Talk:2011 Lab 2 - Week 3: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(Created page with "== Conceptus Cavities Week 2 and Week 3 == {| border='0px' |- | <wikiflv width="214" height="220" autoplay="true" position="left">Chorion 001.flv|File:Chorion 001 icon.jpg</wik...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | |||
{| class="prettytable" | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Human_embryo_day_18.jpg|300px]] | |||
| Gastrulation means "gut forming" and converts the inner cell mass which then formed the bilaminar embryo (epiblast, hypoblast) into the trilaminar embryo (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm). | |||
The process involves the migration of cells from the epiblast layer through the primitive streak to form first the endoderm layer and then a second intermediate layer the mesoderm layer. Once all cells have left the epiblast layer it now becomes the ectoderm layer. | |||
These three germ cell layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) will form in a layer specific manner all the future tissues of the developing embryo. | |||
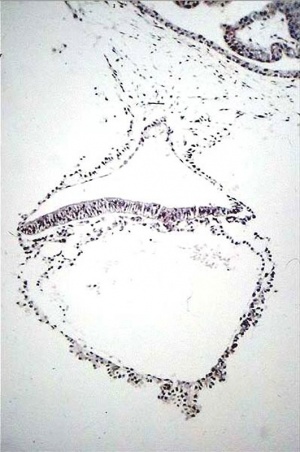
'''Approximate cross-section of an 18 day human conceptus.''' | |||
Identify the 3 layers of the trilaminar embryo: ectoderm (columnar cells), intraembryonic mesoderm (mesenchymal cells, endodermal cells (cuboidal single layer). Identify primitive groove with dense cluster of primitive streak cells below it. | |||
(Image: Nishimura etal., 1977) | |||
| |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
== Conceptus Cavities Week 2 and Week 3 == | == Conceptus Cavities Week 2 and Week 3 == | ||
| Line 22: | Line 47: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Stage 7 == | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage7-sem2.jpg|300px]] | |||
| [[File:Stage7_features.jpg]] | |||
|- | |||
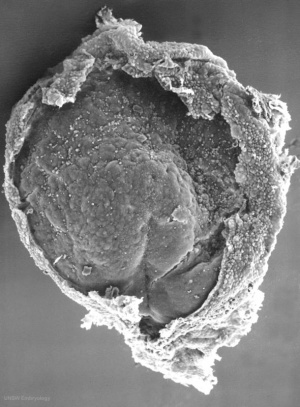
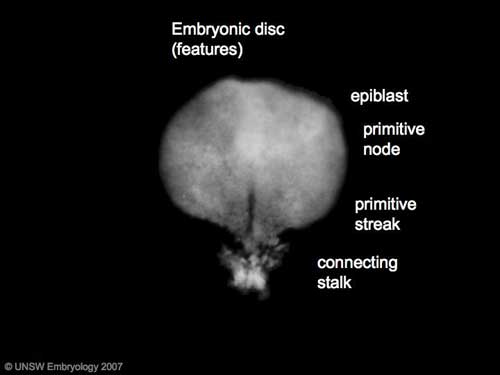
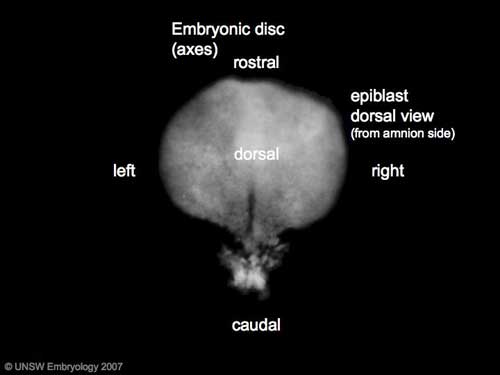
| '''Features:''' embryonic disc, primitive node, primative streak, primitive groove, yolk sac | |||
'''Facts:''' Week 3, 15 - 17 days, 0.4 mm | |||
'''View 1:''' embryonic disc, showing the epiblast viewed from the amniotic (dorsal) side. | |||
'''Events:''' Gastrulation is continuing as cells migrate from the epiblast, continuing to form mesoderm. | |||
Mesoderm lies between the ectoderm and endoderm as a continuous sheet except at the buccopharyngeal and cloacal membranes. These membranes have ectoderm and endoderm only and will lie at the rostral (head) and caudal (tail) of the gastrointestinal tract. | |||
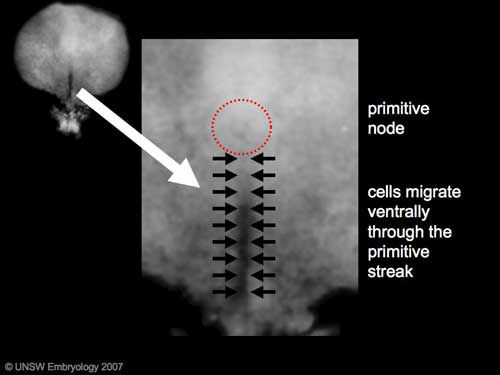
| '''Gastrulation:''' Through the '''primitive streak '''cells migrate continuously through week 3 into week 4. Initial cells replace hypoblast as an epithelial layer the '''endoderm'''. Later migrating cells spread between the two epithelial layers to form '''mesoderm'''. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage7_primitive_streak_labelled.jpg]] | |||
| [[File:Stage7 axes.jpg]] | |||
|- | |||
| '''Axes:''' embryonic disc is shown rostral (head) to top and caudal (tail) to bottom. Left and right are the lateral margins of the disc as shown. | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
== Gastrulation == | |||
Carnegie Stage 7 and 8, gastrulation, migration of cells through the primitive streak to form endoderm and mesodermal layers of embryo. | |||
[[File:Chicken-gastrulation3.jpg]] | |||
[[File:Trilaminar_embryo.jpg]] | |||
Scanning electron micrograph showing the early forming 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. | |||
[[File:Mesoderm 001 icon.jpg|200px|link=Development_Animation_-_Mesoderm]] | |||
Revision as of 13:20, 3 August 2011
Introduction
Conceptus Cavities Week 2 and Week 3
| File:Chorion 001 icon.jpg</wikiflv> | Animation shows the events following implantation and focuses on changes in the the spaces surrounding the embryonic disc, the extraembryonic coelom. The blastoceol cavity is converted into two separate spaces: the yolk sac and the chorionic cavity. The third space lies above the epiblast, the amniotic cavity.
blue - epiblast layer yellow - hypoblast layer red cells - extraembryonic mesoderm layer green - trophoblast layer red spaces - blood-filled spaces, maternal lacunae white cells - (left) endometrial gland (right) endometrial epithelium |
Stage 7
Gastrulation
Carnegie Stage 7 and 8, gastrulation, migration of cells through the primitive streak to form endoderm and mesodermal layers of embryo.
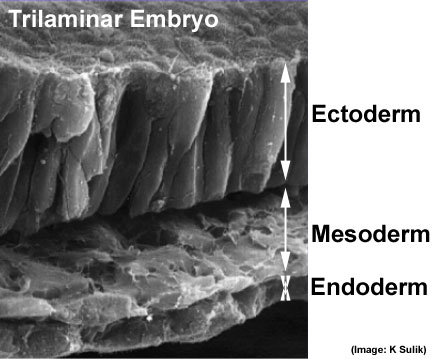 Scanning electron micrograph showing the early forming 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
Scanning electron micrograph showing the early forming 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.