File:Fgf gene family evolution.jpg: Difference between revisions
(==Evolutionary history of the Fgf gene family== Fgf13-like is an ancestral gene of the Fgf family. Fgf4-like is an ancestral gene of the canonical Fgf family. Fgf4-like was generated from Fgf13-like by gene duplication. Fgf15/19-like, an ancestral gene o) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Fgf13-like is an ancestral gene of the Fgf family. Fgf4-like is an ancestral gene of the canonical Fgf family. Fgf4-like was generated from Fgf13-like by gene duplication. Fgf15/19-like, an ancestral gene of the hormone-like Fgf subfamily, was generated from Fgf4-like by local gene duplication early in vertebrate evolution. Later, Fgf15/19, Fgf21, and Fgf23 were generated by two large-scale genome duplication events during the evolution of early vertebrates | Fgf13-like is an ancestral gene of the Fgf family. Fgf4-like is an ancestral gene of the canonical Fgf family. Fgf4-like was generated from Fgf13-like by gene duplication. Fgf15/19-like, an ancestral gene of the hormone-like Fgf subfamily, was generated from Fgf4-like by local gene duplication early in vertebrate evolution. Later, Fgf15/19, Fgf21, and Fgf23 were generated by two large-scale genome duplication events during the evolution of early vertebrates | ||
==Reference== | ===Reference=== | ||
<pubmed>20730630</pubmed> | |||
====Copyright==== | |||
© Itoh N. 2010 | |||
Itoh N. | |||
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited. | |||
Itoh N. Department of Genetic Biochemistry, Kyoto University Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kyoto, Japan. itohnobu@pharm.kyoto-u.ac.jp http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2948652 | |||
Cell Tissue Res. 2010 October; 342(1): 1–11. Published online 2010 August 24. doi: 10.1007/s00441-010-1024-2. | |||
Original file name: Fig. 1 441_2010_1024_Fig1_HTML.jpg http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2948652/figure/Fig1/ | |||
{{Footer}} | |||
Revision as of 09:13, 7 October 2015
Evolutionary history of the Fgf gene family
Fgf13-like is an ancestral gene of the Fgf family. Fgf4-like is an ancestral gene of the canonical Fgf family. Fgf4-like was generated from Fgf13-like by gene duplication. Fgf15/19-like, an ancestral gene of the hormone-like Fgf subfamily, was generated from Fgf4-like by local gene duplication early in vertebrate evolution. Later, Fgf15/19, Fgf21, and Fgf23 were generated by two large-scale genome duplication events during the evolution of early vertebrates
Reference
<pubmed>20730630</pubmed>
Copyright
© Itoh N. 2010
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Itoh N. Department of Genetic Biochemistry, Kyoto University Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kyoto, Japan. itohnobu@pharm.kyoto-u.ac.jp http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2948652
Cell Tissue Res. 2010 October; 342(1): 1–11. Published online 2010 August 24. doi: 10.1007/s00441-010-1024-2. Original file name: Fig. 1 441_2010_1024_Fig1_HTML.jpg http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2948652/figure/Fig1/
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 25) Embryology Fgf gene family evolution.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Fgf_gene_family_evolution.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 09:16, 7 October 2015 | 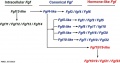 | 759 × 400 (49 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | increase size add PMID 20730630 |
| 23:31, 3 May 2011 | 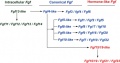 | 488 × 257 (51 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Evolutionary history of the Fgf gene family== Fgf13-like is an ancestral gene of the Fgf family. Fgf4-like is an ancestral gene of the canonical Fgf family. Fgf4-like was generated from Fgf13-like by gene duplication. Fgf15/19-like, an ancestral gene o |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: