File:Xenopus red fluorescence.jpg: Difference between revisions
(Transgenic Xenopus laevis strain expressing ubiquitous red fluorescence. F1 animals of the tom3 strain at the neurula (A), larval (B) or froglet stage (C) seen with the red fluorescence filter set. D: Isolated tissue of a control froglet (left) and a ) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Transgenic Xenopus laevis strain expressing ubiquitous red fluorescence | ==Transgenic Xenopus laevis strain expressing ubiquitous red fluorescence== | ||
F1 animals of the tom3 strain | F1 animals of the tom3 strain seen with the red fluorescence filter set. | ||
D: Isolated tissue of a control froglet (left) and a froglet of the tom3 strain (right) seen in normal light. E: Same tissue samples seen in the red fluorescence filter set. F-H: Isolated muscle of a froglet of the blue fluorescent C5 strain [5] (left) and of the red fluorescent tom3 strain (right) seen in normal light (F), with red fluorescence filter set (G), or blue fluorescence filter set (H). | (A) neurula stage | ||
(B) larval stage | |||
(C) froglet stage | |||
D: Isolated tissue of a control froglet (left) and a froglet of the tom3 strain (right) seen in normal light. | |||
E: Same tissue samples seen in the red fluorescence filter set. | |||
F-H: Isolated muscle of a froglet of the blue fluorescent C5 strain [5] (left) and of the red fluorescent tom3 strain (right) seen in normal light (F), with red fluorescence filter set (G), or blue fluorescence filter set (H). | |||
Scale bars equal 1 mm. | Scale bars equal 1 mm. | ||
1471-213X-9-37-1.jpg | Original file name: 1471-213X-9-37-1.jpg | ||
BMC Dev Biol. 2009; 9: 37. | BMC Dev Biol. 2009; 9: 37. | ||
Published online 2009 June 23. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-37. | Published online 2009 June 23. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-37. | ||
==Reference== | |||
<pubmed>19549299</pubmed> | |||
Copyright © 2009 Waldner et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | Copyright © 2009 Waldner et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | ||
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. | This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. | ||
[[Category:Frog]] | [[Category:Frog]] [[Category:Fluorescence]] | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 28 September 2010
Transgenic Xenopus laevis strain expressing ubiquitous red fluorescence
F1 animals of the tom3 strain seen with the red fluorescence filter set.
(A) neurula stage (B) larval stage (C) froglet stage
D: Isolated tissue of a control froglet (left) and a froglet of the tom3 strain (right) seen in normal light.
E: Same tissue samples seen in the red fluorescence filter set.
F-H: Isolated muscle of a froglet of the blue fluorescent C5 strain [5] (left) and of the red fluorescent tom3 strain (right) seen in normal light (F), with red fluorescence filter set (G), or blue fluorescence filter set (H).
Scale bars equal 1 mm.
Original file name: 1471-213X-9-37-1.jpg
BMC Dev Biol. 2009; 9: 37.
Published online 2009 June 23. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-37.
Reference
<pubmed>19549299</pubmed>
Copyright © 2009 Waldner et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 01:54, 29 March 2010 | 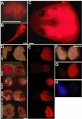 | 600 × 873 (107 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | Transgenic Xenopus laevis strain expressing ubiquitous red fluorescence. F1 animals of the tom3 strain at the neurula (A), larval (B) or froglet stage (C) seen with the red fluorescence filter set. D: Isolated tissue of a control froglet (left) and a |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: