HM Practical - Cardiac Histology: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
* does not cover the pathology content. | * does not cover the pathology content. | ||
==Introduction== | |||
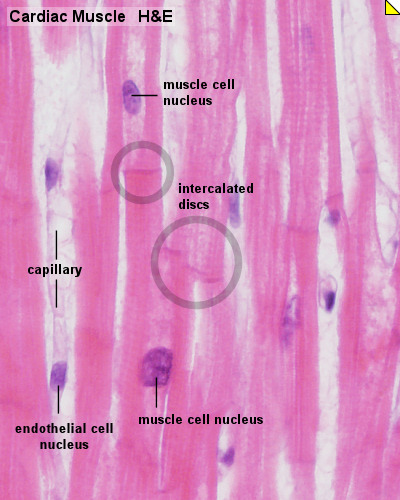
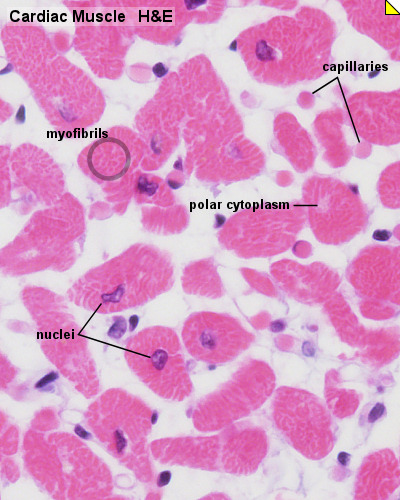
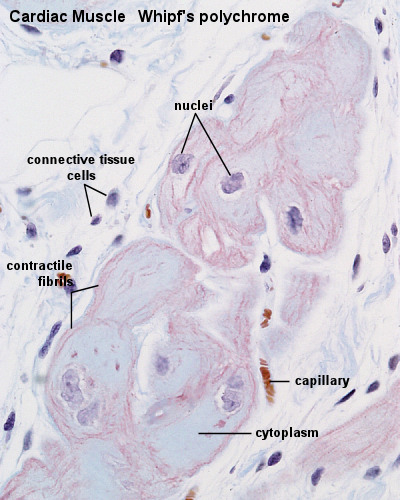
Cardiac muscle, the myocardium, consists of cross-striated muscle cells, cardiomyocytes, with one centrally placed nucleus. | Cardiac muscle, the myocardium, consists of cross-striated muscle cells, cardiomyocytes, with one centrally placed nucleus. | ||
Revision as of 14:29, 24 July 2012
Introduction
HMA Practical 8 Monday August 6 and Wednesday August 8.
HMA Practical 8 Virtual Slides
This page provides histology support information for cardiac histology.
Disclaimers
- does not form part of the actual practical class based upon the virtual slides.
- does not cover the pathology content.
Introduction
Cardiac muscle, the myocardium, consists of cross-striated muscle cells, cardiomyocytes, with one centrally placed nucleus.
- Nuclei are oval, rather pale and located centrally in the muscle cell which is 10 - 15 µm wide.
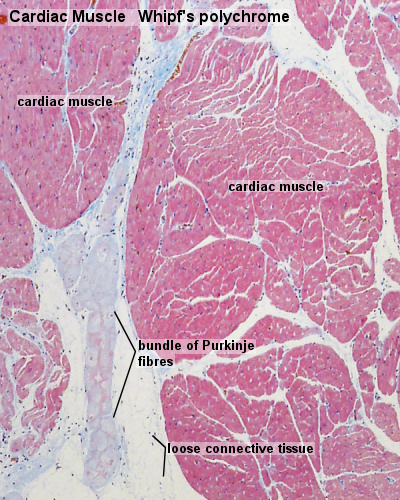
- Cardiac muscle cells excitation is mediated by rythmically active modified cardiac muscle cells.
- Cardiac muscle is innervated by the autonomic nervous system (involuntary), which adjusts the force generated by the muscle cells and the frequency of the heart beat.
- Cardiac muscle cells often branch at acute angles and are connected to each other by specialisations of the cell membrane in the region of the intercalated discs.
- Intercalated discs invariably occur at the ends of cardiac muscle cells in a region corresponding to the Z-line of the myofibrils.
Histology
Unlabeled Images
- Links: Heart Histology | Cardiac AZB Labeled | Cardiac AZB | Cardiac label LS | Cardiac LS | Cardiac label TS | Cardiac TS | Purkinje fibres | Purkinje fibres detail | Histology
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 8) Embryology HM Practical - Cardiac Histology. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/HM_Practical_-_Cardiac_Histology
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G