File:Mouse- facial branchiomotor neuron migration.jpg
Original file (600 × 841 pixels, file size: 104 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
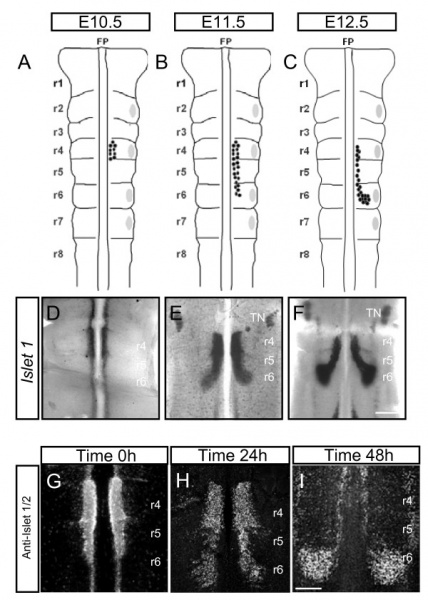
Mouse - Spatiotemporal pattern of facial branchiomotor (FBM) neuronal migration
Migration in vivo and in embryo explants E10.5, E11.5 and E12.5.
(A-C) Schematic representations of mouse embryonic hindbrain at embryonic stages (E)10.5 (A), E11.5 (B) and E12.5 (C). FBM neurons are shown by black dots and migrate from rhombomere (r)4 (E10.5) to r6 (E12.5). Grey patches represent dorsal exit points of motor axons.
(D-F) Islet-1 in situ hybridisation on flatmounted hindbrains showing FBM neurons migrating from r4 to r6 at E10.5 (D), E11.5 (E) and E12.5 (F).
(G-I) Hindbrain explants cultured on filters and immunostained with anti-Islet 1/2 antibody. Time 0 h (G) represents the beginning of culture period when some FBM neurons have started to migrate into r5. Time 24 h (H) shows that more FBM neurons are present in r5 and that some have started to turn dorsally into r6. Time 48 h (I) shows FBM neurons that have reached their final destination in r6 to form a nucleus.
TN - trigeminal motor nucleus.
Scale bars: 500 μm in (D-F); 250 μm in (G-I).
Original file name: Figure 1. 1749-8104-4-7-1.jpg http://www.neuraldevelopment.com/content/4/1/7/figure/F1
- "Here we demonstrate a novel role for Wnt proteins in guiding FBM neurons during their rostral to caudal migration in the hindbrain. We found that Wnt5a is expressed in a caudalhigh to rostrallow gradient in the hindbrain. Wnt-coated beads chemoattracted FBM neurons to ectopic positions in an explant migration assay. The rostrocaudal FBM migration was moderately perturbed in Wnt5a mutant embryos and severely disrupted in Frizzled3 mutant mouse embryos, and was aberrant following inhibition of Wnt function by secreted Frizzled-related proteins. We also show the involvement of the Wnt/PCP pathway in mammalian FBM neuron migration. Thus, mutations in two PCP genes, Vangl2 and Scribble, caused severe defects in FBM migration. Inhibition of JNK and ROCK kinases strongly and specifically reduced the FBM migration, as well as blocked the chemoattractant effects of ectopic Wnt proteins."
Reference
<pubmed>19210786</pubmed>| Neural Dev.
© 2009 Vivancos et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:16, 29 September 2010 |  | 600 × 841 (104 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Mouse - Spatiotemporal pattern of facial branchiomotor (FBM) neuronal migration== Migration in vivo and in embryo explants E10.5, E11.5 and E12.5. '''(A-C)''' Schematic representations of mouse embryonic hindbrain at embryonic stages (E)10.5 (A), E11 |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
There are no pages that use this file.