File:Nephron EM02.jpg: Difference between revisions
(Figure 2. An ultrastructural overview of podocytes and the glomerular endothelium. (A) Scanning electron micrograph of an exposed glomerulus. In this image, the Bowman’s capsule is broken, permitting a striking view of podocytes (Pod) completely wrap...) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Glomerulus Podocyte EM== | |||
An ultrastructural overview of podocytes and the glomerular endothelium. (A) Scanning electron micrograph of an exposed glomerulus. In this image, the Bowman’s capsule is broken, permitting a striking view of podocytes (Pod) completely wrapped around the glomerular capillaries. (B) Higher magnification of a podocyte within the glomerulus revealing the interdigitated FPs. (C) A resin cast of the glomerular capillary tuft with the cells corroded to reveal its highly convoluted shape. Image courtesy of F. Hossler (East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN). (D) Scanning electron micrograph of an exposed glomerular capillary and its numerous perforations (fenestrae). (E) Simplified diagram of the GFB. The GEC and its fenestrae are lined by a filamentous glycocalyx enriched in negatively charged proteoglycans. The glycocalyx and adsorbed plasma components form the thicker ESL. The GBM is a stratified ECM in between podocytes and GECs. Podocytes form the final layer of the GFB. The interdigitating FPs of podocytes are linked by porous SDs where primary urinary filtrate passes through. Bars: (A) 20 µm; (B and D) 1 µm; (C) 50 µm. | An ultrastructural overview of podocytes and the glomerular endothelium. | ||
(A) Scanning electron micrograph of an exposed glomerulus. In this image, the Bowman’s capsule is broken, permitting a striking view of podocytes (Pod) completely wrapped around the glomerular capillaries. | |||
(B) Higher magnification of a podocyte within the glomerulus revealing the interdigitated FPs. | |||
(C) A resin cast of the glomerular capillary tuft with the cells corroded to reveal its highly convoluted shape. Image courtesy of F. Hossler (East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN). | |||
(D) Scanning electron micrograph of an exposed glomerular capillary and its numerous perforations (fenestrae). (E) Simplified diagram of the GFB. The GEC and its fenestrae are lined by a filamentous glycocalyx enriched in negatively charged proteoglycans. The glycocalyx and adsorbed plasma components form the thicker ESL. The GBM is a stratified ECM in between podocytes and GECs. Podocytes form the final layer of the GFB. The interdigitating FPs of podocytes are linked by porous SDs where primary urinary filtrate passes through. | |||
Bars: (A) 20 µm; (B and D) 1 µm; (C) 50 µm. | |||
:'''Links:''' [[:File:Nephron EM02.jpg|colour image version]] | [[:File:Nephron EM01.jpg|BW image version]] | {{renal histology}} | |||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 24: | ||
{{JCB}} | {{JCB}} | ||
Figure 2. | Figure 2. Relabelled. Text above modified from original figure legend. | ||
{{Footer}} | {{Footer}} | ||
[[Category:Renal]] | [[Category:Renal]] | ||
[[Category:Electron Micrograph]] | [[Category:Electron Micrograph]] | ||
Revision as of 08:35, 18 May 2018
Glomerulus Podocyte EM
An ultrastructural overview of podocytes and the glomerular endothelium.
(A) Scanning electron micrograph of an exposed glomerulus. In this image, the Bowman’s capsule is broken, permitting a striking view of podocytes (Pod) completely wrapped around the glomerular capillaries.
(B) Higher magnification of a podocyte within the glomerulus revealing the interdigitated FPs.
(C) A resin cast of the glomerular capillary tuft with the cells corroded to reveal its highly convoluted shape. Image courtesy of F. Hossler (East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN).
(D) Scanning electron micrograph of an exposed glomerular capillary and its numerous perforations (fenestrae). (E) Simplified diagram of the GFB. The GEC and its fenestrae are lined by a filamentous glycocalyx enriched in negatively charged proteoglycans. The glycocalyx and adsorbed plasma components form the thicker ESL. The GBM is a stratified ECM in between podocytes and GECs. Podocytes form the final layer of the GFB. The interdigitating FPs of podocytes are linked by porous SDs where primary urinary filtrate passes through.
Bars: (A) 20 µm; (B and D) 1 µm; (C) 50 µm.
- Links: colour image version | BW image version | renal histology
Reference
Scott RP & Quaggin SE. (2015). Review series: The cell biology of renal filtration. J. Cell Biol. , 209, 199-210. PMID: 25918223 DOI.
Copyright
Rockefeller University Press - Copyright Policy This article is distributed under the terms of an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike–No Mirror Sites license for the first six months after the publication date (see http://www.jcb.org/misc/terms.shtml). After six months it is available under a Creative Commons License (Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 4.0 Unported license, as described at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/ ). (More? Help:Copyright Tutorial)
Figure 2. Relabelled. Text above modified from original figure legend.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 8) Embryology Nephron EM02.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Nephron_EM02.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 08:33, 18 May 2018 | 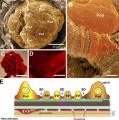 | 1,271 × 1,280 (210 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | Figure 2. An ultrastructural overview of podocytes and the glomerular endothelium. (A) Scanning electron micrograph of an exposed glomerulus. In this image, the Bowman’s capsule is broken, permitting a striking view of podocytes (Pod) completely wrap... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: