Uploads by Z3290270
From Embryology
This special page shows all uploaded files.
| Date | Name | Thumbnail | Size | Description | Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 09:13, 13 October 2011 | Regions of the brain significant in Huntington's disease.jpg (file) |  |
348 KB | Coronal view of the brain, showing the main basal ganglia nuclei. The section is angled rostrocaudally to encounter most of the BG nuclei in a single section. '''C''', cortex; '''STR,''' striatum; '''GPe''', globus pallidus pars externa; '''GPi''', globus | 1 |
| 08:56, 13 October 2011 | Key cellular pathogenic mechanisms in Huntington's disease.jpg (file) |  |
47 KB | Key cellular pathogenic mechanisms in Huntington's disease (HD). Multiple cellular pathways have been implicated in the pathogenesis of HD. These mechanisms could be exclusive or, more likely, have a high degree of cross-talk. '''A:''' the mutation in hun | 1 |
| 06:35, 10 October 2011 | Regions of the brain.jpg (file) | 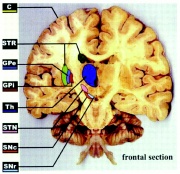 |
348 KB | Coronal view of the brain, showing the main basal ganglia nuclei. The section is angled rostrocaudally to encounter most of the BG nuclei in a single section. C, cortex; STR, striatum; GPe, globus pallidus pars externa; GPi, globus pallidus pars interna; | 1 |
| 09:41, 6 October 2011 | Huntingtin gene.jpeg (file) |  |
15 KB | 1 | |
| 12:24, 22 September 2011 | Inheritance pattern in Huntington's Disease.jpeg (file) |  |
15 KB | Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant disorder. If one parent is affected, the child has a 50% chance of inheriting the mutation on the huntingtin gene on their 4th chromosome. Illustration by: z3290270 Inspiration: Yale Madical group - Yale Sc | 1 |
| 23:55, 21 September 2011 | Healthy Huntingtin protein and Huntingtin gene mutated by Huntington's Disease.jpg (file) |  |
76 KB | The Huntingtin protein in an individual not affected by Huntington's disease will have a CAG (cytosine-guanine-adenine)repeat of 10-26. The Huntigntin gene in an individual affected by Huntington's disease is mutated which causes a CAG repeat of 36-121 t | 1 |
| 06:33, 19 September 2011 | Key cellular pathogenic mechanisms in HD.jpg (file) |  |
47 KB | Key cellular pathogenic mechanisms in Huntington's disease (HD). Multiple cellular pathways have been implicated in the pathogenesis of HD. These mechanisms could be exclusive or, more likely, have a high degree of cross-talk. A: the mutation in huntingti | 1 |
| 21:09, 17 August 2011 | Establishment of HD hybrid cell line.jpg (file) |  |
93 KB | (A) First polar body of mature rhesus macaque oocyte was removed by gentle squeezing through a slit of zona pellucida (A-a). Staining of 1st polar body DNA (arrowhead) and oocyte DNA (arrow) (A-b). HD monkey skin cell was placed under the zona pellucida ( | 1 |