File:Xenopus FoxA4 model.jpg
Original file (1,192 × 565 pixels, file size: 104 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
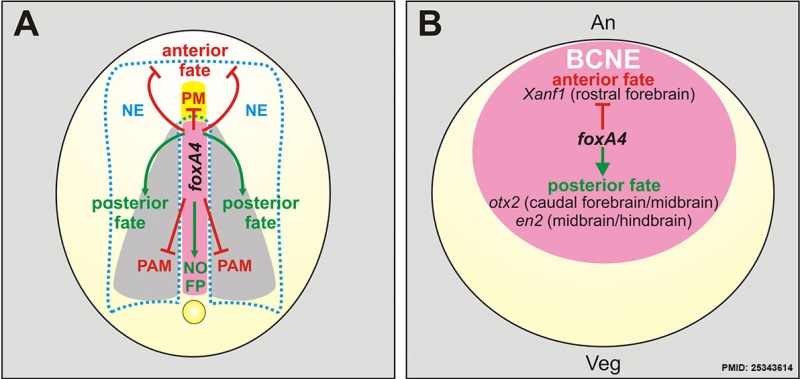
Model for foxA4 function in Xenopus Embryos
| (A) Summary of foxA4 functions in A–P regionalisation and in DML development
For simplicity, they are depicted in a diagram of an embryo at neural plate stage, shown in dorsal view, when foxA4 is only expressed in the DML (pink). FoxA4 modulates A–P development by inhibiting anterior fates (red lines) in the axial mesoderm (prechordal mesoderm, PM) and in the neuroectoderm (NE) and ectoderm, while favouring posterior fates (green arrows) in the neural plate and the dorsal midline (notochord, NO; floor plate, FP). In the trunk, foxA4 prevents the respecification of dorsal midline precursors towards contiguous fates, by inhibiting (red lines) the paraxial mesodermal fate (PAM). Yellow, prechordal mesoderm. Grey, paraxial mesoderm. The dotted light blue line demarcates de neural plate. |
(B) Diagram of a blastula stage embryo in dorsal view
Showing the expression of foxA4 in the BCNE centre (pink), which is composed by precursors of the Spemann's organiser and of the whole forebrain and most of the midbrain and hindbrain [37]. An, animal; Veg, vegetal. FoxA4 modulates the initial CNS regionalisation by operating on the BCNE, favouring posterior fates among BCNE derivatives (green arrow), while restricting anterior fates (red line), as revealed by the markers Xanf1 (rostral forebrain), otx2 (caudal forebrain/midbrain), en2 (midbrain/hindbrain boundary). |
- Links: Notochord | Frog Development | Molecular Development
Reference
<pubmed>25343614</pubmed>| PLoS ONE
Copyright
© 2014 Murgan et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Figure 14. Journal.pone.0110559.g014.jpg
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0110559.g014
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 16:31, 25 April 2015 |  | 1,192 × 565 (104 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Model for foxA4 function in Xenopus Embryos== (A) Summary of foxA4 functions in A–P regionalisation and in DML development. For simplicity, they are depicted in a diagram of an embryo at neural plate stage, shown in dorsal view, when foxA4 is onl... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: