2010 Group Project 2
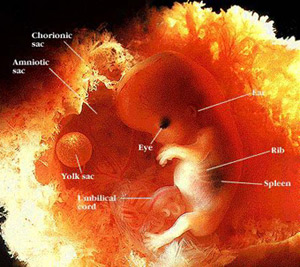
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
Introduction
Chorionic villus sampling or CVS is a type of prenatal diagnosis test performed in the first trimester to detect major fetal abnormalities. In the procedure, tissue is withdrawn from the villi of the chorion and tested for chromosomal defects. It is usually done in women over the age of 37 as the chance of chromosomal defects increase with the mothers age. The advantage of CVS over amniocentesis is that the result is available approx 6 weeks earlier in the pregnancy, so if a termination is needed, it can be done earlier which is much safer, rather than later in the pregnancy.
Historic background
Why would you use CVS over other techniques?
ADVANTAGES
- Can be performed earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis (at around ten weeks).
- Results are available faster
- Cells obtained are mitotically active
- Amount of tissue obtained is preferable for DNA analysis.
- It is almost 100% reliable in detecting chromosomal and genetic defects.
DISADVANTAGES
- It carries a slightly higher risk of miscarriage (1%-2%) than does amniocentesis
- It's less commonly available than amniocentesis, and fewer doctors are experienced in the procedure.
- It entails a greater risk of distorted results than does amniocentesis due to presence of mother's cells in the sample and discrepancies between chorionic villi and fetal genes.
- Metabolic disorders are difficult to diagnose and must be confirmed with amniocentesis.
- Because of the early gestational age at which the test is performed, fetal anatomy cannot be seen as well as it can at the time amniocentesis is performed.
Brief timeline of CVS use
- 1968 - Mohr in Scandinavia introduced the concept of prenatal diagnosis using chorionic villi sampling
- 1973 - Kullander and Sandahl and Hahnemann in 1974 showed further study into chromosomal analysis from CVS
- 1975 - from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology at the Tietung Hospital in Anshan, China was successful in using CVS to determine sex of fetuses for sex pre selection.
- 1980 - Kazy et al. were the first to use ultrasound guidance during chorionic villi sampling.
- 1981 - Niazi et al. improved methods for culturing of fibroblasts from trophoblast villi.
- 1983 - Ward performed transcervical CVS with 67% success rate. In the same year, the Brombati group demonstrated and 96% success rate with obtaining villi with the aid of ultrasound guidance
- 1984 - Smidt-Jensen and Hahnemann introduced transabdominal CVS under ultrasound guidance
- 1986 - The Golbus group had a 3.8% miscarriage rate, and subsequently many other clinics started reporting a much lower rate of miscarriage at 1.7% making the procedure safe for routine use
Jan Mohr (1921-2009)
1968 -- Concept of CVS introduced
In 1968 Jan Mohr introduced the concept of prenatal diagnosis using the CVS technique. He used the transcervical method to get a biopsy of the chorion using an endoscope as the source of vision. The current technique differs by using mostly transabdominal access with ultrasound instead of an endoscope. He reported a 96% success rate in obtaining chorionic material but with a high incidence of bleeding and infection. The approach was abandoned as amniocentesis became more popular due to higher safety levels
1973-1975 -- Further study into chromosomal analysis from CVS
Kullander and Sandahl in 1973 and Hahnemann in 1974 further researched fetal chromosome analysis using transcervical biopsy before termination in early pregnancies. In 1975 the first successful diagnostic use of chorionic villi was reported at the Tietung Hospital in China. This is where fetal sex was diagnosed for the purpose of sex pre-selection. They claimed to have 94% diagnosis success and only 4% miscarriage rate. Researchers in the United States were, however unable to duplicate the results and so the idea of CVS diagnosis was again abandoned for some time.
1980-1983 -- Change from endoscopic examination to ultrasound to guide CVS
With the invention of the ultrasound and advancement in molecular genetics, an earlier prenatal diagnosis was now sought after. So Kazy et al. in 1980, began using both the endoscope and the ultrasound for fetal sexing on chorion biopsies. This was the first report of using ultrasound guidance during chorion sampling. After Kazy et.al. began using the ultrasound for guidance, many others followed. Niazi et al., Ward and the Brombati group all started using ultrasound guided CVS. Techniques quickly improved and success rate of obtaining chorionic material rose from 75% to 96%
1984-1986 -- The introduction of transabdominal CVS
In 1984, Smidt-Jensen and Hahnemann in Copenhagen introduced transabdominal CVS using ultrasound guidance. With less chance of infective complications the procedure has become more popular than the transcervical method in many prenatal diagnostic centers. Other ultrasonic techniques and modifications were explored by the Brambati and Simoni group and the Golbus group in 1985. The Golbus group reported in 1986 a miscarriage rate of 3.8%. Subsequently, many other centres reported a much lower miscarriage rate of 1.5% which made the procedure safe for routine use.
Current associated research
Description of technique
Search Pubmed
Search Bookshelf Chorionic villus sampling
Search Pubmed Now: Chorionic villus sampling
--Mark Hill 01:43, 5 August 2010 (UTC) You can now put your group discussion here. Here is the code to set up a search of PubMed Books - Prenatal Diagnosis and to Search Pubmed Now - Prenatal Diagnosis
References
Woo, J. A short History of Amniocentesis, Fetoscopy and Chorionic Villus Sampling, accessed 2010 http://www.ob-ultrasound.net/amniocentesis.html
Mohr J. (1968) Foetal genetic diagnosis: Development of techniques for early sampling of foetal cells. Acta Pathologica Microbiolabic Scandinavia 73:7377
Ward RHT, Model B, Petrou M, et al (1983) Method of sampling chorionic villi in first trimester of pregnancy under guidance of real time ultrasound. Br Med J 286:1542
Kazy Z, Stygar AM, Bakharev VA (1980) Chorionic biopsy under immediate realtime (ultrasonic) control. Orv Hetil 121:2765.
Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Tietung Hospital, Anshan, China (1975). Fetal sex prediction by sex chromatin of chorionic villi cells during early pregnancy. Chinese Med. J.,1,117-26
2010 ANAT2341 Group Projects
Project 1 - Ultrasound | Project 2 - Chorionic villus sampling | Project 3 - Amniocentesis | Group Project 4 - Percutaneous Umbilical Cord Blood Sampling | Project 5 - Fetal Fibronectin | Project 6 - Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein | Group Assessment Criteria
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 1) Embryology 2010 Group Project 2. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2010_Group_Project_2
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G