Cell Division - Mitosis: Difference between revisions
(Created page with '== Introduction == ==Some Recent Findings== ==References== <references/> ===Reviews=== ===Articles=== ===Search Pubmed=== '''Search Pubmed:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/s…') |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Features 2 mechanical processes | |||
* Mitosis segregation of chromosomes and formation of 2 nuclei | |||
* Cytokinesis splitting of the cell as a whole into 2 daughter cells | |||
* [http://www.nature.com/celldivision/milestones/index.html Cell Division Milestones] | |||
* Recent Nobel Prizes- 2001 Cell Cycle, 2002 Cell Death | |||
==Cell Changes== | |||
* Nucleus | |||
** Chromosome condensation | |||
** Nuclear envelope breakdown | |||
* Cytoplasm | |||
** Cytoskeleton reorganization | |||
** Spindle formation (MT) Contractile ring (MF) | |||
** Organelle redistribution | |||
* Mitosis Energy | |||
** Cell division uses up a lot of energy, so cells ensure they have enough resources to complete the job before committing to it. | |||
==Mitosis Phases== | |||
* Based on light microscopy of living cells light and electron microscopy of fixed and stained cells | |||
* 5 Phases - prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase | |||
** Cytokinesis 6th stage overlaps the end of mitosis | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mcb&part=A5499&rendertype=figure&id=A5500 MBC The stages of mitosis and cytokinesis in an animal cell] | |||
Interphase | |||
* not a mitotic phase (discussed in cell cycle) | |||
* Chromosomes dispersed in nucleus | |||
* Gene expression | |||
* Cytoskeleton and cell organelles - Distributed and functioning | |||
* Mitochondria undergo independent proliferation/division | |||
==Chromosome Changes== | |||
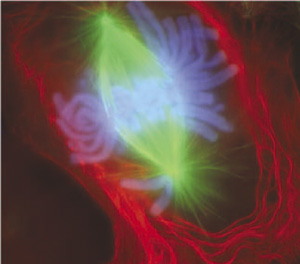
[[Image:Mitosis fl.jpg]] | |||
===Prophase === | |||
[[File:Mammalian cell - prophase.jpg|thumb|Mammalian cell - prophase<ref>Russan NM. Let's Build a Spindle. ASCB Image & Video Library. 2008;CYT-190. Available at: http://cellimages.ascb.org/u?/p4041coll12,521</ref>]] | |||
* Chromosome DNA has been earlier duplicated (S Phase) | |||
* Chromosomes begin condensing | |||
* Chromosome pairs (chromatids) held together at centromere | |||
* Microtubules disassemble | |||
* Mitotic spindle begins to form | |||
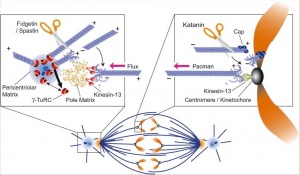
====Spindle Apparatus==== | |||
* 3 sets of microtubules - (+) ends point away from centrosome at each pole. | |||
# astral microtubules - anchor the pole end in position | |||
# kinetochore microtubules - connected to chromosomes | |||
# polar microtubules - form the structure of the spindle apparatus | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mboc4&part=A3349&rendertype=figure&id=A3350 Spindle Apparatus EM] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mcb&part=A5499&rendertype=figure&id=A5505 Spindle Apparatus] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mcb&part=A5499&rendertype=figure&id=A5514 MBC Movie- Microtubule dynamics during mitosis] | |||
At end of prophase nuclear envelope breaks down | |||
===Prometaphase=== | |||
* Microtubules now enter nuclear region | |||
* Nuclear envelope forms vesicles around mitotic spindle | |||
* Kinetochores form on centromere attach to some MTs of spindle | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mcb&part=A5499&rendertype=figure&id=A5520 Dynamic instability and the capture of chromosomes] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mcb&part=A5499&rendertype=figure&id=A5509 Centromeric attachment of microtubules] | |||
At end of prometaphase chromosomes move to metaphase plate | |||
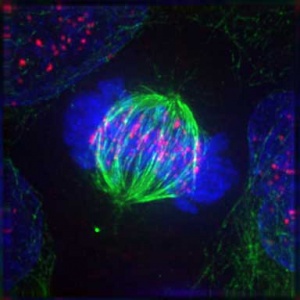
===Metaphase=== | |||
[[File:Mitosis_-_Metaphase.jpg|thumb|Mitosis - Metaphase]] | |||
* Kinetochore MTs align chromosomes in one midpoint plane | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mcb&part=A5499&rendertype=figure&id=A5522 Proposed alternative mechanisms for chromosome congression] | |||
Metaphase ends when sister kinetochores separate | |||
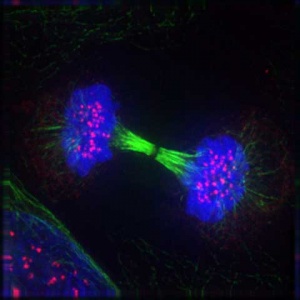
===Anaphase=== | |||
[[Image:Chromosome_motility_anaphase.jpg|thumb|Chromosome motility anaphase]] | |||
* Separation of sister Kinetochores | |||
* shortening of Kinetochore microtubules pulls chromosome to spindle pole | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mcb&part=A5499&rendertype=figure&id=A5526 Experiment - during anaphase A chromosomes move poleward along stationary kinetochore microtubules, which coordinately disassemble from their kinetochore ends] | |||
Anaphase ends as nuclear envelope (membrane) begins to reform | |||
===Telophase=== | |||
[[File:Mitosis - Telophase.jpg|thumb|Mitosis - Telophase]] | |||
* Chromosomes arrive at spindle poles | |||
* Kinetochore MTs lost | |||
* Condensed chromosomes begin expanding | |||
** Continues through cytokinesis | |||
'''Links:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mcb&part=A5499&rendertype=figure&id=A5514 Figure 19-41 Microtubule dynamics during mitosis] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mcb&part=A5499&rendertype=figure&id=A5500 Figure 19-34. The stages of mitosis and cytokinesis in an animal cell] | [http://www.cell.com/trends/cell-biology/fulltext/S0962-8924(09)00158-5 Cytokinetic abscission: cellular dynamics at the midbody] | |||
==Cytokinesis== | |||
* Division of cytoplasmic contents | |||
* Contractile ring forms at midpoint under membrane | |||
* Microfilament ring - contracts forming cleavage furrow | |||
** myosin II is the motor | |||
* Eventually fully divides cytoplasm | |||
'''Links:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=cooper&part=A1790&rendertype=figure&id=A1802 Cytokinesis] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mboc4&part=A3381&rendertype=figure&id=A3396 Cytokinesis in Plants] | |||
== Cell Organelles == | |||
===Mitochondria=== | |||
* Divide independently of cell mitosis | |||
* distributed into daughter cells | |||
===Peroxisomes=== | |||
* localise at spindle poles | |||
===Endoplasmic Reticulum=== | |||
===Golgi=== | |||
[[Image:Post-mitotic Golgi stack formation.png|thumb|Post-mitotic Golgi stack formation]] | |||
* 2 processes - disassembly and reassembly | |||
* Golgi stack undergoes a continuous fragmentation process | |||
* fragments are distributed into daughter cells | |||
* are reassembled into new Golgi stacks | |||
'''Disassembly''' | |||
* Unstacking - mediated by two mitotic kinases (cdc2 and plk) | |||
* Vesiculation - mediated by COPI budding machinery ARF1 and the coatomer complex | |||
'''Reassembly''' | |||
* Fusion - formation of single cisternae by membrane fusion | |||
* Restacking - requires dephosphorylation of Golgi stacking proteins by protein phosphatase PP2A | |||
Links: Tang D, Mar K, Warren G, Wang Y. Molecular mechanism of mitotic Golgi disassembly and reassembly revealed by a defined reconstitution assay. J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 7;283(10):6085-94. Epub 2007 Dec 21. PMID: 18156178 | |||
==Some Recent Findings== | ==Some Recent Findings== | ||
Revision as of 17:06, 14 July 2010
Introduction
Features 2 mechanical processes
- Mitosis segregation of chromosomes and formation of 2 nuclei
- Cytokinesis splitting of the cell as a whole into 2 daughter cells
- Cell Division Milestones
- Recent Nobel Prizes- 2001 Cell Cycle, 2002 Cell Death
Cell Changes
- Nucleus
- Chromosome condensation
- Nuclear envelope breakdown
- Cytoplasm
- Cytoskeleton reorganization
- Spindle formation (MT) Contractile ring (MF)
- Organelle redistribution
- Mitosis Energy
- Cell division uses up a lot of energy, so cells ensure they have enough resources to complete the job before committing to it.
Mitosis Phases
- Based on light microscopy of living cells light and electron microscopy of fixed and stained cells
- 5 Phases - prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
- Cytokinesis 6th stage overlaps the end of mitosis
MBC The stages of mitosis and cytokinesis in an animal cell
Interphase
- not a mitotic phase (discussed in cell cycle)
- Chromosomes dispersed in nucleus
- Gene expression
- Cytoskeleton and cell organelles - Distributed and functioning
- Mitochondria undergo independent proliferation/division
Chromosome Changes
Prophase
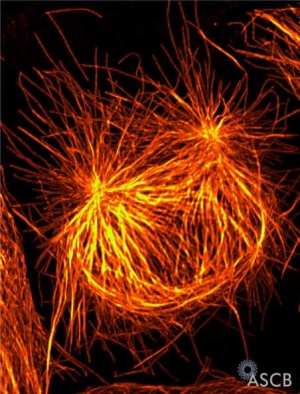
- Chromosome DNA has been earlier duplicated (S Phase)
- Chromosomes begin condensing
- Chromosome pairs (chromatids) held together at centromere
- Microtubules disassemble
- Mitotic spindle begins to form
Spindle Apparatus
- 3 sets of microtubules - (+) ends point away from centrosome at each pole.
- astral microtubules - anchor the pole end in position
- kinetochore microtubules - connected to chromosomes
- polar microtubules - form the structure of the spindle apparatus
Spindle Apparatus EM | Spindle Apparatus | MBC Movie- Microtubule dynamics during mitosis
At end of prophase nuclear envelope breaks down
Prometaphase
- Microtubules now enter nuclear region
- Nuclear envelope forms vesicles around mitotic spindle
- Kinetochores form on centromere attach to some MTs of spindle
Dynamic instability and the capture of chromosomes
Centromeric attachment of microtubules
At end of prometaphase chromosomes move to metaphase plate
Metaphase
- Kinetochore MTs align chromosomes in one midpoint plane
Proposed alternative mechanisms for chromosome congression
Metaphase ends when sister kinetochores separate
Anaphase
- Separation of sister Kinetochores
- shortening of Kinetochore microtubules pulls chromosome to spindle pole
Anaphase ends as nuclear envelope (membrane) begins to reform
Telophase
- Chromosomes arrive at spindle poles
- Kinetochore MTs lost
- Condensed chromosomes begin expanding
- Continues through cytokinesis
Links: Figure 19-41 Microtubule dynamics during mitosis | Figure 19-34. The stages of mitosis and cytokinesis in an animal cell | Cytokinetic abscission: cellular dynamics at the midbody
Cytokinesis
- Division of cytoplasmic contents
- Contractile ring forms at midpoint under membrane
- Microfilament ring - contracts forming cleavage furrow
- myosin II is the motor
- Eventually fully divides cytoplasm
Links: Cytokinesis | Cytokinesis in Plants
Cell Organelles
Mitochondria
- Divide independently of cell mitosis
- distributed into daughter cells
Peroxisomes
- localise at spindle poles
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi
- 2 processes - disassembly and reassembly
- Golgi stack undergoes a continuous fragmentation process
- fragments are distributed into daughter cells
- are reassembled into new Golgi stacks
Disassembly
- Unstacking - mediated by two mitotic kinases (cdc2 and plk)
- Vesiculation - mediated by COPI budding machinery ARF1 and the coatomer complex
Reassembly
- Fusion - formation of single cisternae by membrane fusion
- Restacking - requires dephosphorylation of Golgi stacking proteins by protein phosphatase PP2A
Links: Tang D, Mar K, Warren G, Wang Y. Molecular mechanism of mitotic Golgi disassembly and reassembly revealed by a defined reconstitution assay. J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 7;283(10):6085-94. Epub 2007 Dec 21. PMID: 18156178
Some Recent Findings
References
- ↑ Russan NM. Let's Build a Spindle. ASCB Image & Video Library. 2008;CYT-190. Available at: http://cellimages.ascb.org/u?/p4041coll12,521
Reviews
Articles
Search Pubmed
Search Pubmed: mitosis
Additional Images
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 26) Embryology Cell Division - Mitosis. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Cell_Division_-_Mitosis
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G