User:Z3288827
Lab 4 Online Assessment
- The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
- Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching. (Add to project page and your individual assessment page)
--Z3288827 12:55, 28 July 2011 (EST)
Hello, I'm a student currently enrolled in the embryology course at UNSW. I'm really enjoying the course so far and think it's really great that we get to study the origins of where we came from, and plus the developing embryo looks cute! It's amazing to think that the entire human body forms so seamlessly from this series of events.
Also a member of the group [1] researching DiGeorge Syndrome:
Lab Attendance
Sorry Mark I forgot to do it in the firs half of semester! --Leonard Tiong 12:12, 15 September 2011 (EST) --Leonard Tiong 11:11, 22 September 2011 (EST)
Week 1 Online Assessment
1. Identify the origin of In Vitro Fertilisation and the 2010 nobel prize winner associated with this technique.
In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) was being explored in the 1950's by a scientist named Robert G. Edwards, who decided to investigate the possibility of fertilisation occurring outside of the body. Robert G. Edwards developed the theoretical technique and the media which would allow fertilisation to occur, and with the oocytes obtained by gynaecologist Patrick Steptoe, managed to develop the technique of IVF. Success was granted in 1969, when he first observed successful fertilisation within the test tube. Further success followed in 1977, with the birth of a healthy baby, Louise Brown, through the use of IVF.
2. Identify a recent paper on fertilisation and describe its key findings.
The article: "Obstetric outcome after in vitro fertilization with single or double embryo transfer", written by Sazonova A. et al, published in the journal of human reproduction in December 1, 2010. Generally, children that are born using the technique of in vitro fertilization (IVF) have a poorer outcome when compared to children born without assisted treatment. However, with a new technique, known as single embryo transfer (SET) in which a single blastocyst is implanted into the uterine wall, this poor outcome may be resolved. This paper observed the study of several subtypes of SET and double embryo transfer (DET) used amongst the general Swedish population. The most common complications were premature births and low birth-weights in the babies. The results indicated that any method of IVF, irregardless of whether SET or its variants, or DET were used, still had a higher rate of premature birthdays (<28 weeks) when compared with natural pregnancy.
3. Identify 2 congenital anomalies.
Congenital anomalies are defined as variations from the normal physical structure in a baby that are present at birth. They have a varying range of severity and have the potential to be lethal. A couple of examples of congenital anomalies include anencephaly, where the rostral end of the neural tube fails to develop in utero, resulting in the failure of the brain to develop. This particular condition is lethal. Another congenital anomaly is Sirenomelia, a rare and usually fatal condition in which the legs are formed together. The name of this condition indicates the physical appearance of the child, in which the legs are fused together, similar to that of a mermaids tail. There are usually severe complications associated with this condition, as the lower gastrointestinal system, bladder, and reproductive organs are also fused in a single tube. However, there have been a few instances where the baby is able to survive for a few years after birth.
--Mark Hill 09:38, 3 August 2011 (EST) All 3 questions need to be completed before Lab 2.
--z3288827 22:51, 9 August 2011 (EST)
Week 2 Online Assessment
1. Identify the ZP protein that spermatozoa binds to and how is this changed (altered) after fertilisation.
The ZP protein that the spermatozoa binds to is ZP3. This results in the release of an enzyme known as acrosin, which allows the sperm to penetrate through the oocyte cell membrane. Once the sperm has penetrated the cell membrane, this triggers two key events within the oocyte. Firstly, cortical granules, which are filled with enzymes and located just beneath the cell membrane, release their contents into the space located between the oocyte cell membrane and the zona pellucida. Secondly, a calcium wave spreads along the surface of the oocyte from the point of fertilisation. This changes the nature of the zona pellucida to other sperm, preventing multiple sperm from reaching the oocyte (polyspermy).
2. Review/Journal article - Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Hey guys, just found a review article that I thought was rather interesting, it's an animal model for Duchenne's muscular dystrophy[2]. I also found a primary journal article that discusses drug delivery for the condition [3]. I will print these articles for myself tonight and give them a quick read tomorrow and then paste a quick summary of the articles here just for you guys to consider :)
Week 3 online assessment
--Leonard Tiong 00:08, 17 August 2011 (EST)
1. The maternal dietary supplement required for late neural development is folate. A lack of folate can result in failure of closure of the neural tube, leading to either spinal bifida (failure of the caudal end to close) or anencephaly (failure of the rostral end to close).
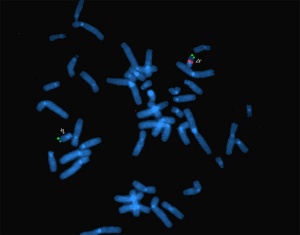
2.
FISH carried out to detect DiGeorge syndrome. FISH is abbreviated as fluorescent in-situ hybridisation and is carried out to detect abnormalities whilst babies are still developing in the womb.
Week 4 Online Assessment
1. The allantois is a structure located in the developing umbilical cord, and is connected to the developing bladder.
2. The three vascular shunts are present mainly because the lungs of the embryo are useless until parturition. They are generally located around the liver and heart to bypass the lungs, and are named as follows:
- The Ductus Arteriosus, which is located between the aorta and pulmonary artery;
- The Ductus Venosus, which is located between the portal vein and inferior vena cava; and
- The Foramen Ovale which is a direct shunt between the right and left atria of the heart.
3. The sections that I am covering for my group project include epidemiology and the pathophysiology of DiGeorge syndrome.
Week 5 Online Assessment
1. Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernias are most common on the left hand side of the body. This condition is caused by the failure of the pleuroperitoneal foramen to fuse, resulting in an opening through which the viscera of the gut can directly articulate with the left lung, resulting in compression.
Week 6 Online Assessment
1. The palatal shelves fuse in week 9 of human development, and are associated with the fusion of the secondary palate. This fusion event occurs between both secondary palates and the primary palate which is formed around week 6 (Carnegie stage 17/18)
2. The quail-chick chimera model helped to identify the neural crest origin and migration of neural crest cells.
3. The abnormality that results from the failure of neural crest cells to migrate to the cardiac outflow tract is known as Tetralogy of Fallot and has numerous presentations including Persistent Truncus Arteriosus in which the pulmonary trunk and aorta fail to divide properly.
Week 7 Online Assessment
1. Satellite cells are not normally necessary for muscle hypertrophy, as it has been shown that this can occur even without satellite cells present. However, they have been associated with muscle hypertrophy as we see their hypertrophy during normal hypertrophy.
2. Fast muscle fibres generally use anaerobic metabolism pathways to generate the energy necessary for a fast, explosive contraction; slow muscle fibres utilize oxidative pathways to generate energy for slower and more sustained contractions. Muscle fibre types are able to transition between fast and slow muscle, but through intermediate stages. Due to the physiological pathways in the muscle fibres, chronic low frequency stimulation will stimulate the slow muscle fibres and cause a shift from the muscle fibre types from fast to a slow muscle type.
Trisomy 21 comments
• The key points relating to the topic that your group allocated are clearly described.
This is generally well done, except that the introduction relies a lot on the external links that are provided. Perhaps there should be more elaboration of the history of Downs syndrome, and specific sections on etiology and epidemiology; these sections require more written on their specific section given the importance of this disease.
• The choice of content, headings and sub-headings, diagrams, tables, graphs show a good understanding of the topic area.
It is well covered, and there is a large number of diagrams tables and graphs which make the information easily accessible. However, at times it seems that the content relies on dot points and diagrams; there are no sections of text that have bodies of text and this makes the information feel artificial; there is not much flow in the information and seems to skip from point to point. Otherwise, the selected images are appropriate; perhaps graphs for each specific section (such as a graph for epidemiology) might be appropriate as well.
• Content is correctly cited and referenced.
Unfortunately the first diagram present on the page isn’t correctly cited or referenced, and there are a few sections which lack references altogether, such as the Heart Defects section. The picture of John Langdon Down also lacks a proper reference.
• The wiki has an element of teaching at a peer level using the student's own innovative diagrams, tables or figures and/or using interesting examples or explanations.
The information is highly information and quite interesting, but I feel lacks a written paragraph to link all of the information together. There is a severe lack of information on treatment and future research directions, as well as the physiological mechanisms that underlie the disease process.
• Evidence of significant research relating to basic and applied sciences that goes beyond the formal teaching activities.
There is extensive research past the formal teaching activities as can be seen by the content provided by the external links; however, it still seems like these links are relied on as opposed to having the critical information presented within the project itself.
• Relates the topic and content of the Wiki entry to learning aims of embryology.
It would be nice to see that the sections are a little better explained, such as the basic mechanisms of growth and development been outlined, followed by a discussion of how the disease process of Downs syndrome alters and changes these basic growth processes. Whilst this information is provided as external links it would be nice to see it elaborated on the actual page, keeping the relevant information specific to the project.
Week 8 Online Assessment
Peer Assessment
Group 1
Group 1 Assessment
- Key Points: Clinical manifestations could probably have a better explanation, as opposed to a list? Perhaps try discussing the presentation of the disease, etc. Is there any history of the disease? Generally sections are of good length and the information is relevant.
- Content is difficult to assess because there are sections that are lists of terms. Many items in the project rely heavily on this point-form, especially the clinical manifestations. Perhaps try using more images to support the clinical presentation/complications of the disease, as well as the prenatal diagnosis. The diagrams are used well when they are used.
- Referencing is generally fine, although the first image doesn't seem to have a correct copyright license. As for the double references in the reference section, we have the same problem too!
- The student-drawn diagram is simple but effective, and the images chosen are adequate to the project. However, the entire project seems a little brief in each section; try to ensure that you've written everything that you can!
- All of the information is well-cited with a large number of sources and clearly shows that further research has been done. However, to make the project flow a bit better maybe have some more images and phrases to allow an explanation as opposed to just dot points on the work.
--Leonard Tiong 09:18, 28 September 2011 (EST)
References
[1] Nakamura A., Takeda S.; Mammalian Models of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Pathological Characteristics and Therapeutic Applications, J. Biomedicine and Biotechnology Vol. 2011, Article ID 184393
[2] Yukihara et al; Effective Drug Delivery System for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Using Hybrid Liposomes Including Gentamicin along with Reduced Toxicity, J. Biol. Pharm. Bull, Volume 34, No. 5 pp. 712-716
[3] Mol Cytogenet. 2011; 4: 6. Published online 2011 February 23. doi: 10.1186/1755-8166-4-6, Link: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3058102/figure/F2/