File:Sinus venosus atrial septal defect 02.jpg: Difference between revisions
(==Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect - Magnetic Resonance Imaging== Sinus venosus atrial septal defects (SV-ASDs) are inter-atrial communications caused by a deficiency of the common wall between the superior or inferior vena cava and the right-sided...) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Sinus venosus atrial septal defects (SV-ASDs) are inter-atrial communications caused by a deficiency of the common wall between the superior or inferior vena cava and the right-sided pulmonary veins. | Sinus venosus atrial septal defects (SV-ASDs) are inter-atrial communications caused by a deficiency of the common wall between the superior or inferior vena cava and the right-sided pulmonary veins. | ||
MRI from a 25-year-old asymptomatic male | MRI from a 25-year-old asymptomatic male - Breath-held fat suppressed three-dimensional steady-state free precession (SSFP) pulse sequence in diastole in the sagittal view demonstrating sinus venosus atrial septal defect (SV-ASD) (arrow) between superior vena cava (SVC) and left atrium (LA). | ||
{{Sinus venosus ASD links}} | {{Sinus venosus ASD links}} | ||
Revision as of 09:59, 22 February 2015
Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect - Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Sinus venosus atrial septal defects (SV-ASDs) are inter-atrial communications caused by a deficiency of the common wall between the superior or inferior vena cava and the right-sided pulmonary veins.
MRI from a 25-year-old asymptomatic male - Breath-held fat suppressed three-dimensional steady-state free precession (SSFP) pulse sequence in diastole in the sagittal view demonstrating sinus venosus atrial septal defect (SV-ASD) (arrow) between superior vena cava (SVC) and left atrium (LA).
- Atrial Septal Defect Links: image - MRI modes | image - MRI SSFP sagittal view | image - MRI SSFP axial view | image - MRI Turbo spin-echo axial plane | image - MRI SSFP dilated right ventricle | Atrial Septal Defects | Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Reference
<pubmed>24987269</pubmed>| Ann Pediatr Cardiol.
Copyright
© 2008 Annals of Pediatric Cardiology
The entire contents of the Annals of Pediatric Cardiology are protected under Indian and international copyrights. The Journal, however, grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship and ownership of the rights.
Figure 1 Original figure adjusted in size and labelling.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 09:44, 22 February 2015 | 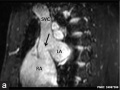 | 600 × 449 (29 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect - Magnetic Resonance Imaging== Sinus venosus atrial septal defects (SV-ASDs) are inter-atrial communications caused by a deficiency of the common wall between the superior or inferior vena cava and the right-sided... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: