File:Organoids overview 01.jpg
Original file (685 × 776 pixels, file size: 146 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Summary
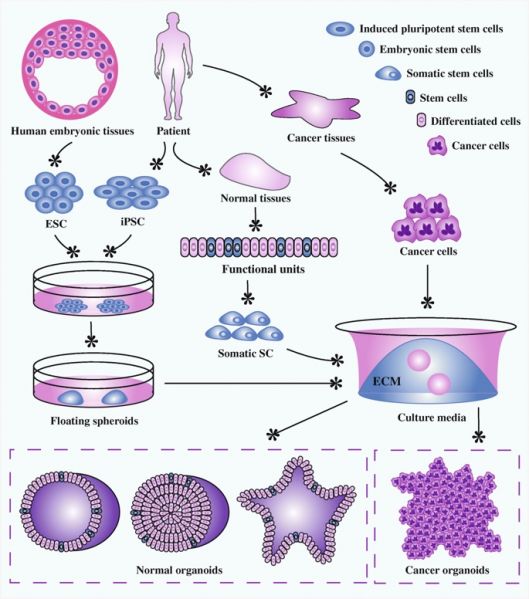
Organoid establishment from stem cells and cancer cells. Embryonic stem cells from human embryonic tissues and induced pluripotent stem cells from adult tissues firstly experience directed differentiation, generate floating spheroids, and subsequently are planted on extracellular matrix in specific culture medium to initiate organoid culture. Primary tissues from patients can be dissociated into functional units, which contain somatic stem cells. These somatic stem cells are enriched and cultured in three-dimensional medium to form organoids. Tumor cells isolated from cancer tissues can also form tumoroids in well-defined three-dimensional culture
13045_2018_662_Fig1_HTML.jpg
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 05:59, 30 July 2019 |  | 685 × 776 (146 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | Organoid establishment from stem cells and cancer cells. Embryonic stem cells from human embryonic tissues and induced pluripotent stem cells from adult tissues firstly experience directed differentiation, generate floating spheroids, and subsequently... |
You cannot overwrite this file.