2010 BGD Practical 12 - Second Trimester
Practical 12: Embryo to Fetus | Second Trimester | Third Trimester | Birth | Neonatal | Abnormalities
Introduction
- Early fetal - week 12
- placental changes and fetal membrane changes
- length changes
- clinical diagnosis (ultrasound)
- Fetal Endocrine
Week 12
Size
- Crown Rump Length (CRL) 85 mm (week 10 CRL 40mm), femur length 15 mm, biparietal diameter 25 mm
Systems
- Genital male and female external genital differences observable
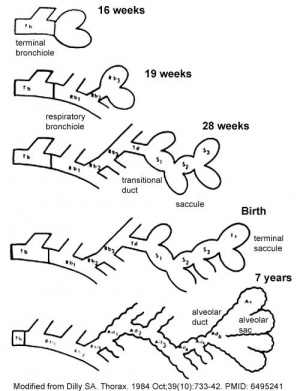
- Respiratory Month 3-6 - lungs appear glandular, end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant
- Tongue Week 12 - first differentiated epithelial cells (Type II and III)
Week 16+ (4 months)
- Respiratory - histology canalicular (Week 16 to 25)
- Skin - basal cell- proliferation generates folds in basement membrane; neural crest cells- (melanocytes) migrate into epithelium; embryonic connective tissue- differentiates into dermis, a loose ct layer over a dense ct layer. Beneath the dense ct layer is another loose ct layer that will form the subcutaneous layer. Ectoderm contributes to nails, hair follictles and glands. Nails form as thickening of ectoderm epidermis at the tips of fingers and toes. These form germinative cells of nail field. Cords of these cells extend into mesoderm forming epithelial columns. These form hair follocles, sebaceous and sweat glands.
- Gonad - primary follicles begin to form in the ovary and are characterized by an oocyte
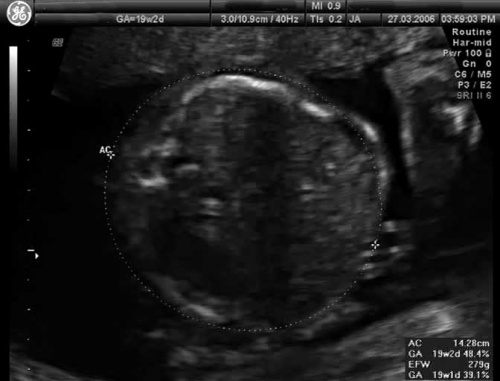
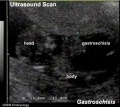
|
| Ultrasound Fetal (GA 19 weeks)
Ultrasound scan through the fetal trunk to measure abdominal circumference (AC). |
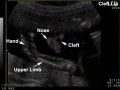
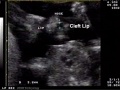
Ultrasound - Abnormalities
Practical 12: Embryo to Fetus | Second Trimester | Third Trimester | Birth | Neonatal | Abnormalities
Additional Information
The following information is a detailed timeline of second trimester development and content does not form part of the current practical class.
Second Trimester
(Clinical Week 14)
| Event | ||
| Clinical second trimester |  Week 12 - CRL 85 mm, femur length 15 mm, biparietal diameter 25 mm Week 12 - CRL 85 mm, femur length 15 mm, biparietal diameter 25 mm
Sense - Hearing Week 12-16 - Capsule adjacent to membranous labrynth undegoes vacuolization to form a cavity (perilymphatic space) around membranous labrynth and fills with perilymph Genital male and female external genital differences observable Respiratory Month 3-6 - lungs appear glandular, end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant Tongue Week 12 - first differentiated epithelial cells (Type II and III) female genital canal (80 days) formed with absorption of the median septum | |
| Tongue Week 12 to 13 - maximum synapses between cells and afferent nerve fibers
| ||
| Tongue Week 14 to 15 - taste pores develop, mucous
Ovary Development 100 days - primary follicles present | ||
| Pancreas glucagon detectable in fetal plasma | ||
| 14 cm |  Sense - Hearing Week 16-24 - Centres of ossification appear in remaining cartilage of otic capsule form petrous portion of temporal bone. Continues to ossify to form mastoid process of temporal bone. Sense - Hearing Week 16-24 - Centres of ossification appear in remaining cartilage of otic capsule form petrous portion of temporal bone. Continues to ossify to form mastoid process of temporal bone.
Pituitary adenohypophysis fully differentiated Respiratory Week 16 to 25 lung histology - canalicular Skin 4 months - basal cell- proliferation generates folds in basement membrane; neural crest cells- (melanocytes) migrate into epithelium; embryonic connective tissue- differentiates into dermis, a loose ct layer over a dense ct layer. Beneath the dense ct layer is another loose ct layer that will form the subcutaneous layer. Ectoderm contributes to nails, hair follictles and glands. Nails form as thickening of ectoderm epidermis at the tips of fingers and toes. These form germinative cells of nail field. Cords of these cells extend into mesoderm forming epithelial columns. These form hair follocles, sebaceous and sweat glands. primary follicles begin to form in the ovary and are characterized by an oocyte glandular urethra forms and skin folds present | |
| Tongue Week 18 - substance P detected in dermal papillae, not in taste bud primordia
Skin vernix caseosa covers skin Spleen -SMA-positive reticulum cells increase in number and begin to form a reticular framework. PMID: 1925578 | ||
| Pituitary week 20 to 24 growth hormone levels peak, then decline
Skin lanugo, skin hair Skin 5 months - Hair growth initiated at base of cord, lateral outgrowths form associated sebaceous glands; Other cords elongate and coil to form sweat glands; Cords in mammary region branch as they elongate to form mammary glands. | ||
 Neural brain cortical sulcation - sylvian fissure, interhemispheric fissure, callosal sulcus, parietooccipital fissure, and hippocampic fissures present(PMID:11158907 Neural brain cortical sulcation - sylvian fissure, interhemispheric fissure, callosal sulcus, parietooccipital fissure, and hippocampic fissures present(PMID:11158907
Spleen - antigenic reticular framework diversity, T and B lymphocytes segregated in the framework PMID: 1925578 | ||
| Respiratory Week 24 to 40 lung histology - terminal sac
Earliest potential survival expected if born ovarian follicles can consist of growing oocytes surrounded by several layers of granulosa cells | ||
| Respiratory end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
- 2010 BGD: Lecture 1 | Lecture 2 | Practical 3 | Practical 6 | Practical 12
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 21) Embryology 2010 BGD Practical 12 - Second Trimester. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2010_BGD_Practical_12_-_Second_Trimester
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G