File:Schwann and axon interactions.jpg: Difference between revisions
(==Model of interactions between myelinating Schwann cells and axons== Showing proteins that localize to the node, paranode, juxtaparanode, and internode. Schwann cell, blue; axon, yellow. PN, paranode; JPN, juxtaparanode. Analysis of the Necl proteins pr) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Model of interactions between myelinating Schwann cells and axons== | ==Model of interactions between myelinating Schwann cells and axons== | ||
* Showing proteins that localize to the node, paranode, juxtaparanode, and internode. | |||
* Schwann cell, blue; axon, yellow. PN, paranode; JPN, juxtaparanode. | |||
Analysis of the Necl proteins provides important new insight into molecular complexes along the internode (Maurel et al., 2007; Spiegel et al., 2007), which had not been as well defined as for the other domains. | |||
The polarity protein Par-3 colocalizes with Necl-4 in the adaxonal region of the Schwann cell (Chan et al., 2006), and it is possible that these proteins interact via PDZ and PDZ-binding motifs (red). The Necl proteins can also interact with FERM domain proteins via the FERM-binding domain (blue). Necls are also present at the Schmidt-Lanterman incisures (inset). Necl-2 is not depicted but localizes to the axon–Schwann cell interface and to the incisures. | |||
The figure was adapted from Voas et al. (2007). | |||
http://jcb.rupress.org/content/178/5/721/F1.large.jpg | http://jcb.rupress.org/content/178/5/721/F1.large.jpg | ||
Revision as of 12:42, 24 September 2010
Model of interactions between myelinating Schwann cells and axons
- Showing proteins that localize to the node, paranode, juxtaparanode, and internode.
- Schwann cell, blue; axon, yellow. PN, paranode; JPN, juxtaparanode.
Analysis of the Necl proteins provides important new insight into molecular complexes along the internode (Maurel et al., 2007; Spiegel et al., 2007), which had not been as well defined as for the other domains.
The polarity protein Par-3 colocalizes with Necl-4 in the adaxonal region of the Schwann cell (Chan et al., 2006), and it is possible that these proteins interact via PDZ and PDZ-binding motifs (red). The Necl proteins can also interact with FERM domain proteins via the FERM-binding domain (blue). Necls are also present at the Schmidt-Lanterman incisures (inset). Necl-2 is not depicted but localizes to the axon–Schwann cell interface and to the incisures.
The figure was adapted from Voas et al. (2007).
http://jcb.rupress.org/content/178/5/721/F1.large.jpg
Reference
<pubmed>17724116</pubmed>| PMC2064536 | JCB
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:41, 24 September 2010 | 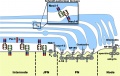 | 1,280 × 807 (196 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Model of interactions between myelinating Schwann cells and axons== Showing proteins that localize to the node, paranode, juxtaparanode, and internode. Schwann cell, blue; axon, yellow. PN, paranode; JPN, juxtaparanode. Analysis of the Necl proteins pr |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: