File:Adult epidermis histology 01.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Adult Thin Skin Histology - Epidermis== | ==Adult Thin Skin Histology - Epidermis== | ||
This image focusses on the epidermis (epithelial) layer of the thin skin. | This image focusses on the epidermis (epithelial) layer of the thin skin. {{HE}} | ||
* | * '''stratum corneum''' - the most superficial part of the epidermis. Nuclei are not visible in this layer. | ||
* Cell outlines may be visible at high magnification or, in the form of artefacts, as cracks or clefts in the stratum corneum. | * Cell outlines may be visible at high magnification or, in the form of artefacts, as cracks or clefts in the stratum corneum. | ||
* | * '''stratum granulosum''' - is formed by a single layer of very dark and flattened cells in thin skin. | ||
* Several layers of cells containing keratohyalin granules are visible in thick skin. | ** Several layers of cells containing keratohyalin granules are visible in thick skin. | ||
* | * '''stratum spinosum''' - polyhedral cells with clear outlines. | ||
* | * '''stratum basale''' is formed by a single layer of cuboidal or columnar cells and delimits the epidermis from the dermis. This layer contains the keratinocyte stem cell population required for the continual replacement of cells as they differentiate and are shed from the skin (squams). | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
{{ | {{Blue Histology}} | ||
[[Category:Integumentary]] [[Category:Histology]] | [[Category:Integumentary]] [[Category:Histology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:24, 24 February 2013
Adult Thin Skin Histology - Epidermis
This image focusses on the epidermis (epithelial) layer of the thin skin. (Stain - Haematoxylin Eosin)
- stratum corneum - the most superficial part of the epidermis. Nuclei are not visible in this layer.
- Cell outlines may be visible at high magnification or, in the form of artefacts, as cracks or clefts in the stratum corneum.
- stratum granulosum - is formed by a single layer of very dark and flattened cells in thin skin.
- Several layers of cells containing keratohyalin granules are visible in thick skin.
- stratum spinosum - polyhedral cells with clear outlines.
- stratum basale is formed by a single layer of cuboidal or columnar cells and delimits the epidermis from the dermis. This layer contains the keratinocyte stem cell population required for the continual replacement of cells as they differentiate and are shed from the skin (squams).
- Integument Histology Links: Adult Skin | Epidermis and Dermis | Thin Skin Epidermis | Thick Skin Epidermis | Elastic Fibres | Basal Cell Melanin | Foundations Practical Support | Integumentary System Development | Histology Stains
Links: Histology | Histology Stains | Blue Histology images copyright Lutz Slomianka 1998-2009. The literary and artistic works on the original Blue Histology website may be reproduced, adapted, published and distributed for non-commercial purposes. See also the page Histology Stains.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 17) Embryology Adult epidermis histology 01.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Adult_epidermis_histology_01.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
Skthin040he.jpg
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:37, 29 September 2011 | 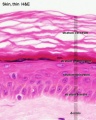 | 600 × 750 (83 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Adult Thin Skin Epidermis== * The most superficial part of the epidermis is formed by the stratum corneum. * Nuclei are not visible in this layer. * Cell outlines may be visible at high magnification or, in the form of artefacts, as cracks or clefts i |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 5 pages use this file: