2010 Group Project 2: Difference between revisions
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
ADVANTAGES | ADVANTAGES | ||
*Can be performed earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis (at around ten weeks). | *Can be performed earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis (at around ten weeks). | ||
*Results are available faster | |||
*Cells obtained are mitotically active | |||
*Amount of tissue obtained is preferable for DNA analysis. | |||
*It is almost 100% reliable in detecting chromosomal and genetic defects. | *It is almost 100% reliable in detecting chromosomal and genetic defects. | ||
DISADVANTAGES | |||
*It carries a slightly higher risk of miscarriage (1%-2%) than does amniocentesis | |||
*It's less commonly available than amniocentesis, and fewer doctors are experienced in the procedure. | |||
*It entails a greater risk of distorted results than does amniocentesis due to presence of mother's cells in the sample and discrepancies between chorionic villi and fetal genes. | |||
*Metabolic disorders are difficult to diagnose and must be confirmed with amniocentesis. | |||
*Because of the early gestational age at which the test is performed, fetal anatomy cannot be seen as well as it can at the time amniocentesis is performed. | |||
=Current associated research= | =Current associated research= | ||
Revision as of 14:54, 11 August 2010
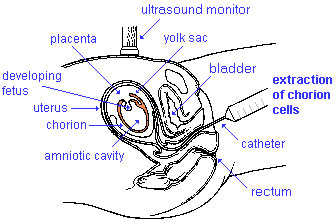
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
Introduction
Chorionic villus sampling or CVS is a type of prenatal diagnosis test performed in the first trimester to detect major fetal abnormalities. In the procedure, tissue is withdrawn from the villi of the chorion and tested for chromosomal defects. It is usually done in women over the age of 37 as the chance of chromosomal defects increase with the mothers age. The advantage of CVS over amniocentesis is that the result is available approx 6 weeks earlier in the pregnancy, so if a termination is needed, it can be done earlier which is much safer, rather than later in the pregnancy.
Historic background
Why would we use CVS over other techniques?
ADVANTAGES
- Can be performed earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis (at around ten weeks).
- Results are available faster
- Cells obtained are mitotically active
- Amount of tissue obtained is preferable for DNA analysis.
- It is almost 100% reliable in detecting chromosomal and genetic defects.
DISADVANTAGES
- It carries a slightly higher risk of miscarriage (1%-2%) than does amniocentesis
- It's less commonly available than amniocentesis, and fewer doctors are experienced in the procedure.
- It entails a greater risk of distorted results than does amniocentesis due to presence of mother's cells in the sample and discrepancies between chorionic villi and fetal genes.
- Metabolic disorders are difficult to diagnose and must be confirmed with amniocentesis.
- Because of the early gestational age at which the test is performed, fetal anatomy cannot be seen as well as it can at the time amniocentesis is performed.
Current associated research
Description of technique
Search Pubmed
Search Bookshelf Chorionic villus sampling
Search Pubmed Now: Chorionic villus sampling
--Mark Hill 01:43, 5 August 2010 (UTC) You can now put your group discussion here. Here is the code to set up a search of PubMed Books - Prenatal Diagnosis and to Search Pubmed Now - Prenatal Diagnosis
References
2010 ANAT2341 Group Projects
Project 1 - Ultrasound | Project 2 - Chorionic villus sampling | Project 3 - Amniocentesis | Group Project 4 - Percutaneous Umbilical Cord Blood Sampling | Project 5 - Fetal Fibronectin | Project 6 - Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein | Group Assessment Criteria
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 1) Embryology 2010 Group Project 2. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2010_Group_Project_2
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G