File:Streeter027.jpg
Original file (774 × 1,000 pixels, file size: 51 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
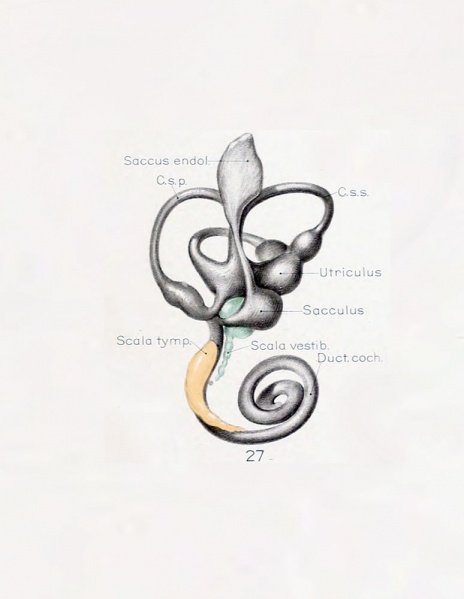
Fig. 27. Median view of a model reconstructed from a human fetus 50 mm crown-rump length
Median view of a model reconstructed from a human fetus 50 mm. crown-rump length (Carnegie Collection, No. 84).
This view shows the topography of the scala tympani. Its large proximal end lies opposite the fenestra cochleae (rotunda) and corresponds to the focus at which its development originates. Distally it tapers off rapidly where the spaces are smaller and their coalescence less complete. Enlarged 11.4 diameters.
The figures shown on this plate 4 represent a series of median and lateral views of wax-plate reconstructions of the membranous labyrinth and the surrounding periotic tissue-spaces. They illustrate under the same scale of enlargement three typical stages in the development of these spaces.
Abbreviations
- C. s. 1. - ductus semicircuiaris lateralis
- C. s. p. - ductus semicircularis posterior
- C. s. s. - ductus semicircularis superior
- Duct, coch., = ductus cochlearis
- Impressio rotund. - area opposite the fenestra cochleae
- Impressio staped., area in contact with base of stapes
- Saccus endol. - saccus endolymphaticus
- Scala tymp. - scala tynipani
- Scala vestib. - scala vestibule.
Reference
Streeter G.L. The histogenesis and growth of the otic capsule and its contained periotic tissue-spaces in the human embryo Contributions to Embryology Carnegie Institution No.20 (1918) pp5-54, 4 text-figures and 4 plates.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 21:51, 22 April 2012 |  | 774 × 1,000 (51 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ====Fig. 27==== Median view of the same model shown in figure 26. This view shows the topography of the scala tympani. Its large proximal end lies opposite the fenestra cochleae (rotunda) and corresponds to the focus at which its development originates. D |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: