File:Intraepithelial lymphocyte differentiation 02.jpg

Original file (1,200 × 557 pixels, file size: 79 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Kinetics of the accumulation of natural and induced IELs
Natural intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) gain their antigen-experienced phenotype and gut-homing capacity in the thymus during their initial agonist-based selection in response to self antigens.
They populate the gut compartment early, before environmental antigens have been encountered.
Conventional naive T cells differentiate into effector cells in response to peripherally encountered antigens and gradually accumulate over time as antigen-experienced induced IELs in the gut.
- Immune Images: Oesophagus MALT | Colon MALT | Peyer's patch overview | Peyer's patch detail | Cartoon - IEL development | Cartoon - IEL function | Cartoon - IEL differentiation | Mesenteric Lymph Nodes overview | Palatine Tonsil | Tonsil | Immune System Development
Reference
<pubmed>21681197</pubmed>| Nat Rev Immunol.
Copyright
© 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
Licensee: Mark A Hill License Date: Jan 25, 2015 License Number: 3556220285761 Publication: Nature Reviews Immunology Title: The light and dark sides of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes Type Of Use: post on a website Figure 2.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Intraepithelial lymphocyte differentiation 02.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Intraepithelial_lymphocyte_differentiation_02.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:17, 26 January 2015 | 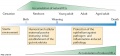 | 1,200 × 557 (79 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Kinetics of the accumulation of natural and induced IELs== Natural intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) gain their antigen-experienced phenotype and gut-homing capacity in the thymus during their initial agonist-based selection in response to self ant... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: