File:Limb induction-initiation signal 01.jpg: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Molecular Mechanisms of Limb Bud Formation== | ==Molecular Mechanisms of Limb Bud Formation== | ||
Nishimoto et al. reveal the regulatory network including retinoic acid (RA), b-catenin pathway, and Tbx genes controlling the early steps of limb formation. This study demonstrates the shared role of RA in forelimb and hindlimb and an evolutionarily conserved role of the b-catenin pathway in limb induction. | |||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
<pubmed>26212321</pubmed> | |||
====Copyright==== | ====Copyright==== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 13: | ||
{{Footer}} | {{Footer}} | ||
[[Category:Limb | [[Category:Limb]][[Category:Cartoon]] | ||
Revision as of 13:03, 13 September 2016
Molecular Mechanisms of Limb Bud Formation
Nishimoto et al. reveal the regulatory network including retinoic acid (RA), b-catenin pathway, and Tbx genes controlling the early steps of limb formation. This study demonstrates the shared role of RA in forelimb and hindlimb and an evolutionarily conserved role of the b-catenin pathway in limb induction.
Reference
<pubmed>26212321</pubmed>
Copyright
Copyright © 2015 The Authors This is an open access article under the CC BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 18) Embryology Limb induction-initiation signal 01.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Limb_induction-initiation_signal_01.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 13:00, 13 September 2016 | 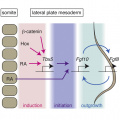 | 664 × 664 (204 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file: