File:Spleen anatomy.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
m (→Spleen Anatomy) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
* Blood enters the spleen through the splenic artery, moves through the sinuses where it is filtered, then leaves through the splenic vein. | * Blood enters the spleen through the splenic artery, moves through the sinuses where it is filtered, then leaves through the splenic vein. | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 29: | ||
** This squeezes the blood out of the spleen into the general circulation. | ** This squeezes the blood out of the spleen into the general circulation. | ||
===Reference=== | |||
'''Image and Modified text source:''' National Cancer Institute - SEER Training Modules | '''Image and Modified text source:''' National Cancer Institute - SEER Training Modules | ||
| Line 38: | Line 37: | ||
http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/lymphatic/components/ | http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/lymphatic/components/ | ||
{{Spleen}} | |||
[[Category:Spleen]] [[Category:Cartoon]] [[Category:Immune]] | [[Category:Spleen]] [[Category:Cartoon]] [[Category:Immune]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:06, 26 July 2019
Spleen Anatomy
- The spleen is located in the upper left abdominal cavity, just beneath the diaphragm, and posterior to the stomach.
- It is similar to a lymph node in shape and structure but it is much larger.
- The spleen is the largest lymphatic organ in the body.
- Surrounded by a connective tissue capsule, which extends inward to divide the organ into lobules, the spleen consists of two types of tissue called white pulp and red pulp.
White pulp - is lymphatic tissue consisting mainly of lymphocytes around arteries.
Red pulp - consists of venous sinuses filled with blood and cords of lymphatic cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages.
- Blood enters the spleen through the splenic artery, moves through the sinuses where it is filtered, then leaves through the splenic vein.
Function
Immune
- filters blood in much the way that the lymph nodes filter lymph.
- Lymphocytes in the spleen react to pathogens in the blood and attempt to destroy them.
- Macrophages then engulf the resulting debris, the damaged cells, and the other large particles.
Red Blood Cell Removal
- The spleen (and liver) removes old and damaged erythrocytes from the circulating blood.
- Like other lymphatic tissue, it produces lymphocytes, especially in response to invading pathogens.
Blood Reservoir
- The sinuses in the spleen also act as a reservoir for blood.
- In emergencies, such as hemorrhage, smooth muscle in the vessel walls and in the capsule of the spleen contracts.
- This squeezes the blood out of the spleen into the general circulation.
Reference
Image and Modified text source: National Cancer Institute - SEER Training Modules
http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/lymphatic/components/spleen.html
http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/lymphatic/components/
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:27, 21 February 2011 | 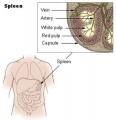 | 275 × 285 (19 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file: