2009 BGD-B Lecture Face and Ear: Difference between revisions
(New page: '''Links:''' [../../Notes/head.htm Systems Notes - Head and Neck] | [../../Notes/ear.htm Systems Notes - Hearing] [../../Sections/anat2300/2004/ANAT2300L09.htm Lecture Slides (2004) ANAT23...) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Links:''' [.. | '''Links:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/head.htm Systems Notes - Head and Neck] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ear.htm Systems Notes - Hearing] [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Sections/anat2300/2004/ANAT2300L09.htm Lecture Slides (2004) ANAT2300 Head Development] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Sections/anam1006/2003/ANAM1006L7.htm Lecture Slides (2003) ANAM1006 Head Development] | ||
= 1. Lecture Overview = | = 1. Lecture Overview = | ||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| | | * Face and Neck == | ||
* Pharyngeal Arches == | |||
* origins == | |||
* components == | |||
* structures formed == | |||
* Pharynx == | |||
* Ear Development == | |||
* origins == | |||
* otic placode == | |||
* external, middle, inner ear == | |||
* Abnormalities == | |||
|} | |} | ||
'''Links:''' [.. | '''Links:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/head.htm Systems Notes - Head and Neck] | ||
= 2. Human Embryo Comparison = | = 2. Human Embryo Comparison = | ||
[[Image:stage14compare23.jpg]]'''More:''' Note the great change beween the middle of embryological development to the end. | [[Image:stage14compare23.jpg]]'''More:''' Note the great change beween the middle of embryological development to the end. | ||
'''Links:''' [.. | '''Links:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwhuman/Stages/Stages.htm Embryo Stages] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwhuman/Stages/Images/stage14compare23.jpg Stage Comparison] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwhuman/Stages/Stage14L.htm Stage 14] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwhuman/Stages/Stage23L.htm Stage 23] | ||
= 3. Human Embryo External Appearance = | = 3. Human Embryo External Appearance = | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | * Stage 14 == | ||
| | | * Stage 23 == | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
'''More:''' Externally the pharyngeal arches are initially the most obvious external feature. Sensory placodes are present on the surface (but not obvious). By stage 14 the sensory placode that contributes to hearing (otic placode) has already been lots from the surface and now lies in the mesenchyme in the neck region. The '''cervical sinus''' is a surface landmark shwing the region where arch 2 is growing down over the | '''More:''' Externally the pharyngeal arches are initially the most obvious external feature. Sensory placodes are present on the surface (but not obvious). By stage 14 the sensory placode that contributes to hearing (otic placode) has already been lots from the surface and now lies in the mesenchyme in the neck region. The '''cervical sinus''' is a surface landmark shwing the region where arch 2 is growing down over the | ||
'''Links:''' [.. | '''Links:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwhuman/Stages/Stages.htm Embryo Stages] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwhuman/Stages/Images/stage14compare23.jpg Stage Comparison] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwhuman/Stages/Stage14L.htm Stage 14] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwhuman/Stages/Stage23L.htm Stage 23] | ||
= 4. Pharynx = | = 4. Pharynx = | ||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| | | * common forgut cavity == | ||
* begins at buccopharyngeal membrane == | |||
* "arched" == | |||
* beneath the brain == | |||
* over the pharyngeal eminence == | |||
* changes orientation as descends == | |||
| [[Image:head_arches.jpg]] | | [[Image:head_arches.jpg]] | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
|} | |} | ||
= 5. Pharyngeal Arches = | = 5. Pharyngeal Arches = | ||
* derived from pharyngeal or branchial arches == | |||
* Humans have 5 arches == | |||
* 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 == | |||
* arch 5 either does not form or rapidly regresses == | |||
* forms in rostro-caudal sequence == | |||
* Arch 1 to 6 from week 4 onwards == | |||
* Arch 1 and 2 appear at time of closure of cranial neuropore == | |||
= 6. Early Pharyngeal Arches = | = 6. Early Pharyngeal Arches = | ||
<center> </center> | <center> </center> | ||
* Stage 13/14 pharyngeal arch appearance == | |||
= 7. Pharyngeal Arch Components = | = 7. Pharyngeal Arch Components = | ||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| | | * each arch has initially similar components == | ||
* contributions from all 3 germ layers == | |||
* Ectoderm - outside surface and Neural Crest of core == | |||
* Mesoderm - core of mesenchyme == | |||
* Endoderm - inside pharyngeal surface == | |||
| <center>[[Image:head1.gif]]</center> | | <center>[[Image:head1.gif]]</center> | ||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
= 8. Pharyngeal Arch Features = | = 8. Pharyngeal Arch Features = | ||
* arch == | |||
* groove/cleft - externally separates each arch == | |||
* only first pair persist as external auditory meatus == | |||
* pouch - internally separates each arch == | |||
* pockets from the pharynx == | |||
* membrane - ectoderm and endoderm contact regions == | |||
* only first pair persist as tympanic membrane == | |||
= 9. Neck and Face = | = 9. Neck and Face = | ||
* each arch has initially similar components == | |||
* each arch though forms many different structures == | |||
* Face - mainly arch 1 and 2 == | |||
* Neck - mainly arch 3 and 4 == | |||
* arch 4 and 6 fuse == | |||
= 10. Pharyngeal Arch Neural Crest = | = 10. Pharyngeal Arch Neural Crest = | ||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| | | * Cranial neural crest (midbrain and hindbrain region) enters pharyngeal arch mesenchyme == | ||
* Forms connective tissues (cartilage, bone, ligaments): == | |||
* jaw cartilage and bone == | |||
* middle ear in mammals == | |||
* frontonasal process bones == | |||
* teeth dentine == | |||
* cranial nerve peripheral neurons and glia == | |||
| [[Image:head_arches.jpg]][[Image:ba2qt2.gif]] | | [[Image:head_arches.jpg]][[Image:ba2qt2.gif]] | ||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
'''More:''' The cranial neural crest therefore contributes much of the underlying structure of the face. Rhombomeres are the transient segmentation of the hindbrain. | '''More:''' The cranial neural crest therefore contributes much of the underlying structure of the face. Rhombomeres are the transient segmentation of the hindbrain. | ||
'''Links:''' [.. | '''Links:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest Notes] | | ||
= 11. Pharyngeal Arch Core = | = 11. Pharyngeal Arch Core = | ||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| | | * Each arch contains == | ||
* artery == | |||
* cartilage == | |||
* nerve == | |||
* muscular component == | |||
| [[Image:archcartilage.jpg]] | | [[Image:archcartilage.jpg]] | ||
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| | | * Mandibular Arch == | ||
* has 2 prominances == | |||
* upper - smaller, maxillary == | |||
* forms maxilla, zygomatic bone and squamous part of temporal == | |||
* lower - larger, mandibular == | |||
* mandible == | |||
| [[Image:pb2.gif]][[Image:mandible_sm.jpg]] | | [[Image:pb2.gif]][[Image:mandible_sm.jpg]] | ||
| Line 166: | Line 166: | ||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| | | * Pharyngeal Arch 2 == | ||
* Hyoid Arch == | |||
* forms most of hyoid bone == | |||
* 5 segments: body, two greater cornua, two lesser cornua == | |||
* Arch 3 and 4 == | |||
* neck structures == | |||
* hyoid bone, thyroid and cricoid cartilages == | |||
| [[Image:archcartilage_sm.jpg]][[Image:hyoid_bone_sm.jpg]] | | [[Image:archcartilage_sm.jpg]][[Image:hyoid_bone_sm.jpg]] | ||
| Line 186: | Line 186: | ||
= 14. Pharyngeal Arch Derivatives = | = 14. Pharyngeal Arch Derivatives = | ||
* Structures derived from Arches == | |||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| | | * Arch == | ||
| | | * Nerve == | ||
| | | * Muscles == | ||
| | | * Skeletal == | ||
| | | * Artery == | ||
| Line 251: | Line 251: | ||
|} | |} | ||
* Structures derived from Pouches == | |||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| | | * POUCH == | ||
| | | * Overall Structure == | ||
