BGDB Gastrointestinal - Activity 1: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
File:Week1 summary.jpg | [[File:Week1 summary.jpg]] | ||
File:Trilaminar embryo.jpg | File:Trilaminar embryo.jpg | ||
Revision as of 05:06, 16 March 2019
| Practical 1: Activity 1 | Activity 2 | Activity 3 | Activity 4 |
Learning Activity 1
- Identify the different contributions of the trilaminar embryo to the formation of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
- Describe the development and folding of the yolk sac and endoderm.
- List the adult structures developed from the foregut, midgut and hindgut.
1. Trilaminar Embryo Contributions
The gastrointestinal tract has contributions from all 3 germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm). Identify the specific components that each germ layer contributes to the tract. We will discuss the associated organs later in Activity 3.
File:Trilaminar embryo.jpg
File:Endoderm cartoon.jpg
File:Mesoderm-cartoon4.jpg
2. Folding
In week 3 to 4 (GA week 5 and 6) folding of the entire embryonic disc occurs ventrally. The notochord forms a midline rod-like region running rostro-caudally.
Watch the two animations below and discuss the GIT folding that is occurring within the embryo.
| <html5media height="360" width="360">File:Endoderm 003.mp4</html5media> | <html5media height="540" width="390">File:Week3_folding.mp4</html5media> |
| Page | Play | Page | Play |
In relation to the notochord:
- Laterally (either side of the notochord) lies mesoderm.
- Rostrally (above the notochord end) lies the buccopharyngeal membrane, above this again is the mesoderm region forming the heart.
- Caudally (below the notochord end) lies the primitive streak (where gastrulation occurred), below this again is the cloacal membrane.
- Dorsally (above the notochord) lies the neural tube then ectoderm.
- Ventrally (beneath the notochord) lies the mesoderm then endoderm.
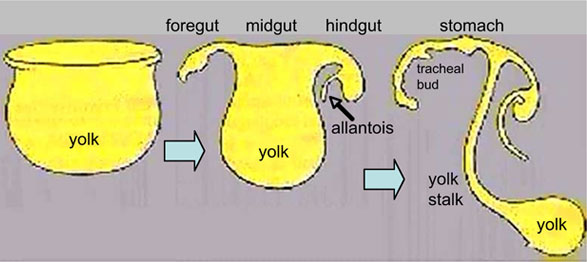
Folding of the embryonic disc "pinches off" part of the yolk sac forming the first primitive GIT.
3. Gut Parts
| Interactive component |
|---|
| Practical 1: Activity 1 | Activity 2 | Activity 3 | Activity 4 |
BGDB: Lecture - Gastrointestinal System | Practical - Gastrointestinal System | Lecture - Face and Ear | Practical - Face and Ear | Lecture - Endocrine | Lecture - Sexual Differentiation | Practical - Sexual Differentiation | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 17) Embryology BGDB Gastrointestinal - Activity 1. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDB_Gastrointestinal_-_Activity_1
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G