User:Z3387190
Lab 4 Online Assessment
- The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
- Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching. (Add to project page and your individual assessment page)
--Z3387190 12:55, 28 July 2011 (EST)
Lab1 Assessment:
1. Identify the origin of In Vitro Fertilization and the 2010 nobel prize winner associated with this technique.
The first in vitro fertilization studies were related to non- mammalian aquatic species. These studies on animals with external fertilization played an important role in the comprehension of the fertilization process. Further studies engaged in mammals. In 1959 experiments with rabbits succeeded which led to the first viable mammal offspring via IVF. The in vitro fertilization therapy in humans was developed by Robert G. Edwards and the gynaecologist Patrick C. Steptoe. In 1978 the first human baby was born by means of IVF. In 2010 the English scientist Robert G. Edwards received the “Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine” for the development of human IVF. [1]
2. Identify a recent paper on fertilisation and describe its key findings.
The paper [2] shows that the chance of becoming pregnant for infertile women undergoing a fertility treatment is not correlated with emotional stress. The meta- analysis included fourteen studies with 3583 infertile women receiving a single cycle of fertility treatment. The effect of pretreatment anxiety or depression was measured with the standardised mean difference between women with a successful conception and those without.
3. Identify 2 congenital anomalies.
- Transposition of the great vessels
- Anencephaly
--Z3387190 19:37, 31 July 2011 (EST)
--Mark Hill 10:02, 3 August 2011 (EST) These answers are good.
Lab2 Assessment:
1. Identify the ZP protein that spermatozoa binds and how is this changed (altered) after fertilisation.
Responsible for the binding of the sperm is a zona pellucida glycoprotein, called ZP3. After the fusion of the sperm and oozyte mambranes contents of the cortical granules remove a carbohydrate from ZP3, resulting in the lack of the ZP3 to bind to sperm membrane. This is part of the block to avoid polyspermy.[3]
2. Identify a review and a research article related to your group topic. (Paste on both group discussion page with signature and on your own page)
--Theodora Retzl 23:17, 10 August 2011 (EST)
Lab3 Assessment:
1. What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development?
Iodine deficiency can lead to disorders in neuro development varying from mental retardation to cretinism.[4]
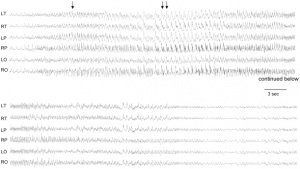
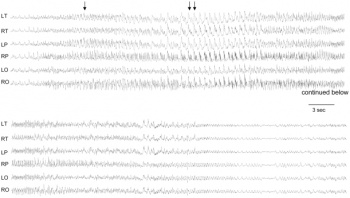
2. Upload a picture relating to you group project. Add to both the Group discussion and your online assessment page. Image must be renamed appropriately, citation on "Summary" window with link to original paper and copyright information. As outlined in the Practical class tutorial.
File:EEG in Angelman syndrome mice with a maternal deletion from Ube3a to Gabrb3
--Theodora Retzl 23:39, 17 August 2011 (EST)
Lab4 Assessment:
1. The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
The allantois is continuous with the urinary bladder. The bladder enlarges and the allantois forms the urachus. This is a stalk, which runs from the urinary bladder to the umbilical region.
2. Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
In the fetal circulation system three shunts are essential for the blood to bypass the liver and lungs, ductus venosus, oval foramen, and ductus arteriosus. The umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood and runs from the placenta to the right atrium. Approximately one half of the blood bypasses the liver through the ductus venosus. The oval foramen is an opening in the right atrium, allowing blood to run into the left atrium. The ductus arteriosus allows most of the blood from the right ventricle to pass the lungs and to run into the aorta.
3. Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching. (Add to project page and your individual assessment page)
Signs and Symptoms in Angelman Syndrome
--Theodora Retzl 19:40, 22 August 2011 (EST)
Lab5 Assessment:
1. Which side (L/R) is most common for diaphragmatic hernia and why?
Diaphragmatic hernia accures more frequent on the left side with about 85% of all cases. The reason is probably that the left pericardioperitoneal canal closes later in development, and it is also greater in size than the right one.
Lab6 Assessment:
1.What week of development do the palatal shelves fuse?
In the human embryo, the two palatal shelves fuse in week 9.
2.What animal model helped elucidate the neural crest origin and migration of cells?
Cell transplantation from a quail into a chicken helped to exemplify the origin and migration of neuro crest cells.
3.What abnormality results from neural crest not migrating into the cardiac outflow tract?
CHARGE Syndrome and DiGeorge Syndrome
Lab7 Assessment:
1. Are satellite cells (a) necessary for muscle hypertrophy and (b) generally involved in hypertrophy?
Satellite cells are important for the onset of new muscle fibres, and involved in hypertrophy, but they are not essential for it.
2. Why does chronic low frequency stimulation cause a fast to slow fibre type shift?
CLFS causes the fast muscle to vary first the metabolic and then the contractile properties, and causes them to act like a slow fibre. Satellite cells play an important role in fibre regeneration. The fibre type transition cannot take place, if they are absent in a muscle.
--Mark Hill 10:42, 16 September 2011 (EST)
I would like each student to now also look at the following online page before the next Lab and write a comment based upon the group project assessment criteria.
http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php?title=Trisomy_21 Paste your comment on the Trisomy 21 discussion page and also on your own student page.
3. Peer review “Trisomy 21”
- The introduction appears not quite complete.
- The “some recent findings” section would fit better at the end of the page.
- Adding some historic background to the page would be interesting.
- The key points relating to the topic were well described and illustrated.
- The choice of content shows a good understanding of the topic area.
- Some images (e.g Human ideogram- chromosome or Chromosome trisomy) lack a reference and or copyright notice.
- No student drawing included.
- The term descriptions tear the page apart, they would fit better in the glossary.
- Relates the topic and content of the Wiki entry to learning aims of embryology.
- Use of a broad variety of reliable resources.
References:
- ↑ [Höög 2011] C. Höög. Human in vitro fertilization. "The 2010 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine - Advanced Information". Nobelprize.org. http://static.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/2010/adv.pdf (31/07/2011)
- ↑ [Boivin et al. 2011] J. Boivin, E. Griffiths, C. A. Venetis. Emotional distress in infertile women and failure of assisted reproductive technologies: meta-analysis of prospective psychosocial studies. BMJ 2011; 342:d223; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21345903
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26843/
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1964355
Lab Attendance
--z3387190 13:06, 4 August 2011 (EST)
--User:Z3387190 13:05, 4 August 2011 (EST)
--Mark Hill 13:32, 18 August 2011 (EST) Attended Lab 3.
--z3387190 11:11, 18 August 2011 (EST)
--z3387190 12:50, 25 August 2011 (EST)
--z3387190 12:37, 1 September 2011 (EST)
--z3387190 12:15, 15 September 2011 (EST)
--Theodora Retzl 12:56, 22 September 2011 (EST)