Template:X Inactivation Vignette 2: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
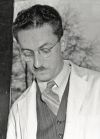
[Murray L. Barr (1908-1995) was a Canadian researcher who, along with E. Bertram, first identified the inactivated x chromosome ({{Barr body}}) as an extension from the nucleus in female cells. | [Murray L. Barr (1908-1995) was a Canadian researcher who, along with E. Bertram, first identified the inactivated x chromosome ({{Barr body}}) as an extension from the nucleus in female cells. | ||
"An interesting and useful variant is the study of blood films. In females only, there is an appendage with special characteristics and probably containing the sex chromatin, attached to a lobe of the nucleus in a small proportion of neutrophilic leukocytes."{{#pmid:13304780|PMID13304780}} | |||
"An interesting and useful variant is the study of blood films. In females only, there is an appendage with special characteristics and probably containing the sex chromatin, attached to a lobe of the nucleus in a small proportion of neutrophilic leukocytes." | |||
|}<noinclude>[[Category:Historic Embryology]][[Category:Female]][[Category:X Chromosome]]</noinclude> | |}<noinclude>[[Category:Historic Embryology]][[Category:Female]][[Category:X Chromosome]]</noinclude> | ||
Revision as of 15:04, 18 January 2020
|
[Murray L. Barr (1908-1995) was a Canadian researcher who, along with E. Bertram, first identified the inactivated x chromosome (Barr body) as an extension from the nucleus in female cells. "An interesting and useful variant is the study of blood films. In females only, there is an appendage with special characteristics and probably containing the sex chromatin, attached to a lobe of the nucleus in a small proportion of neutrophilic leukocytes."[1] |