File:Mouse cranial nerve model SHH.jpg
Original file (954 × 900 pixels, file size: 74 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
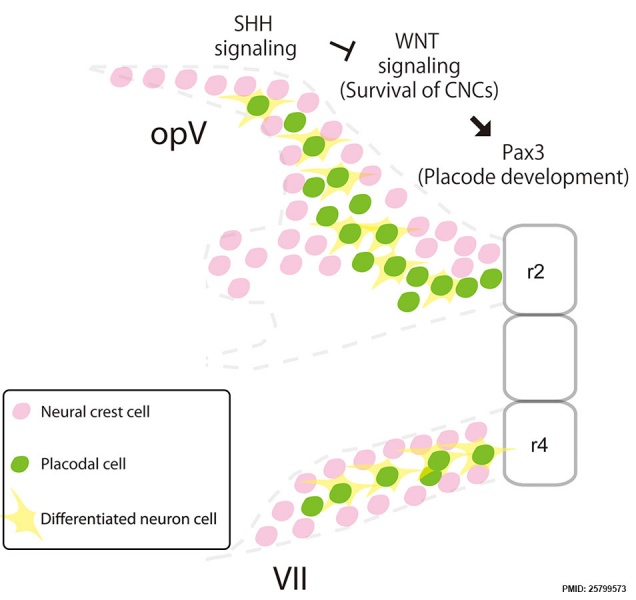
Mouse Cranial Nerve Model - Sonic Hedgehog
During mouse normal development, neural crest cells migrating from rhombomere 2 (r2) or 4 (r4) interact with placodal cells to develop the cranial nerves.
- Links: sonic hedgehog | cranial nerve | mouse
Reference
Kurosaka H, Trainor PA, Leroux-Berger M & Iulianella A. (2015). Cranial nerve development requires co-ordinated Shh and canonical Wnt signaling. PLoS ONE , 10, e0120821. PMID: 25799573 DOI.
Copyright
© 2015 Kurosaka et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Fig. 7 . Journal.pone.0120821.g007.jpg Panel A cropped from full figure and relabelled.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Mouse cranial nerve model SHH.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Mouse_cranial_nerve_model_SHH.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 18:27, 14 April 2016 |  | 954 × 900 (74 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | During mouse normal development, neural crest cells migrating from rhombomere 2 (r2) or 4 (r4) interact with placodal cells to develop the cranial nerves PLoS One. 2015 Mar 23;10(3):e0120821. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120821. eCollection 2015. Crania... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: