File:Implantation cartoon 01.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(This is a hybrid cartoon, based on mouse and human studies, portraying compartment- and cell-type–specific expression of molecules and their potential functions necessary for uterine receptivity, implantation and decidualization. Interplay of ovarian...) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This is a hybrid cartoon, based on mouse and human studies, portraying compartment- and cell-type–specific expression of molecules and their potential functions necessary for uterine receptivity, implantation and decidualization. Interplay of ovarian P4- and/or E2-dependent and P4- and/or E2-independent factors in the pregnant uterus in specific compartments contributes to the success of implantation in a juxtacrine/paracrine/autocrine manner. During attachment, interactions between the blastocyst and luminal epithelium (LE) involve ErbB1/4 (blue) and both transmembrane (TM) and soluble (Sol) forms of HB-EGF, as well as L-selectin ligands (sLE) expressed by the luminal epithelium to L-selectin receptors on the blastocyst. The other key signaling pathways for uterine receptivity and implantation are also shown. | ==Molecular Implantation Cartoon== | ||
{| | |||
| | |||
! Compartment colours | |||
|- | |||
| This is a hybrid cartoon, based on mouse and human studies, portraying compartment- and cell-type–specific expression of molecules and their potential functions necessary for uterine receptivity, implantation and decidualization. Interplay of ovarian P4- and/or E2-dependent and P4- and/or E2-independent factors in the pregnant uterus in specific compartments contributes to the success of implantation in a juxtacrine/paracrine/autocrine manner. During attachment, interactions between the blastocyst and luminal epithelium (LE) involve ErbB1/4 (blue) and both transmembrane (TM) and soluble (Sol) forms of HB-EGF, as well as L-selectin ligands (sLE) expressed by the luminal epithelium to L-selectin receptors on the blastocyst. The other key signaling pathways for uterine receptivity and implantation are also shown. | |||
| valign=top width =250px| | |||
* blue - stroma | |||
* pink - luminal epithelium | |||
* orange - glandular epithelium | |||
* purple - epithelium at the attachment site. | |||
|} | |||
{| | |||
! Legend | |||
|- | |||
| valign=top| | |||
* '''AA''' - arachidonic acid | |||
* '''BMP2''' - bone morphogenetic protein 2 | |||
* '''cPLA2α''' - cytosolic phospholipase A2α | |||
* '''COUP-TFII''' - chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor-2 | |||
* '''Cox2''' - cyclooxygenase-2 | |||
* '''E''' - estrogens | |||
* '''EC''' - epithelial cell (luminal and glandular epithelia) | |||
* '''ENaC''' - epithelium sodium channel | |||
* '''ER''' - estrogen receptor | |||
| valign=top| | |||
* '''ErbB1/4''' - epidermal growth factor receptor 1/4 | |||
* '''ERK''' - extracellular signal–regulated kinase | |||
* '''FGF''' - fibroblast growth factor | |||
* '''GE''' - glandular epithelium | |||
* '''gp130''' - glycoprotein 130 | |||
* '''Hand2''' - heart- and neural crest derivatives-expressed protein 2 | |||
* '''HB-EGF''' - heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor | |||
* '''Hoxa10/11''' - homeobox A10/11 | |||
* '''ICM''' - inner cell mass | |||
| valign=top| | |||
* '''IHH''' - Indian hedgehog | |||
* '''KLF5''' - Kruppel-like factor 5 | |||
* '''LIF''' - leukemia inhibitory factor | |||
* '''LIFR''' - LIF receptor | |||
* '''LPA3''' - lysophosphatidic acid receptor 3 | |||
* '''MSX1''' - Muscle segment homeobox 1 | |||
* '''P4''' - progesterone | |||
* '''PG''' - prostaglandin | |||
* '''PPAR-δ''' - peroxisome proliferators–activating receptor δ | |||
| valign=top| | |||
* '''PR''' - progesterone receptor | |||
* '''Ptc''' - Patched | |||
* '''RXR''' - retinoid X receptor | |||
* '''SC''' - stromal cell | |||
* '''SGK1''' - serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 | |||
* '''Smo''' - Smoothened | |||
* '''STAT3''' - signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 | |||
* '''Tr''' - trophectoderm | |||
* '''Wnt4/5a''' - Wingless-Type MMTV integration site family members 4/5a. | |||
|} | |||
:'''Links:''' [[Implantation]] | |||
===Reference=== | |||
{{#pmid:23223073}} | |||
====Copyright==== | |||
Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature Medicine (Mechanisms of implantation: strategies for successful pregnancy. | |||
Cha J, Sun X, Dey SK. Nat Med. 2012 Dec;18(12):1754-67. doi: 10.1038/nm.3012. Review. PMID 23223073), copyright (2012) | |||
[[Category:Implantation]] [[Category:Cartoon]] | |||
Nm.3012-F1.jpg | Nm.3012-F1.jpg | ||
{{footer}} | |||
Latest revision as of 09:56, 29 April 2020
Molecular Implantation Cartoon
| Compartment colours | |
|---|---|
| This is a hybrid cartoon, based on mouse and human studies, portraying compartment- and cell-type–specific expression of molecules and their potential functions necessary for uterine receptivity, implantation and decidualization. Interplay of ovarian P4- and/or E2-dependent and P4- and/or E2-independent factors in the pregnant uterus in specific compartments contributes to the success of implantation in a juxtacrine/paracrine/autocrine manner. During attachment, interactions between the blastocyst and luminal epithelium (LE) involve ErbB1/4 (blue) and both transmembrane (TM) and soluble (Sol) forms of HB-EGF, as well as L-selectin ligands (sLE) expressed by the luminal epithelium to L-selectin receptors on the blastocyst. The other key signaling pathways for uterine receptivity and implantation are also shown. |
|
| Legend | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
- Links: Implantation
Reference
Cha J, Sun X & Dey SK. (2012). Mechanisms of implantation: strategies for successful pregnancy. Nat. Med. , 18, 1754-67. PMID: 23223073 DOI.
Copyright
Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature Medicine (Mechanisms of implantation: strategies for successful pregnancy. Cha J, Sun X, Dey SK. Nat Med. 2012 Dec;18(12):1754-67. doi: 10.1038/nm.3012. Review. PMID 23223073), copyright (2012)
Nm.3012-F1.jpg
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 20) Embryology Implantation cartoon 01.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Implantation_cartoon_01.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 17:46, 18 March 2013 | 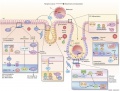 | 1,000 × 756 (154 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | This is a hybrid cartoon, based on mouse and human studies, portraying compartment- and cell-type–specific expression of molecules and their potential functions necessary for uterine receptivity, implantation and decidualization. Interplay of ovarian... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 4 pages use this file: