User:Z3329495: Difference between revisions
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
| style="white-space: nowrap" | Electrocardiogram (ECG) | | style="white-space: nowrap" | Electrocardiogram (ECG) | ||
| Provides graphic presentation of the electrical activity or beat pattern of the heart | | Provides graphic presentation of the electrical activity or beat pattern of the heart | ||
| If '''T wave inversion''' present, it may be an indication of myocardial infarction or hypertrophy which is a hallmark of FRDA. | | If '''T wave inversion''' is present, it may be an indication of myocardial infarction or hypertrophy which is a hallmark of FRDA <refname="PMID:3593615"><pubmed>3593615</pubmed></ref>. | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Blood tests | | Blood tests | ||
| Checks for elevated glucose levels and vitamin E levels | | Checks for elevated glucose levels (in the event of diabetes developing) and vitamin E levels | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
Revision as of 22:06, 8 September 2011
Lab 4 Online Assessment
- The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
- Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching. (Add to project page and your individual assessment page)
Group Project notes
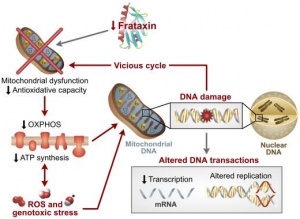
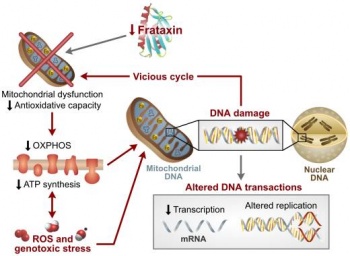
Cardiomyopathy is caused by build up of iron overload in mitochondria producing excessive amounts of free radicals and anti-oxidants which damages cells. As Frataxin is most expressed in the heart, skeletal muscles, (as well as liver and pancreas)[1], it impacts most significantly on musculature and cardiac muscles.
Prior to 1996, FA could not be genetically confirmed and many older individuals with FA were not diagnosed with FA as their presenting age went over the norm of FA onset. Now with genetic testing available, the mean age of onset for symptoms of FA has increased[2].
| Availability of genetic testing | Diagnostic symptoms |
| Prior to genetic testing availability | Only physical complaints, age of onset and typical FA progression could identify it as FA. |
| After genetic testing is available | Physical complaints are used in conjunction with genetic testing to confirm FA. Due to genetic testing, [2]it has been discovered that FA can occur in individuals older than the typical diagnostic age (first two decades of life[3]). |
| Diagnostic tool | What it does | How it diagnoses FRDA | Image if available |
| Electromyogram (MG) | Measures the electrical activity of muscle cells | ||
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Provides graphic presentation of the electrical activity or beat pattern of the heart | If T wave inversion is present, it may be an indication of myocardial infarction or hypertrophy which is a hallmark of FRDA <refname="PMID:3593615"><pubmed>3593615</pubmed></ref>. | |
| Echocardiogram | Records the position and motion of the heart muscle | Identifies abnormalities in heart muscle such as hypertrophy of ventricles(useful for determining cardiac involvement)<refname="PMID:2940284"><pubmed>2940284</pubmed></ref>. | |
| Blood tests | Checks for elevated glucose levels (in the event of diabetes developing) and vitamin E levels | ||
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | Provide brain and spinal cord images that are useful for ruling out other neurological conditions | ||
| Computed tomography scans (CT scan) | Similar to MRI | ||
| Nerve conduction studies | Measures the speed with which nerves transmit impulses | Determines how far/if neurodegeneration has occurred. |
Lab 1
Questions
- Identify the origin of In Vitro Fertilization and the 2010 nobel prize winner associated with this technique.
- Identify a recent paper on fertilisation and describe its key findings.
- Identify 2 congenital anomalies.
Answers
- Robert G. Edwards won the 2010 Nobel Prize for his IVF work which led to the birth of the first IVF baby Louise Brown, born at the Royal Oldham Hospital Manchester, England.
- A recent paper on predicting how sucessful IVF treatment would be for specific individuals has come out with its finding that predetermined factors (such as maternal age, how long infertility has persisted for and if the maternal oocyte was used) can indicate the sucess of fertility treatment as opposed to a simple probability for a sucessful treatment. PLoS Medicine: Predicting Live Birth Preterm Delivery, and Low Birth Weight in Infants Born from In Vitro Fertilisation: A Prospective Study of 144,018 Treatment Cycles
- Downs Syndrome and hemophilia
--Z3329495 14:14, 28 July 2011 (EST)
--Z3329495 12:55, 28 July 2011 (EST)
--Mark Hill 10:07, 3 August 2011 (EST)These answers are fine.
Lab 2
--Z3329495 13:00, 4 August 2011 (EST)
Questions
- Identify the ZP protein that spermatozoa binds and how is this changed (altered) after fertilisation.
- Identify a review and a research article related to your group topic. (Paste on both group discussion page with signature and on your own page)
Answers
- the ZP protein that spermatozoa binds to is ZP3. After fertilisation, enzymes in the cortical reaction alters ZP3 so that it no longer binds to sperm.
- Angelman's Syndrome:
Review article: http://jmg.bmj.com/content/40/2/87.short Research article: http://jmg.bmj.com/content/38/12/834.abstract --Z3329495 12:07, 9 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 3
--Amanda Tan 11:07, 11 August 2011 (EST)
Differentially expressed RefSeq genes in human trisomy 21
Questions
- What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development?
- Upload a picture relating to you group project.
Answers
- Folate has been found to reduce the incidence of neural tube defects and many countries have fotified food staples (flour etc) with folic acid. A recent study found that more cases of neural tube defects can be avoided if more countries implemented policies to fortify foods with folic acid. Update on prevention of folic acid-preventable spina bifida and anencephaly.
Iodine also prevents Cretin from developing and has been recommended that pregnant women consume supplemented iodine. http://www.thyroid.org/professionals/publications/statements/documents/ATAIodineRec.pdf
A model of Pathogenesis of Friedreich Ataxia
--z3329495 20:58, 13 August 2011 (EST)
--Mark Hill 12:22, 16 August 2011 (EST) Not bad and the image contains all the correct citation information. The file would more correctly be named "A Model of....."
Lab 4
--Z3329495 11:07, 18 August 2011 (EST)
Questions
- The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
- Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching. (Add to project page and your individual assessment page)
Answers
- It is an invagination of the developing hindgut and is connected to the yolk sac via the connecting stalk.
- Foramen Ovale (between right and left atrium), Ductus arteriosus (connects pulmonary artery to aortic arch) and Ductus venosus (allow portal and umbilical veins to connect to inferior vena cava - lets oxygenated blood bypass liver)
- pahology of cardiomyopathy and musculature sections of Friedreich's Ataxia and parts of pathogenesis.
Lab 5
--z3329495 12:27, 25 August 2011 (EST)
Questions
- Which side (L/R) is most common for diaphragmatic hernia and why?
Answers
- left side is more common because during embryonic development the left pericardioperitoneal canal is much larger than the right side and is takes longer than the right side to close up.
Lab 6
--z3329495 11:08, 1 September 2011 (EST)
Questions
- What week of development do the palatal shelves fuse?
- What animal model helped elucidate the neural crest origin and migration of cells?
- What abnormality results from neural crest not migrating into the cardiac outflow tract?
Answers
- week 10 is when the palatal shelves fuse.
- Chicken-quail model - a genetic mix of chicken and quail allowed researchers to identify origin and migration of neural crest cells before fluorescent marking of genes were available.
- Shortening or truncation of cardiac outflow tract.