File:Mouse eye TGF-beta model.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Summary of the TGFβ-dependent development of anterior and posterior ocular structures. | Summary of the TGFβ-dependent development of anterior and posterior ocular structures. | ||
{| | |||
'''a''' Neural crest-derived cells (NC, blue) contribute to structures of the anterior eye segment and the primary vitreous (PV). | | valign=top|'''a''' Neural crest-derived cells (NC, blue) contribute to structures of the anterior eye segment and the primary vitreous (PV). | ||
* TGFβ signaling is involved in the formation of the ciliary body (CB) and the trabecular meshwork (TM), and in control of PV growth. | * TGFβ signaling is involved in the formation of the ciliary body (CB) and the trabecular meshwork (TM), and in control of PV growth. | ||
* Moreover, normal PV development and/or TGFβ signaling are important for correct retinal patterning. | * Moreover, normal PV development and/or TGFβ signaling are important for correct retinal patterning. | ||
| valign=top|'''b''' In the cornea, prospective stromal keratocytes and endothelial cells are of neural crest origin. | |||
'''b''' In the cornea, prospective stromal keratocytes and endothelial cells are of neural crest origin. | |||
* Here, TGFβ signaling is needed for the expression of the transcription factors Foxc1 and Pitx2 and for normal differentiation of NC-derived cells into collagen-synthesizing stromal keratocytes. | * Here, TGFβ signaling is needed for the expression of the transcription factors Foxc1 and Pitx2 and for normal differentiation of NC-derived cells into collagen-synthesizing stromal keratocytes. | ||
* Moreover, in forming corneal endothelial cells (and in the TM), expression of Foxc1 and cell survival requires TGFβ signalling. | * Moreover, in forming corneal endothelial cells (and in the TM), expression of Foxc1 and cell survival requires TGFβ signalling. | ||
|} | |||
Revision as of 14:12, 30 August 2014
Mouse Eye TGF-beta Model
Summary of the TGFβ-dependent development of anterior and posterior ocular structures.
a Neural crest-derived cells (NC, blue) contribute to structures of the anterior eye segment and the primary vitreous (PV).
|
b In the cornea, prospective stromal keratocytes and endothelial cells are of neural crest origin.
|
- Links: Image - Mouse eye neural crest | Image - Mouse eye TGF-beta model TGF-beta | Cornea Development | Vision Development | Neural Crest Development | Head Development
Reference
<pubmed>16403239</pubmed>| J Biol.
Copyright
© 2005 Ittner et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Ittner et al. Journal of Biology 2005 4:11 doi:10.1186/jbiol29
Original file name: Figure 9. http://jbiol.com/content/4/3/11/figure/F9
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 18:32, 30 August 2011 | 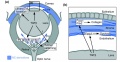 | 1,000 × 519 (88 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Mouse eye TGF-beta model== Summary of the TGFβ-dependent development of anterior and posterior ocular structures. (a) NC-derived cells (blue) contribute to structures of the anterior eye segment and the primary vitreous (PV). TGFβ signaling is invo |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 5 pages use this file: