File:Mouse E10.5 gene expression.jpg: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Analysis of Mouse Stage E10.5 Specific Gene Expression== | ==Analysis of Mouse Stage E10.5 Specific Gene Expression== | ||
1140 transcripts were found to be significantly up-regulated exclusively at one developmental time point. A large fraction of these stage specific genes were found to be novel, in particular at | 1140 transcripts were found to be significantly up-regulated exclusively at one developmental time point. A large fraction of these stage specific genes were found to be novel, in particular at {{ME13.5}} only 5% of the transcripts had confirmed musculoskeletal knockout phenotypes and 6% of the genes have been validated by in situ hybridization. A survey of available in situ expression profiles for genes with peak expression levels at {{ME10.5}} revealed that they display a wide range of patterns, and include closely related members of gene families such as Irx, Smarc and zinc finger transcription factors. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Figure 6. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028358.g006 | Figure 6. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028358.g006 | ||
{{Footer}} | |||
[[Category:Mouse E10.5]] | [[Category:Mouse E10.5]] | ||
Revision as of 09:46, 5 April 2019
Analysis of Mouse Stage E10.5 Specific Gene Expression
1140 transcripts were found to be significantly up-regulated exclusively at one developmental time point. A large fraction of these stage specific genes were found to be novel, in particular at E13.5 only 5% of the transcripts had confirmed musculoskeletal knockout phenotypes and 6% of the genes have been validated by in situ hybridization. A survey of available in situ expression profiles for genes with peak expression levels at E10.5 revealed that they display a wide range of patterns, and include closely related members of gene families such as Irx, Smarc and zinc finger transcription factors.
- Limb Links: Mouse limb skeleton cartoon | Mouse limb tissue development | Limb Development | Mouse Development
Reference
Taher L, Collette NM, Murugesh D, Maxwell E, Ovcharenko I & Loots GG. (2011). Global gene expression analysis of murine limb development. PLoS ONE , 6, e28358. PMID: 22174793 DOI.
Copyright
This is an open-access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Figure 6. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028358.g006
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 7) Embryology Mouse E10.5 gene expression.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Mouse_E10.5_gene_expression.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 19:16, 13 February 2013 | 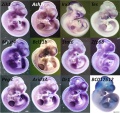 | 1,747 × 1,650 (404 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Analysis of Mouse Stage E10.5 Specific Gene Expression== 1140 transcripts were found to be significantly up-regulated exclusively at one developmental time point. A large fraction of these stage specific genes were found to be novel (A), in particular |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: