File:Hippo pathway on-off cartoon.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
{{#pmid:24336504}} | |||
====Copyright==== | ====Copyright==== | ||
Revision as of 09:01, 21 March 2018
The Hippo Pathway and its mode of action
- A - When the Hippo pathway is ON, MST1/2 phosphorylate SAV1 and together they phosphorylate and activate MOB1A/B and LATS1/2, which then phosphorylate YAP and TAZ. Phosphorylated YAP and TAZ are sequestered in the cytoplasm by the 14-3-3 phosphopeptide binding proteins and shunted for proteasomal degradation. As a result, the TEAD transcription factors associate with VGL4 and suppress target gene expression.
- B - When the Hippo pathway is OFF, the MST1/2 and LATS1/2 kinases are inactive, YAP and TAZ are not phosphorylated and accumulate in the nucleus where they displace VGL4 and complex with TEADs. YAP and TAZ are transcriptional co-activators and in complex with TEADs promote the expression of target genes.
Reference
Johnson R & Halder G. (2014). The two faces of Hippo: targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and cancer treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov , 13, 63-79. PMID: 24336504 DOI.
Copyright
Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (Randy Johnson, Georg Halder The two faces of Hippo: targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and cancer treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov: 2014, 13(1);63-79), copyright (2015)
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:52, 10 June 2015 | 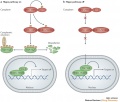 | 946 × 808 (124 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | |
| 10:47, 10 June 2015 | 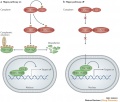 | 946 × 808 (124 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ===Reference=== <pubmed>25986053</pubmed> |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: