ACPS Seminar 2014 - Implantation: Difference between revisions
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
[[File:Microarray_technology.jpg|400px]] | [[File:Microarray_technology.jpg|400px]] | ||
==Immune Protection== | ==Immune Protection== | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 17 March 2014
Understanding Implantation and the new Uterine Tube Biobank
|
Human Development - Week 1
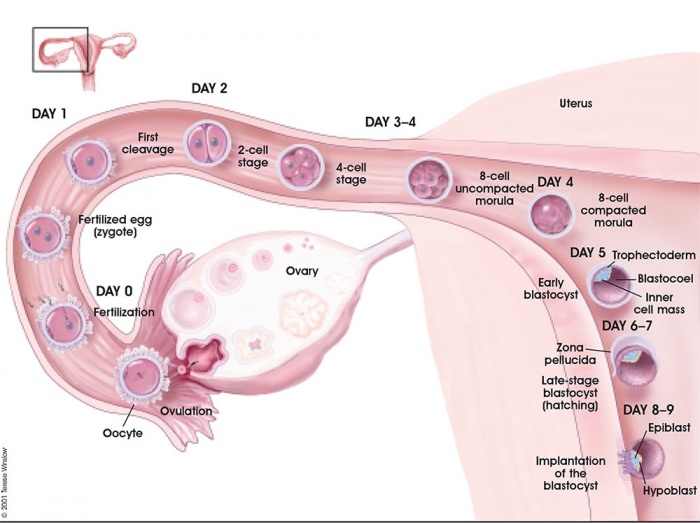
|
<mediaplayer width='500' height='450' image="http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/images/0/07/Human_blastocyst_day_1-5.jpg">File:Human_blastocyst_day_3-6.mp4</mediaplayer>
|
Human Development - Week 2
| <mediaplayer width='250' height='260' image="http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/images/a/a9/Week2_001_icon.jpg">File:Week2_001.mp4</mediaplayer> |
This animation shows the process of implantation, occurring during week 2 (GA week 4) of development in humans. The beginning of the animation shows adplantation to the the uterus lining (endometrium epithelium). The hatched blastocyst with a flat outer layer of trophoblast cells (green), the inner cell mass which has formed into the bilaminar embryo (epiblast and hypoblast) and the large fluid-filled space (blastocoel).
|
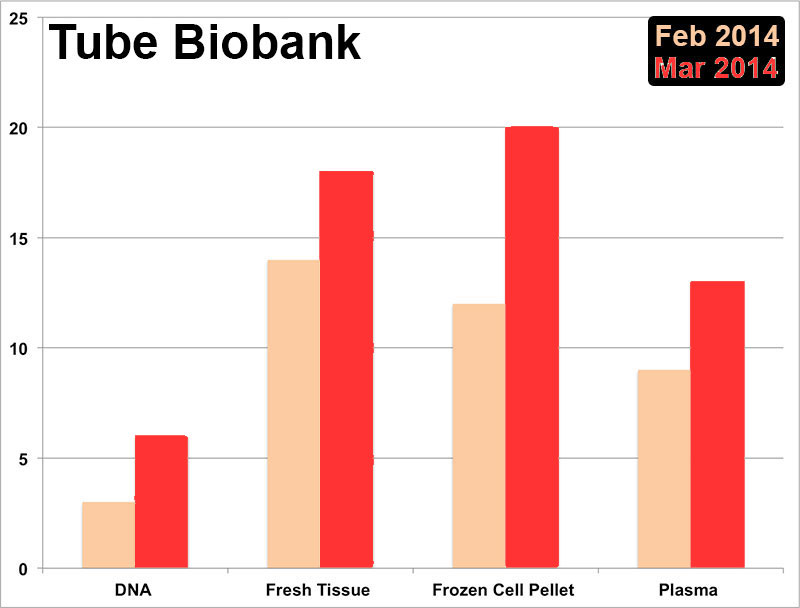
Tube Biobank
Tube Analysis Techniques
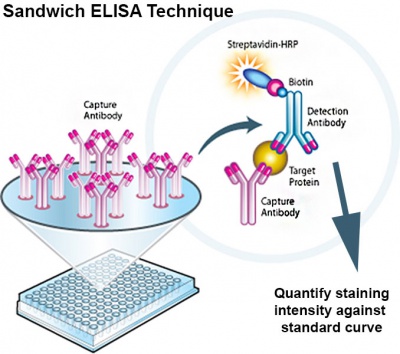
Protein Expression
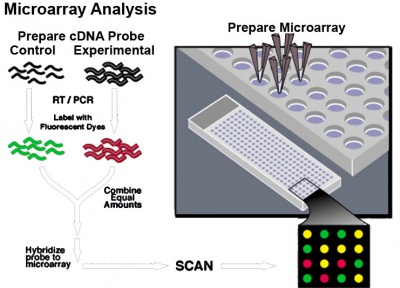
mRNA Expression
Immune Protection
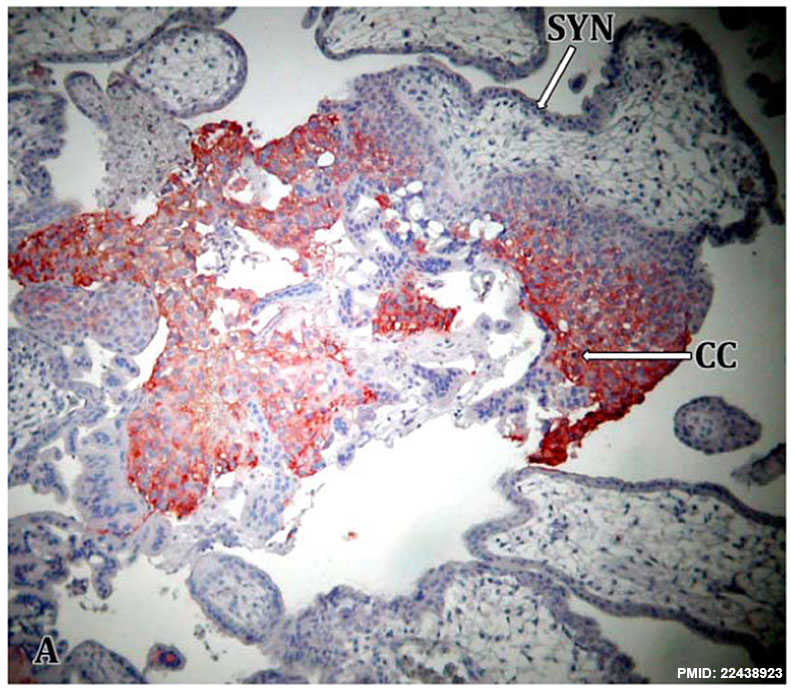
HLA-G - Human leukocyte antigen G (HLA-G, HLA-6.0; HLA60, T-CELL A LOCUS; TCA)
- Expression by feral cells protects from immune rejection.
- HLA-G is a non-classical HLA class-Ib molecule expressed by the extravillous cytotrophoblasts (EVT) of the placenta.
- 338 AA protein, mRNA differential splicing gives rise to 7 isoforms: 4 membrane-bound forms (HLA-G1, G2, G3, G4) and 3 soluble forms (sHLA-G5, G6, G7)
HLA-G expression (red) on trophoblast cell columns (CC) and extravillous trophoblasts and not seen for syncitiotrophoblast (SYN) cells.[2]
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
References
- ↑ <pubmed>20890283</pubmed>| Nat Biotechnol.
- ↑ <pubmed>22438923</pubmed>| PLoS One.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 2) Embryology ACPS Seminar 2014 - Implantation. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ACPS_Seminar_2014_-_Implantation
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G