| | | * Specific Structures == | ||
| Line 287: | Line 287: | ||
|} | |} | ||
* Grooves- 1st groove forms part of the external acoustic meatus == | |||
* Membranes- 1st membrane forms the tympanic membrane == | |||
'''More:''' The above table is not for you to learn by heart but an indication of the structures formed from each arch. | '''More:''' The above table is not for you to learn by heart but an indication of the structures formed from each arch. | ||
| Line 301: | Line 301: | ||
4th arch- about the neck and endocrine. | 4th arch- about the neck and endocrine. | ||
'''Links:''' [.. | '''Links:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/head.htm#fate Arch Derivatives] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=dbio.table.3135 Dev Biol - Some derivatives of the pharyngeal arches] | | ||
= 15. Pharyngeal Abnormalities = | = 15. Pharyngeal Abnormalities = | ||
* Sinuses - when a portion of groove persists == | |||
* Fistula - a tract extending from pharynx to open on side of neck == | |||
* Cysts - remants of cervical sinus == | |||
* Vestiges - cartilaginous or bony developmental remnants under skin on side of neck == | |||
'''More:''' | '''More:''' | ||
'''Links:''' [.. | '''Links:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/head2.htm Head and Neck Abnormalities] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ear2.htm Hearing Abnormalities] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Defect/page5a.htm Abnormal Development - Fetal Alcohol Syndrome] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/usoundab/Cleft1.htm Abnormal Ultrasound - Cleft Lip] | | ||
= 16. Face = | = 16. Face = | ||
* Face develops from week 4 to 10. == | |||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| Line 320: | Line 320: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | * 1 Frontonasal prominence - Nasal (medial, lateral) == | ||
* 2 Maxillary2 Mandibular == | |||
| | | | ||
* Face Development cartoon == | |||
| Line 331: | Line 331: | ||
'''More:''' | '''More:''' | ||
'''Links:''' [.. | '''Links:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/face.htm Face Development] | [http://connection.lww.com/products/sadler/images/figurelarge15-21.jpg Sadler Image Bank - Frontal aspect of the face 5 week and 6 week embryo] | [http://connection.lww.com/products/sadler/images/figurelarge15-22.jpg Sadler Image Bank - Frontal aspect of the face 7 week embryo] | | ||
= 17. Palate = | = 17. Palate = | ||
| Line 342: | Line 342: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <center>[.. | | <center>[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/usoundab/Cleft1.htm Ultrasound Movie - Facial Cleft 1 ]</center> | ||
| <center>[.. | | <center>[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/usoundab/Cleft2.htm Ultrasound Movie - Facial Cleft 2 ]</center> | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''More:''' Cleft lip and palate develop between the 4th and 8th week of gestation and is dominated by changes resulting in the formation of the nose. Palatal development occurs between the 7th and 12th week of gestation and is divided into the formation of the '''primary palate''' (prolabium), premaxilla and cartilaginous septum) and formation of the '''secondary palate''' (hard and soft palate). The animation above shows the early fusion of the primary palate in the human embryo between stage 17 and 18, going from an epithelial seam to the mesenchymal bridge. | '''More:''' Cleft lip and palate develop between the 4th and 8th week of gestation and is dominated by changes resulting in the formation of the nose. Palatal development occurs between the 7th and 12th week of gestation and is divided into the formation of the '''primary palate''' (prolabium), premaxilla and cartilaginous septum) and formation of the '''secondary palate''' (hard and soft palate). The animation above shows the early fusion of the primary palate in the human embryo between stage 17 and 18, going from an epithelial seam to the mesenchymal bridge. | ||
'''Links:''' [.. | '''Links:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/face6.htm Face Development - Primary Palate] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/face2.htm Face Development Abnormalities] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/usoundab/Cleft1.htm Abnormal Ultrasound - Cleft Lip] | | ||
= 18. Tongue = | = 18. Tongue = | ||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| | | * Derived from all pharyngeal arches contributing different components == | ||
* Somites - tongue muscle cells == | |||
* Somitomeres - muscles of mastication == | |||
| | | | ||
| Line 363: | Line 363: | ||
'''More:''' The tongue develops "inside" the floor of the oral cavity, therefre it is not readily visible in the external views of the embryonic (Carnegie) stages of development. Somitomeres are the unsegmented mesoderm found in the head region, in a similar location to that of somites in the body. | '''More:''' The tongue develops "inside" the floor of the oral cavity, therefre it is not readily visible in the external views of the embryonic (Carnegie) stages of development. Somitomeres are the unsegmented mesoderm found in the head region, in a similar location to that of somites in the body. | ||
'''Links:''' [.. | '''Links:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/head6.htm Tongue Development] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/tongue.htm Sensory Development - Taste] | ||
= Ear = | = Ear = | ||
* Next set of slides - Hearing == | |||
[[Image:hearingcartoon.jpg]] | [[Image:hearingcartoon.jpg]] | ||
| Line 373: | Line 373: | ||
[.. | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/CSthead.htm Quicktime movie 179 Kb] in new window. | ||
Movie of the human head covering the Carnegie stages from 16 to 18. | Movie of the human head covering the Carnegie stages from 16 to 18. | ||
| Line 384: | Line 384: | ||
[[Image:face.jpg]] | [[Image:face.jpg]] | ||
[.. | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/larsen/face.mov Face Development Overview] (300 Kb) | ||
[[Image:fetus.jpg]] | [[Image:fetus.jpg]] | ||
[.. | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/larsen/fetus.mov Fetal Development Overview] (800 Kb) | ||
[.. | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/larsen/tongue.mov Development of the Tongue] (187Kb) | ||
= References = | = References = | ||
| Line 437: | Line 437: | ||
== Glossary == | == Glossary == | ||
[.. | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/A.htm A] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/B.htm B] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/C.htm C] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/D.htm D] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/E.htm E] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/F.htm F] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/G.htm G] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/H.htm H] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/I.htm I] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/J.htm J] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/K.htm K] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/L.htm L] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/M.htm M] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/N.htm N] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/O.htm O] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/P.htm P] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/Q.htm Q] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/R.htm R] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/S.htm S] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/T.htm T] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/U.htm U] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/V.htm V] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/W.htm W] |[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/X.htm X] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/Y.htm Y] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/Z.htm Z] | ||
== COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA | == Copyright Notice == | ||
<center>COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA</center> | |||
<center>Copyright Regulations 1969</center> | |||
<center>WARNING</center> | |||
<center>This material has been copied and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of New South Wales pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further copying or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act.</center> | <center>This material has been copied and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of New South Wales pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further copying or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act.</center> | ||
<center>Do not remove this notice.</center> | <center>Do not remove this notice.</center> | ||
:© '''Dr M. A. Hill''', 2007, Cell Biology Laboratory, School of Medical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia. | |||
[mailto:m.hill@unsw.edu.au Email]Copyright: Dr Mark Hill UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G | |||
=== Slide Links === | |||
[#Intro Introduction][#1 1. Overview][#2 2. Embryo Comparison][#3 3. External Appearance][#4 4. Pharynx][#5 5. Pharyngeal Arches][#6 6. Early Arches][#7 7. Arch Components][#8 8. Arch Features][#9 9. Neck and Face][#10 10. Arch Neural Crest][#11 11. Arch Core][#12 12. Pharyngeal Arch 1][#13 13. Pharyngeal Arch 2-4][#14 14. Arch Derivatives][#14 15. Abnormalities][#15 16. Face][#17 17. Palate][#18 18. Tongue][#19 19. Ear][#References References][#Terms Terms][#Glossary Glossary] | [#Intro Introduction][#1 1. Overview][#2 2. Embryo Comparison][#3 3. External Appearance][#4 4. Pharynx][#5 5. Pharyngeal Arches][#6 6. Early Arches][#7 7. Arch Components][#8 8. Arch Features][#9 9. Neck and Face][#10 10. Arch Neural Crest][#11 11. Arch Core][#12 12. Pharyngeal Arch 1][#13 13. Pharyngeal Arch 2-4][#14 14. Arch Derivatives][#14 15. Abnormalities][#15 16. Face][#17 17. Palate][#18 18. Tongue][#19 19. Ear][#References References][#Terms Terms][#Glossary Glossary] | ||
Revision as of 12:19, 13 May 2009
Links: Systems Notes - Head and Neck | Systems Notes - Hearing Lecture Slides (2004) ANAT2300 Head Development | Lecture Slides (2003) ANAM1006 Head Development
1. Lecture Overview
* Face and Neck ==
|
Links: Systems Notes - Head and Neck
2. Human Embryo Comparison
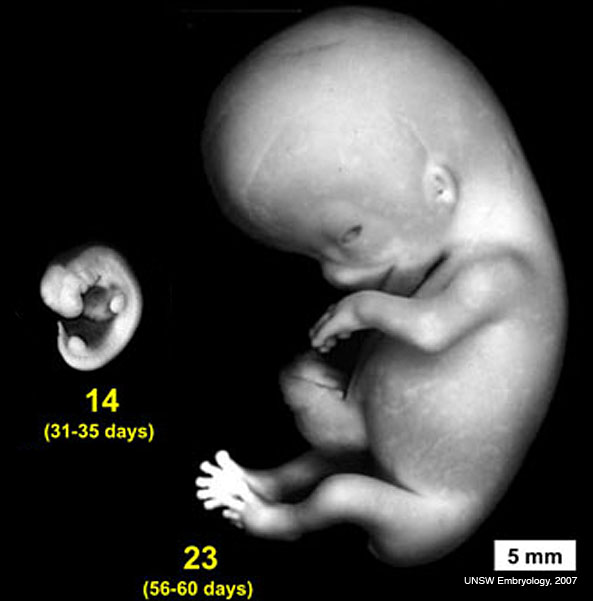 More: Note the great change beween the middle of embryological development to the end.
More: Note the great change beween the middle of embryological development to the end.
Links: Embryo Stages | Stage Comparison | Stage 14 | Stage 23
3. Human Embryo External Appearance
| File:600stage14.jpg | File:600stage23.jpg |
| * Stage 14 == | * Stage 23 ==
|
More: Externally the pharyngeal arches are initially the most obvious external feature. Sensory placodes are present on the surface (but not obvious). By stage 14 the sensory placode that contributes to hearing (otic placode) has already been lots from the surface and now lies in the mesenchyme in the neck region. The cervical sinus is a surface landmark shwing the region where arch 2 is growing down over the
Links: Embryo Stages | Stage Comparison | Stage 14 | Stage 23
4. Pharynx
* common forgut cavity ==
|
File:Head arches.jpg |
| File:Pb2.gif |
5. Pharyngeal Arches
- derived from pharyngeal or branchial arches ==
- Humans have 5 arches ==
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 ==
- arch 5 either does not form or rapidly regresses ==
- forms in rostro-caudal sequence ==
- Arch 1 to 6 from week 4 onwards ==
- Arch 1 and 2 appear at time of closure of cranial neuropore ==
6. Early Pharyngeal Arches
- Stage 13/14 pharyngeal arch appearance ==
7. Pharyngeal Arch Components
* each arch has initially similar components ==
|
|
8. Pharyngeal Arch Features
- arch ==
- groove/cleft - externally separates each arch ==
- only first pair persist as external auditory meatus ==
- pouch - internally separates each arch ==
- pockets from the pharynx ==
- membrane - ectoderm and endoderm contact regions ==
- only first pair persist as tympanic membrane ==
9. Neck and Face
- each arch has initially similar components ==
- each arch though forms many different structures ==
- Face - mainly arch 1 and 2 ==
- Neck - mainly arch 3 and 4 ==
- arch 4 and 6 fuse ==
10. Pharyngeal Arch Neural Crest
* Cranial neural crest (midbrain and hindbrain region) enters pharyngeal arch mesenchyme ==
|
File:Head arches.jpgFile:Ba2qt2.gif |
More: The cranial neural crest therefore contributes much of the underlying structure of the face. Rhombomeres are the transient segmentation of the hindbrain.
Links: Neural Crest Notes |
11. Pharyngeal Arch Core
* Each arch contains ==
|
File:Archcartilage.jpg | File:Meckelsm.jpg |
More:
Links: Sadler Image Bank - Pharyngeal Arches | Sadler Image Bank - Pharyngeal Arch Arteries | Embryo Images - Aortic Arch Vessels |
12. Pharyngeal Arch 1
* Mandibular Arch ==
|
File:Pb2.gifFile:Mandible sm.jpg |
More:
Links: Embryo Stage 12 | Embryo Stage 13 | Embryo Images - Pharyngeal Arch 1 and 2 early | [%20http://www.med.unc.edu/embryo_images/unit-hednk/hednk_htms/hednk011.htm Embryo Images - Pharyngeal Arch 1 and 2 later] | Dev Biol - Jaw structure in the fish, reptile, and mammal |
13. Pharyngeal Arch 2 - 4
* Pharyngeal Arch 2 ==
|
File:Archcartilage sm.jpgFile:Hyoid bone sm.jpg |
More: Hyoid bone ossified from six centres (2 body, 1 for each cornu). Ossiification - late fetal in the greater cornua, then in the body, then postnatally (1-2 years) in the lesser cornua.
Links: Embryo Stage 13 |
14. Pharyngeal Arch Derivatives
- Structures derived from Arches ==
| * Arch == | * Nerve == | * Muscles == | * Skeletal == | * Artery ==
|
| mastication
(temporalis, masseter, medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid) |
mandible model
malleus, incus Meckel's cartilage |
maxillary
(terminal branches) | ||
| facial expression
( buccinator, platysma, stapedius, stylohyoid, digastric posterior belly) |
stapes, styloid process, lesser cornu of hyoid, upper part of body of hyoid bone
Reichert's cartilage |
stapedial (embryonic)
corticotympanic (adult)
| ||
| Stylopharyngeus | greater cornu of hyoid, lower part of body of hyoid bone | common carotid, internal carotid (root) | ||
| intrinsic muscles of larynx, pharynx; levator palati | thyroid, cricoid, arytenoid, corniculate and cuneform cartilages | 4 - aortic arch, right subclavian
6 - ductus arteriosus, pulmonary (roots) |
- Structures derived from Pouches ==
| * POUCH == | * Overall Structure == | * Specific Structures ==
|
| tubotympanic recess | tympanic membrane, tympanic cavity, mastoid antrum, auditory tube | |
| intratonsillar cleft | crypts of palatine tonsil, lymphatic nodules of palatine tonsil | |
| inferior parathyroid gland, thymus gland | ||
| superior parathyroid gland, ultimobranchial body | ||
| becomes part of 4th pouch |
- Grooves- 1st groove forms part of the external acoustic meatus ==
- Membranes- 1st membrane forms the tympanic membrane ==
More: The above table is not for you to learn by heart but an indication of the structures formed from each arch.
It is easy to remember that:
1st arch - about the mouth (chewing, jaw) and the external and middle ear.
2nd arch - about the face, hyoid and external and middle ear.
3rd arch - about the neck and endocrine.
4th arch- about the neck and endocrine.
Links: Arch Derivatives | Dev Biol - Some derivatives of the pharyngeal arches |
15. Pharyngeal Abnormalities
- Sinuses - when a portion of groove persists ==
- Fistula - a tract extending from pharynx to open on side of neck ==
- Cysts - remants of cervical sinus ==
- Vestiges - cartilaginous or bony developmental remnants under skin on side of neck ==
More:
Links: Head and Neck Abnormalities | Hearing Abnormalities | Abnormal Development - Fetal Alcohol Syndrome | Abnormal Ultrasound - Cleft Lip |
16. Face
- Face develops from week 4 to 10. ==
| File:Face16to18.jpg | File:Face16to18.gif |
* 1 Frontonasal prominence - Nasal (medial, lateral) ==
|
|
More:
Links: Face Development | Sadler Image Bank - Frontal aspect of the face 5 week and 6 week embryo | Sadler Image Bank - Frontal aspect of the face 7 week embryo |
17. Palate
File:Primarypalate1718.gif File:CleftPrimaryPalate1619.jpg
| File:Cleft1label.jpg | File:Cleft2label.jpg |
More: Cleft lip and palate develop between the 4th and 8th week of gestation and is dominated by changes resulting in the formation of the nose. Palatal development occurs between the 7th and 12th week of gestation and is divided into the formation of the primary palate (prolabium), premaxilla and cartilaginous septum) and formation of the secondary palate (hard and soft palate). The animation above shows the early fusion of the primary palate in the human embryo between stage 17 and 18, going from an epithelial seam to the mesenchymal bridge.
Links: Face Development - Primary Palate | Face Development Abnormalities | Abnormal Ultrasound - Cleft Lip |
18. Tongue
* Derived from all pharyngeal arches contributing different components ==
|
More: The tongue develops "inside" the floor of the oral cavity, therefre it is not readily visible in the external views of the embryonic (Carnegie) stages of development. Somitomeres are the unsegmented mesoderm found in the head region, in a similar location to that of somites in the body.
Links: Tongue Development | Sensory Development - Taste
Ear
- Next set of slides - Hearing ==
#. Movies
Movie of the human head covering the Carnegie stages from 15 to 22. Note the images are not to scale.
Quicktime movie 179 Kb in new window.
Movie of the human head covering the Carnegie stages from 16 to 18.
Movie of stage 13/14 pig embryo sections showing the head region of the nasal placodes.
Face Development Overview (300 Kb)
Fetal Development Overview (800 Kb)
Development of the Tongue (187Kb)
References
Textbooks
Human Embryology (3rd ed.) Larson Chapter 12 pp 351-378
The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (6th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 10 pp 201- 240
Online Textbooks
Developmental Biology (6th ed.) Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000. : Cranial neural crest cell migration in the mammalian head | Regions of the neural crest | Jaw structure in the fish, reptile, and mammal | Some derivatives of the pharyngeal arches |
Eurekah Bioscience Collection Chapters taken from the Eurekah Bioscience database. Eurekah.com and Landes Bioscience; 2003. : Cranial Neural Crest and Development of the Head Skeleton |
Clinical Methods (3rd ed.) Walker, H.K.; Hall, W.D.; Hurst, J.W.; editors Stoneham (MA): Butterworth Publishers; c1990 : 63. Cranial Nerves IX and X: The Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves | The Tongue |
Anatomy of the Human Body Gray, H. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1918.
Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.) Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter New York and London: Garland Science; c2002.
Online Resources
Embryo Images Unit: Embryo Images Online | Craniofacial Development | Cell Populations | Pharyngeal Arches | Tongue | Nose and Upper Lip | Palate Development
Journals: GI Motility online (2006) Anatomy and development of oral cavity and pharynx| [NlmId&doptcmdl=Expanded&cmd=search The Cleft Palate Journal]
Terms
branchial arch (= pharyngeal arch) (Greek, branchia = gill) is a misnomer.
buccopharyngeal membrane (= oral membrane), apposition of ectoderm with endoderm with no mesoderm between. Lies at a ventral central depression (stomadeum). This external to internal junctionl region wiil break down, creating an opening and allows amniotic fluid to fill the foregut.
calveria
chondrocranium in humans, forms base of skull (in lower vertebrates encases brain).
cranial vault
facial skeleton
pharyngeal arch
pharynx
sensory placode
Glossary
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W |X | Y | Z
Copyright Notice
- © Dr M. A. Hill, 2007, Cell Biology Laboratory, School of Medical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia.
EmailCopyright: Dr Mark Hill UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
Slide Links
[#Intro Introduction][#1 1. Overview][#2 2. Embryo Comparison][#3 3. External Appearance][#4 4. Pharynx][#5 5. Pharyngeal Arches][#6 6. Early Arches][#7 7. Arch Components][#8 8. Arch Features][#9 9. Neck and Face][#10 10. Arch Neural Crest][#11 11. Arch Core][#12 12. Pharyngeal Arch 1][#13 13. Pharyngeal Arch 2-4][#14 14. Arch Derivatives][#14 15. Abnormalities][#15 16. Face][#17 17. Palate][#18 18. Tongue][#19 19. Ear][#References References][#Terms Terms][#Glossary Glossary]