File:Trisomy21female.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) Female Karyotype== | |||
Down syndrome or [[trisomy 21]] is caused by nondisjunction of chromosome 21 in a parent who is chromosomally normal and is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities in liveborn children. The frequency of trisomy 21 in the population is approximately 1 in 650 to 1,000 live births, in Australia between 1991-97 there were 2,358 Trisomy 21 (Down) infants. | |||
* The normal human karyotypes contain 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. | |||
* The karyotype is the characteristic chromosome complement as identified by staining and can only be identified during cell division when chromosomes are folded. | |||
* The chromosomes when organised as an image in sequence are called a karyogram or idiogram. | |||
{{Trisomy 21 karyotype links}} | |||
===Chromosome 21=== | |||
* the smallest human chromosome | |||
* about 47 million base pair | |||
* about 1.5 % of the total DNA in cells | |||
* contains between 300 and 400 genes (of human estimated 20,000 to 25,000 total genes) | |||
* [[trisomy 21]] or Downs Syndrome - additional copy of this chromosome | |||
* partial monosomy 21 - missing segment of the chromosome in each cell | |||
* ring chromosome 21 - circular structure, occurs when there are two breaks in a chromosome and the ends of the chromosome then fuse together | |||
{{Footer}} | |||
[[Category:Abnormal Development]] [[Category:Genetic Abnormalities]] [[Category:Human Embryo]] [[Category:Human Fetus]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:10, 20 July 2015
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) Female Karyotype
Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is caused by nondisjunction of chromosome 21 in a parent who is chromosomally normal and is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities in liveborn children. The frequency of trisomy 21 in the population is approximately 1 in 650 to 1,000 live births, in Australia between 1991-97 there were 2,358 Trisomy 21 (Down) infants.
- The normal human karyotypes contain 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes.
- The karyotype is the characteristic chromosome complement as identified by staining and can only be identified during cell division when chromosomes are folded.
- The chromosomes when organised as an image in sequence are called a karyogram or idiogram.
- Trisomy 21 Links: Trisomy 21 | Image T21 female karyotype | Image T21 male karyotype | chromosome 21 | Category:Trisomy 21 | Genetic Abnormalities | Prenatal Diagnosis
Chromosome 21
- the smallest human chromosome
- about 47 million base pair
- about 1.5 % of the total DNA in cells
- contains between 300 and 400 genes (of human estimated 20,000 to 25,000 total genes)
- trisomy 21 or Downs Syndrome - additional copy of this chromosome
- partial monosomy 21 - missing segment of the chromosome in each cell
- ring chromosome 21 - circular structure, occurs when there are two breaks in a chromosome and the ends of the chromosome then fuse together
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 26) Embryology Trisomy21female.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Trisomy21female.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 16:19, 27 July 2009 | 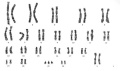 | 480 × 284 (12 KB) | MarkHill (talk | contribs) | Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is caused by nondisjunction of chromosome 21 in a parent who is chromosomally normal and is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities in liveborn children. The frequency of trisomy 21 in the population is approximately 1 |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 27 pages use this file:
- 2009 Lecture 2
- 2010 BGD Practical 3 - Gametogenesis
- 2010 Group Project 3
- 2010 Lecture 2
- 2011 Lab 1 - Gametogenesis
- ANAT2341 Fertilization Quiz
- ANAT2341 Lab 1 - Gametogenesis
- ANAT2341 Lab 1 - Quiz
- Abnormal Development - Genetic
- BGDA Practical 3 - Gametogenesis
- BGD Practical - Fertilization to Implantation Quiz
- Cell Division - Meiosis
- Foundations Quiz
- G
- Histology Stains
- Human Abnormal Development
- In Vitro Oogenesis
- K
- Lecture - Fertilization
- Molecular Development - Genetics
- Oocyte Development
- Trisomy 21
- Week 1 and 2 Quiz
- Talk:BGDA Practical 3 - Oogenesis and Ovulation
- Talk:BGD Practical - Fertilization to Implantation Quiz
- Talk:Mesoderm Quiz
- Template:Genetic menu gallery