Fetal Development: Difference between revisions
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
'''Search Pubmed:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=fetal | '''Search Pubmed:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=fetal%20development fetal+development] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=Second%20Trimester Second Trimester] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=Third%20Trimester Third Trimester] | ||
Revision as of 16:42, 20 May 2010
Introduction
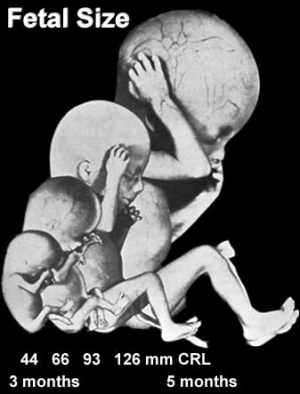
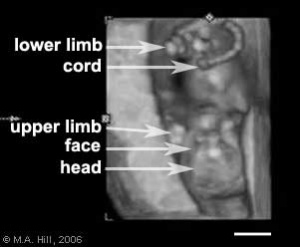
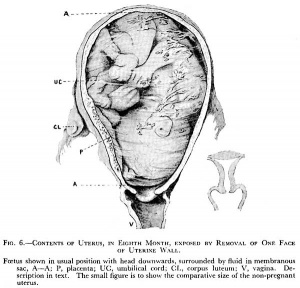
This page shows some key events of human development during the fetal period (weeks 9 to 37) following fertilization. Clinically this period is generally described as the Second Trimester and Third Trimester. Many of the critical measurements of growth are now carried out by ultrasound and this period ends at birth.
Links: Lecture - Fetal Development | original page
<Flowplayer height="300" width="285" autoplay="true">fetal growth.flv</Flowplayer>
Animation shows the changing proportions of the fetus, not the growth in size.
Many different systems formed in the embryonic period (organogenesis) grow and differentiate further during the fetal period and do so at different times. For example, the brain continues to grow and develop extensively during this period (and postnatally), the respiratory system differentiates (and completes only just before birth), the urogenital system further differentiates between male/female, endocrine and gastrointestinal tract begins to function.
The Embryonic period involved transient structures to establish body and placental tissues, folding and form.
The long Fetal period (4x the embryonic period) is a time of extensive growth in size and mass as well as ongoing differentiation of organ systems established in the embryonic period.
Also consider the systems (respiratory, cardiac, neural) that will still not have their final organization and function determined until after birth.
Reading
- Human Embryology (3rd ed.) Larson Ch15: Fetal development and the Fetus as Patient p481-499
- Color Atlas of Clinical Embryology (2nd ed.) Moore, Persaud and Shiota Ch3: 9th to 38th weeks of human development p50-68
Second Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Week 12 - CRL 85 mm, femur length 15 mm, biparietal diameter 25 mm.
Third Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle respone in fetus.
- Month 7 - respiratory bronchioles proliferate and end in alveolar ducts and sacs.
- Week 37 to 38 Birth.
References
Reviews
- Fetal assessment during pregnancy. Farley D, Dudley DJ. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2009 Jun;56(3):489-504, Table of Contents. Review. PMID: 19501688
- Regimens of fetal surveillance for impaired fetal growth. Grivell RM, Wong L, Bhatia V. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jan 21;(1):CD007113. Review. PMID: 19160321
Articles
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: fetal+development | Second Trimester | Third Trimester
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 2) Embryology Fetal Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Fetal_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G