File:Spindle assembly motors 01.jpg: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
! Box 5 | ! Box 5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Motor-dependent mechanisms establish bipolarity as Eg5 (kinesin-5) motors slide antiparallel microtubules apart with their minus ends leading and their plus ends directed toward the spindle equator. | ||
| | | Minus end–directed motors such as dynein move microtubules poleward with their minus ends leading, thereby incorporating K-fibers into the spindle and focusing spindle poles. | ||
| | | Kinetochore-associated dynein transports chromosomes along astral microtubules toward the spindle poles from the periphery. | ||
| | | Plus end–directed chromokinesins (kinesin-4 and -10) eject chromosome arms outward. | ||
| | | CENP-E (kinesin-7) transports unattached kinetochores toward the equator along spindle microtubules. MTOC, microtubule organizing centre. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Category:Mitosis]][[Category:Meiosis]][[Category:Cartoon]] | [[Category:Mitosis]][[Category:Meiosis]][[Category:Cartoon]] | ||
[[Category:Cell Division]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:16, 22 March 2016
Motor activities in spindle assembly
Microtubule (MT)-bound motors promote bipolar spindle formation, whereas chromosome-associated motors drive proper kinetochore orientation and chromosome movement to the equator.
| Box 1 | Box 2 | Box 3 | Box 4 | Box 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motor-dependent mechanisms establish bipolarity as Eg5 (kinesin-5) motors slide antiparallel microtubules apart with their minus ends leading and their plus ends directed toward the spindle equator. | Minus end–directed motors such as dynein move microtubules poleward with their minus ends leading, thereby incorporating K-fibers into the spindle and focusing spindle poles. | Kinetochore-associated dynein transports chromosomes along astral microtubules toward the spindle poles from the periphery. | Plus end–directed chromokinesins (kinesin-4 and -10) eject chromosome arms outward. | CENP-E (kinesin-7) transports unattached kinetochores toward the equator along spindle microtubules. MTOC, microtubule organizing centre. |
Reference
<pubmed>26668328</pubmed>
http://jcb.rupress.org/content/211/6/1103.full Figure 3.
© 2015 Heald and Khodjakov.
Copyright
Rockefeller University Press - Copyright Policy This article is distributed under the terms of an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike–No Mirror Sites license for the first six months after the publication date (see http://www.jcb.org/misc/terms.shtml). After six months it is available under a Creative Commons License (Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 4.0 Unported license, as described at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/ ). (More? Help:Copyright Tutorial)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 16:04, 22 March 2016 | 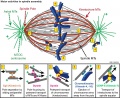 | 1,200 × 978 (314 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ===Reference=== <pubmed>26668328</pubmed> http://jcb.rupress.org/content/211/6/1103.full © 2015 Heald and Khodjakov. {{JCB}} |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: