Template:Main Page News: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (124 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| | {| width=800px| | ||
|-bgcolor="CEDFF2" | |-bgcolor="CEDFF2" | ||
| <span style="font-size:150%">'''News - Complete human day 14 post-implantation embryo models from naïve Embryonic Stem Cells'''</span> | |||
|-bgcolor="F5FAFF" | |-bgcolor="F5FAFF" | ||
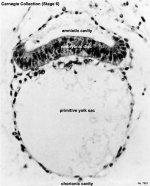
| valign=top|[[File: | | valign=top|[[File:Stage6 bf03.jpg|thumb|150px|alt=Carnegie Stage 6 Embryo|Carnegie Stage 6 Embryo]] | ||
[[Template_talk:Main_Page_News|Older News Articles]] [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News# | This recent Nature paper{{#pmid:37673118|PMID37673118}} describes the use of naïve human Embryonic Stem Cells to recapitulate the early stages of human development. | ||
|} | |||
"The ability to study human post-implantation development remains limited due to ethical and technical challenges associated with intrauterine development after implantation....only genetically unmodified human naïve human ES cells...recapitulate the organization of nearly all known lineages and compartments of post-implantation human embryos including epiblast, hypoblast, extra-embryonic mesoderm, and trophoblast surrounding the latter layers...These human complete SEMs demonstrated developmental growth dynamics that resemble key hallmarks of post-implantation stage embryogenesis up to 13-14 days post-fertilization (dpf) (Carnegie stage 6a)." | |||
:'''Links:''' {{stem cells}} | Carnegie stage {{CS6}} | |||
<references/> | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! Older News Articles | |||
|- | |||
| [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News|'''Older News Articles''']] - [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News#January|Climate Change Abnormal Development]] | [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News#December|Air Pollution]] | [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News#February|Rare Sesquizygotic Twinning]] | [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News#June|Australia's mothers and babies 2017]] | [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News#October|Spinal Muscular Atrophy Screening]] | [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News#February|Australian 2018 Pregnancy Care Guidelines]] | [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News#July|CRISPR]] | [[Template_talk:Main_Page_News#June|Ronan O’Rahilly]] | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
Latest revision as of 16:10, 8 September 2023
| News - Complete human day 14 post-implantation embryo models from naïve Embryonic Stem Cells |
|
This recent Nature paper[1] describes the use of naïve human Embryonic Stem Cells to recapitulate the early stages of human development. "The ability to study human post-implantation development remains limited due to ethical and technical challenges associated with intrauterine development after implantation....only genetically unmodified human naïve human ES cells...recapitulate the organization of nearly all known lineages and compartments of post-implantation human embryos including epiblast, hypoblast, extra-embryonic mesoderm, and trophoblast surrounding the latter layers...These human complete SEMs demonstrated developmental growth dynamics that resemble key hallmarks of post-implantation stage embryogenesis up to 13-14 days post-fertilization (dpf) (Carnegie stage 6a)."
|