File:Blood-brain barrier EM01.jpg: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Mouse Blood-brain barrier (EM)== | ==Mouse Blood-brain barrier (EM)== | ||
{| | |||
| width=300px valign=top|'''Fig. 11''' Regions of overlap between neighboring endothelial cells, illustrating range of variation in structure of the intercellular cleft. In Fig. 11, the cleft is obliterated by a tight junction (arrow) extending throughout most of its length. The region of the intercellular cleft indicated by the arrow in Fig. 11 is shown in inset at higher magnification to illustrate that the total width of the tight junc- tion (between arrows at right) is less than twice the width of the adjacent plasma membrane (between arrows at left). | |||
| width=300px valign=top|'''Fig. 12''' Astrocytic end feet (A) lying between a myelinated axon and the basement lamina of the vascular endothelium. A cleft between the astrocytic end feet extends from the basement lamina to a perivascular myelinated axon and appears open except near the blood vessel where it is invaded by some basement lamina material. | |||
| width= | |- | ||
| Normal mouse; uranyl acetate block stain. Fig. 11, X 170,000. Fig. 11 inset, X 420,000. | |||
| Normal mouse; uranyl acetate block stain. X 150,000. | |||
|} | |||
:'''Links:''' [[Neural - Vascular Development]] | | :'''Links:''' [[Neural_-_Vascular_Development#Blood-Brain_Barrier|Blood-Brain Barrier]] | [[Neural - Vascular Development]] | [[:File:Blood-brain barrier cartoon.jpg|Blood-brain barrier cartoon]] | ||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
{{#pmid:6033532}} | |||
{{JCB}} | {{JCB}} | ||
Latest revision as of 19:52, 27 March 2018
Mouse Blood-brain barrier (EM)
| Fig. 11 Regions of overlap between neighboring endothelial cells, illustrating range of variation in structure of the intercellular cleft. In Fig. 11, the cleft is obliterated by a tight junction (arrow) extending throughout most of its length. The region of the intercellular cleft indicated by the arrow in Fig. 11 is shown in inset at higher magnification to illustrate that the total width of the tight junc- tion (between arrows at right) is less than twice the width of the adjacent plasma membrane (between arrows at left). | Fig. 12 Astrocytic end feet (A) lying between a myelinated axon and the basement lamina of the vascular endothelium. A cleft between the astrocytic end feet extends from the basement lamina to a perivascular myelinated axon and appears open except near the blood vessel where it is invaded by some basement lamina material. |
| Normal mouse; uranyl acetate block stain. Fig. 11, X 170,000. Fig. 11 inset, X 420,000. | Normal mouse; uranyl acetate block stain. X 150,000. |
Reference
Reese TS & Karnovsky MJ. (1967). Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J. Cell Biol. , 34, 207-17. PMID: 6033532
Copyright
Rockefeller University Press - Copyright Policy This article is distributed under the terms of an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike–No Mirror Sites license for the first six months after the publication date (see http://www.jcb.org/misc/terms.shtml). After six months it is available under a Creative Commons License (Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 4.0 Unported license, as described at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/ ). (More? Help:Copyright Tutorial)
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 27) Embryology Blood-brain barrier EM01.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Blood-brain_barrier_EM01.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 11:31, 29 May 2017 | 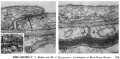 | 1,656 × 810 (250 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | |
| 11:30, 29 May 2017 | 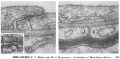 | 1,656 × 810 (223 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | FIGURE 11 Regions of overlap between neighboring endothelial cells, illustrating range of variation in structure of the intercellular cleft. In Fig. 11, the cleft is obliterated by a tight junction (arrow) extending throughout most of its length. The... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: