File:Adult epidermis histology 01.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(==Adult Thin Skin Epidermis== * The most superficial part of the epidermis is formed by the stratum corneum. * Nuclei are not visible in this layer. * Cell outlines may be visible at high magnification or, in the form of artefacts, as cracks or clefts i) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Adult Thin Skin Epidermis== | ==Adult Thin Skin Histology - Epidermis== | ||
This image focusses on the epidermis (epithelial) layer of the thin skin. | |||
* The most superficial part of the epidermis is formed by the stratum corneum. | * The most superficial part of the epidermis is formed by the stratum corneum. | ||
* Nuclei are not visible in this layer. | * Nuclei are not visible in this layer. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 10: | ||
* Polyhedral cells with clear outlines form the stratum spinosum. | * Polyhedral cells with clear outlines form the stratum spinosum. | ||
* The stratum basale is formed by a single layer of cuboidal or columnar cells and delimits the epidermis from the dermis. | * The stratum basale is formed by a single layer of cuboidal or columnar cells and delimits the epidermis from the dermis. | ||
{{Integument Histology}} | |||
{{Template:Blue Histology}} | {{Template:Blue Histology}} | ||
Revision as of 17:30, 24 March 2012
Adult Thin Skin Histology - Epidermis
This image focusses on the epidermis (epithelial) layer of the thin skin.
- The most superficial part of the epidermis is formed by the stratum corneum.
- Nuclei are not visible in this layer.
- Cell outlines may be visible at high magnification or, in the form of artefacts, as cracks or clefts in the stratum corneum.
- The stratum granulosum is formed by a single layer of very dark and flattened cells in thin skin.
- Several layers of cells containing keratohyalin granules are visible in thick skin.
- Polyhedral cells with clear outlines form the stratum spinosum.
- The stratum basale is formed by a single layer of cuboidal or columnar cells and delimits the epidermis from the dermis.
- Integument Histology Links: Adult Skin | Epidermis and Dermis | Thin Skin Epidermis | Thick Skin Epidermis | Elastic Fibres | Basal Cell Melanin | Foundations Practical Support | Integumentary System Development | Histology Stains
Links: Histology | Histology Stains | Blue Histology images copyright Lutz Slomianka 1998-2009. The literary and artistic works on the original Blue Histology website may be reproduced, adapted, published and distributed for non-commercial purposes. See also the page Histology Stains.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 17) Embryology Adult epidermis histology 01.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Adult_epidermis_histology_01.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
Skthin040he.jpg
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:37, 29 September 2011 | 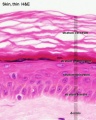 | 600 × 750 (83 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Adult Thin Skin Epidermis== * The most superficial part of the epidermis is formed by the stratum corneum. * Nuclei are not visible in this layer. * Cell outlines may be visible at high magnification or, in the form of artefacts, as cracks or clefts i |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 5 pages use this file: