2010 BGD Lecture - Development of the Embryo/Fetus 1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Gametogenesis== | ==Gametogenesis== | ||
===Male=== | |||
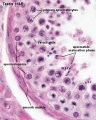
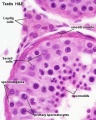
The testes have two functions. | |||
# produce the male gametes or '''spermatozoa''' | |||
# produce male sexual hormone, '''testosterone''' (external genitalia, sex characteristics) | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Historic-testis.jpg|Historic testis drawing | |||
File:Seminiferous-tubule-HEx40.jpg|Adult Seminiferous tubule showing spermatozoa developmental stages | |||
File:Testis_histology_2.jpg|Seminiferous tubule cross-section and supporting cells | |||
<gallery> | |||
==Fertilization== | ==Fertilization== | ||
Revision as of 22:18, 5 May 2010
Introduction
--Mark Hill 20:53, 3 May 2010 (EST) I am currently updating the notes that will appear here before the lecture on Thursday this week for 2010. Previous 2008 Lecture
- Begin by reviewing the recent Foundations Lecture and Practical.
- This lecture covers conceptus development from fertilization to implantation to trilaminar embryo formation.
- The lecture will also introduce early fetal membranes and placentation.
For those that cannot wait, here are some images to get you started......
Gametogenesis
Male
The testes have two functions.
- produce the male gametes or spermatozoa
- produce male sexual hormone, testosterone (external genitalia, sex characteristics)
- ==Fertilization==
- ==Week 1 and 2==
- ===Week 2 Implantation===
- ==Week 3 Gastrulation==
- * '''primitive node''' - region in the middle of the early embryonic disc epiblast from which the primitive streak extends caudally (tail)
- ** nodal cilia establish the embryo left/right axis
- ** axial process extends from the nodal epiblast
- * '''primitive streak''' - region of cell migration from the epiblast layer forming sequentially the two germ cell layers (endoderm and mesoderm)
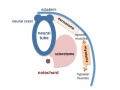
- == Notochord ==
- * '''axial process''' an initial epiblast hollow epithelial tube which extends in the midline from the primitive pit, cranially in the embryonic disc (toward the oral membrane).
- ** '''neuroenteric canal''' is a transient communication between the amnionic cavity and the yolk sac cavity formed by the axial process.
- * '''notochordal plate''' forms from the axial process merging with the endoderm layer.
- * '''notochord''' forms from the notochordal plate which then separates back into the mesoderm layer as a solid column of cells lying in the midline of the embryonic disc and running rostro-caudally (head to tail).
- ** An alternate name for the notochord is "axial mesoderm".
- ==Somitogenesis==
Somite initially forms 2 main components
- ventromedial- sclerotome forms vertebral body and intervertebral disc
- dorsolateral - dermomyotome forms dermis and skeletal muscle
Week 4 Neuralation
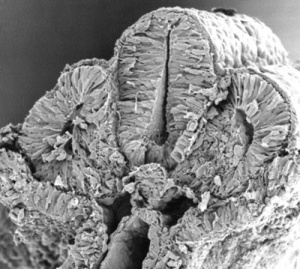
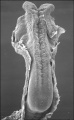
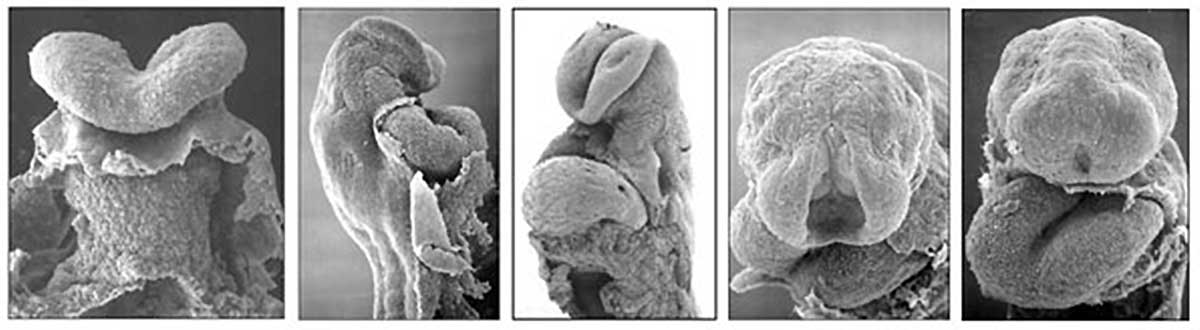
- Stage11 SEM1.jpg
Stage 11 Embryo (Week 4, 23 - 26 days)
Ectoderm - 2 parts
- midline neural plate
- columnar
- lateral surface ectoderm
- cuboidal
- sensory placodes
- epidermis of skin, hair, glands, anterior pituitary, teeth enamel
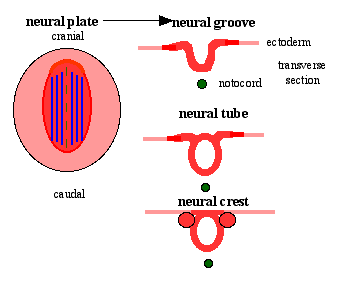
Neural Plate
- extends from buccopharyngeal membrane to primitive node
- forms above notochord and paraxial mesoderm
- neuroectodermal cells
- broad brain plate
- narrower spinal cord
- 3 components form: floor plate, neural plate, neural crest
Cardiogenesis
The Human Heart from day 10 to 25 (scanning electron micrograph)
- forms initially in splanchnic mesoderm of prechordal plate region - cardiogenic region
- growth and folding of the embryo moves heart ventrallly and downward into anatomical position
- week 3 begins as paired heart tubes that fuse to form single heart tube
- begins to beat in Humans- day 22-23
Blood Islands
- 2 populations of cells
- peripheral- form endothelial cells
- core- form blood cells (haemocytoblasts)
- all vessels (arteries and veins) appear initially the same
Blood Formation
- blood formation from stem cells occurs initially in the extraembryonic mesoderm of the yolk sac
- then later (week 5) throughout embryonic mesenchyme
- blood stem cells then migrate into the liver
- then spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes
Red Blood Cells
The only cells in the blood are nearly entirely fetal red blood cells. These cells differ from adult red blood cells in:
- often remaining nucleated
- contain fetal haemoglobin - which has different oxygen and carbon dioxide binding characteristics
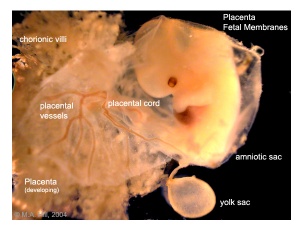
Early Placentation
The trophoblast layer has now differentiated into two morphologically distinct cellular layers.
- Syncitiotrophoblasts - form a multinucleated cytoplasmic mass by cytotrophoblast cell fusion and both invade the decidua and secrete hCG
- Cytotrophoblasts - form a cellular layer around the blastocyst, proliferates and extends behind syncitiotrophoblasts
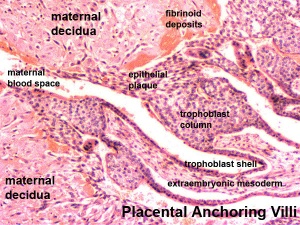
Early Utero-Placental exchange - transfer of nutrition from maternal lacunae filled with secretions from uterine glands and maternal blood from blood vessels. The development of trophoblast villi extending into the uterine decidua.
There are three stages of villi development:
- Primary Villi - cytotrophoblast
- Secondary Villi - cytotrophoblast + extraembryonic mesoderm
- Tertiary Villi - cytotrophoblast + extraembryonic mesoderm+ blood vessels
There are two main types of early villi:
- Anchoring villi - attached to decidua
- Floating villi - not attached to decidua, floating in maternal lacunae.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
- 2010 BGD: Lecture 1 | Lecture 2 | Practical 3 | Practical 6 | Practical 12
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 1) Embryology 2010 BGD Lecture - Development of the Embryo/Fetus 1. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2010_BGD_Lecture_-_Development_of_the_Embryo/Fetus_1
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G