File:Trisomy21 hand.jpg
Trisomy21_hand.jpg (360 × 295 pixels, file size: 12 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
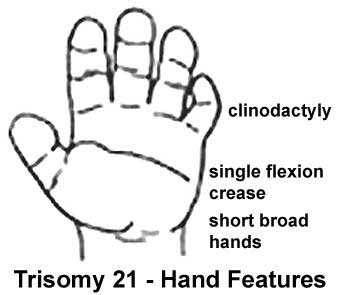
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) Hand
Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is caused by nondisjunction of chromosome 21 in a parent who is chromosomally normal and is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities in liveborn children. The frequency of trisomy 21 in the population is approximately 1 in 650 to 1,000 live births, in Australia between 1991-97 there were 2,358 Trisomy 21 (Down) infants.
The normal human karyotypes contain 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. The karyotype is the characteristic chromosome complement as identified by staining and can only be identified during cell division when chromosomes are folded. The chromosomes when organised as an image in sequence are called a karyogram or idiogram.
Image Source: UNSW Embryology http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Defect/page21.htm
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:00, 5 August 2009 |  | 360 × 295 (12 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) Hand Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is caused by nondisjunction of chromosome 21 in a parent who is chromosomally normal and is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities in liveborn children. The frequency of trisomy 21 |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 7 pages use this file: