Hovatta O. The derivation of clinical-grade human embryonic stem cell lines. FEBS Lett. 2006 May 22;580(12):2875-8.
- Skottman H, Dilber MS, Hovatta O. The derivation of clinical-grade human embryonic stem cell lines. FEBS Lett. 2006 May 22;580(12):2875-8.
- Hammarberg K, Tinney L. Deciding the fate of supernumerary frozen embryos: a survey of couples' decisions and the factors influencing their choice. Fertil Steril. 2006 May 20
- Szotek PP, Pieretti-Vanmarcke R, Masiakos PT, Dinulescu DM, Connolly D, Foster R, Dombkowski D, Preffer F, Maclaughlin DT, Donahoe PK. Ovarian cancer side population defines cells with stem cell-like characteristics and Mullerian Inhibiting Substance responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 18
Search PubMed
May 2006 "stem cell" 154,176 reference articles of which 16,449 were reviews.
Search PubMed Now: stem cell | embryonic stem cell | adult stem cell |
Earlier Links (2002 - 2004)
California Governor Schwarzenegger Endorses Stem-Cell Bonds Oct. 18, 2004 California Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger endorsed a proposal to sell $3 billion of bonds to fund stem-cell research, two weeks before a vote that may make California the biggest U.S. sponsor of such studies. The initiative is a response to President George W. Bush's decision to limit federal funding of research with embryonic stem cells, which are seen as a potential source of cures for disease. The governor's endorsement may benefit a campaign that only has a narrow lead among voters, according to a recent opinion poll. "Research that we do now holds the promise of cures for tomorrow," Schwarzenegger said in an e-mail statement to reporters. "California has always been a pioneer. We daringly led the way for the high-tech industry and now voters can help ensure we lead the way for the biotech industry." Read Bloomberg Article
Sydney Stem Cells "Embryonic stem cells created in Australian first"ABC News Thursday, June 24, 2004
The medical director of Sydney IVF, Robert Jansen, says while mainstream uses are still a few years away, the team's breakthrough will lead the way for new research. "They can be used by researchers for developing or learning more about how cells become other more specialised cells that might be used, for instance, to repopulate someone's pancreas if they have juvenile diabetes," he said.
May 2004 NIH Clinical Trials Launches Study of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe, Treatment-Resistant Lupus (NIAMS, May 13,2004)
A clinical therapeutic trial in the USA for hematopoietic stem cells in an autoimmune disease.
"A five-year study to see whether a therapy using transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells, blood stem cells found in bone marrow, can produce long-term remission for patients with severe, treatment-resistant systemic lupus erythematosus (or lupus), a rheumatic autoimmune disease that can affect the body's major organs. The study will include a basic research component to examine the roles of B and T cells, white blood cells in the immune system, in triggering lupus symptoms."
Read more of the NIH Press Release
Note that a May search of NIH Clinical Trials with "stem cell" found 302 study results.
Repeat search: NIH Clinical Trials with "stem cell"
As of 2002, there were available up to 60 human stem cell lines (according to information supplied to President Bush). ([#NIH(USA) More? NIH (USA) Stem Cell Information]) These cell lines exist in many different countries including: Australia, India, Israel, Sweden and USA. ([#lab list More? see list of Labs])
Australian NHMRC
INFORMATION FOR HUMAN RESEARCH ETHICS COMMITTEES SHEET NUMBER 5 - STEM CELL RESEARCH The Australian Health Ethics Committee has been approached by human research ethics committees (HRECs) seeking advice on how to review research protocols that involve stem cell research.The following guidance is interim. Formal guidelines will be developed by AHEC in the context of its review of the 1996 NHMRC Ethical guidelines on assisted reproductive technology.
(USA) NIH - Stem Cell Information
NIH Stem Cell Reports | Regenerative Medicine 2006 | Stem Cells: Scientific Progress and Future Research Directions (2001)
National Human Genome Research Institute - Cloning/Embryonic Stem Cells
Stem Cells (2001)
- FDA Letter to Senator Edward M. Kennedy Regarding Stem Cells, September 5, 2001
- Secretary Thompson's Oral Testimony before the Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee, September 5, 2001
- National Institutes of Health and WiCell Research Institute, Inc., Sign Stem Cell Research Agreement, September 5, 2001
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) Update on Existing Human Embryonic Stem Cells, August 27, 2001
- Statement by Tommy G. Thompson, Secretary of Health and Human Services, Regarding Stem Cell Lines, August 27, 2001
- Video Broadcast - Briefing by HHS Secretary Tommy G. Thompson on Federal Funding of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research, August 10, 2001
- NIH Statement on the President's Stem Cell Address, August 9, 2001
- White House Fact Sheet on Embryonic Stem Cell Research, August 9, 2001
- Statement by HHS Secretary Tommy G. Thompson Regarding the President's Decision on Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research, August 9, 2001
- Approval Process for the Documentation of Compliance with the NIH Guidelines on the Use of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in NIH Research Proposed for Support Under Grants and Cooperative Agreements, November 21, 2000
- Approval Process for the Documentation of Compliance with NIH Guidelines on the Use of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in NIH Intramural Research, January 16, 2001
Stem Cells in The News
(More? [../News/news.htm see Embryology News])
WWW Links
International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) is an independent, nonprofit organization formed in 2002 to foster the exchange of information on stem cell research.
University of Michigan Stem Cells Explained
Transcript of discussion on ABC Radio (Dr. J Kahn , Dr. JWagner) on Genetic Technology And Ethics
A brief article on Cord Blood stem cells and their therapeutic potential from the BBC.
Monash University (Australia) [%20http://www.med.monash.edu.au/miscl/ Monash Immunology and Stem Cell Laboratories (MISCL)]
Human Stem cells in the News mainly in regard to USA political position on Human Stem Cell Research (BBC links)
- Bush stem cell move widely (10 August)
- Press see 'political' stem cell decision (10 August)
- Bush facing stem cell storm (10 August)
- Stem cell compromise angers hardliners (10 August)
- Stem cells: Q & A (10 August)
- Japan set to embrace stem cell research (1 August)
- Read this May 2000 article on Stem Cells from NIH USA
The external link to CNN requires Quicktime Stem Cell Animation === Navigation ===
Internal Links Stem Cells
Stem Cell Ethics | Cord BloodAdult Stem Cells | Week 2 Stem Cells | Cloning
Breakthroughs in stem cell research appear frequently in the news, governments legislate about research, origin and use, community groups argue the ethics of human stem cells, individuals seek answers for fertility and disease.
More recently the finding of [#FakeResult faked results] by a key Korean stem cell researcher has drawn attention to not only to stem cell work, but also the pressure upon researchers to generate "results".
With so many levels this area of embryology has become extremely complex. This current page looks only at the embryonic stage related to the origin of first stem cells which will go on to form the entire embryo.
I include links to recent news (see also [../News/news.htm Embryology News]) items and sites which cover the research behind the stem cell "phenomena".
The term "stem cell" is now used widely to cover many different cells derived from both embryo and adult tissues.
There is still controversy over the use of excess IVF embryos as a source of stem cells (More? see [#Stem Cell Debate in Australia Stem Cell Debate in Australia]) for research as apposed to the possibility of getting some stem cells from adult tissues. The debate at present is on focusses on the social, legal and ethical use of stem cells.