File:Sox transcription factors cartoon 01.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(==Involvement of SOX proteins in various developmental pathways== Some have also been associated with tumorigenesis. Oncoscience. 2014 Jun 2;1(5):326-35. eCollection 2014. SOX15 and other SOX family members are important mediators of tumorigenesis in...) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Involvement of SOX proteins in various | ==Involvement of SOX proteins in various Developmental Pathways== | ||
Some have also been associated with tumorigenesis. | Some of these signalling pathways have also been associated with tumorigenesis. | ||
:'''Links:''' [[Developmental Signals - Sox]] | |||
===Reference=== | |||
<pubmed>25594027</pubmed> | |||
http://www.impactjournals.com/oncoscience/index.php?abs=46 | http://www.impactjournals.com/oncoscience/index.php?abs=46 | ||
====Copyright==== | |||
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | ||
[[Category:Developmental Signal]] [[Category:Sox]] [[Category:Molecular]][[Category:Cartoon]] | |||
Revision as of 18:38, 4 February 2015
Involvement of SOX proteins in various Developmental Pathways
Some of these signalling pathways have also been associated with tumorigenesis.
- Links: Developmental Signals - Sox
Reference
<pubmed>25594027</pubmed>
http://www.impactjournals.com/oncoscience/index.php?abs=46
Copyright
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 18:35, 4 February 2015 | 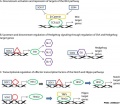 | 800 × 695 (81 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Involvement of SOX proteins in various developmental pathways== Some have also been associated with tumorigenesis. Oncoscience. 2014 Jun 2;1(5):326-35. eCollection 2014. SOX15 and other SOX family members are important mediators of tumorigenesis in... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: